

Palynziq 聚戊二酸酶




| 通用中文 | 聚戊二酸酶 | 通用外文 | Pegvaliase -pqpz |
| 品牌中文 | 品牌外文 | Palynziq | |
| 其他名称 | |||
| 公司 | BioMarin(BioMarin) | 产地 | 美国(USA) |
| 含量 | 10mg/0.5ml | 包装 | 1支/盒 |
| 剂型给药 | 皮下注射 | 储存 | 2度-8度(冰箱冷藏,禁止冷冻)室温下不超过30天。一旦在室温保存,请勿再退回冰箱 |
| 适用范围 | 治疗苯基丙胺酸苯基丙胺酸尿(PKU) | ||
| 通用中文 | 聚戊二酸酶 |
| 通用外文 | Pegvaliase -pqpz |
| 品牌中文 | |
| 品牌外文 | Palynziq |
| 其他名称 | |
| 公司 | BioMarin(BioMarin) |
| 产地 | 美国(USA) |
| 含量 | 10mg/0.5ml |
| 包装 | 1支/盒 |
| 剂型给药 | 皮下注射 |
| 储存 | 2度-8度(冰箱冷藏,禁止冷冻)室温下不超过30天。一旦在室温保存,请勿再退回冰箱 |
| 适用范围 | 治疗苯基丙胺酸苯基丙胺酸尿(PKU) |
使用说明书
新颖酶治疗为成年有PKU患者有未控制的血苯基丙按酸[苯基丙氨酸]浓度用当前治疗
2018年5月24日美国食品和药品监管局今天批准Palynziq(pegvaliase-pqpz)为成年有一种罕见和严重的遗传疾病被称为苯基丙胺酸苯基丙胺酸尿(PKU)。患者有PKU被出生有一种失能裂解苯基丙胺酸(Phe),一种氨基酸存在在含蛋白食物和高强度含蛋白食物和高-强度甜味剂被使用在各种食物和饮料。Palynziq是一种新颖酶治疗为成年PKU患者有未控制血Phe浓度用当前治疗。
FDA的药物评价和研究中心内药物评价III办公室主任Julie Beitz,M.D说:“这是一种新颖酶取代治疗帮助面对一种显著未满足需要在用当前治疗选择已不能控制他们的血Phe水平的PKU患者,” “这个新批准显示我们的承诺批准进展在治疗将给予有PKU患者对医护不同的选择。”
PKU影响约1在10,000至15,000在美国的人们。如未治疗,PKU可能致慢性智力的,神经发育和精神失能。苯基丙胺酸的通过膳食摄取终生受限是一种需要预防Palynziq 在体内的积蓄,它可能致中枢神经系统长期损伤。
在两项临床试验在成年患者有 苯基丙胺酸苯基丙胺酸尿(PKU)有血苯基丙胺酸浓度大于600 µmol/L 对存在的处理研究Palynziq的安全性和疗效。在Palynziq试验中大多数PKU患者在试验前和期间是用一种不受限制的膳食。第一个试验是一个随机化,开放试验在被治疗患者中用增加剂量的Palynziq 给予作为一个皮下注射至一个目标剂量的或20 mg每天一次或40 mg每天一次。第二个试验为一个8-周,安慰剂-对照,随机化撤出试验在患者以前用Palynziq治疗患者。患者用Palynziq治疗实现从他们的治疗前基线血Phe浓度在血苯基丙胺酸浓度统计上显著减低。
在 Palynziq试验中被报道的最常见不良事件包括注射部位反应,关节疼痛,超敏性反应,头痛,普遍性皮肤反应持续至少14天,瘙痒,恶心,眩晕,腹痛,喉痛,疲乏,呕吐,咳嗽和腹泻。在大多数患者中发生超敏性反应,可能地由于形成对产品的抗体。.
在Palynziq试验中最严重不良反应为过敏反应,它发生最频在治疗的头一年向上滴定调整剂量期间。因为这个严重的风险,对Palynziq说明书包括包括一个黑框警告和产品仅通过一个受限制的程序在一个风险评价和缓解策略(REMS)被称为Palynziq REMS程序才能得到。Palynziq REMS 程序的令人注目要求包括以下:
● 处方者必须合格通过纳入REMS 程序和完成训练
● 处方者必须处方自动-可注射的肾上腺素与 Palynziq
● 药房必须合格有程序和必须仅分发至患者被授权接受Palynziq
● 患者必须纳入程序和被合格处方者教育关于 过敏反应的风险处方者确保他们了解用Palynziq治疗的风险和获益
● 患者必须有自动-可注射的肾上腺素可得到在当采用Palynziq所有时间
FDA赋予Palynziq的批准给予BioMarin Pharmaceutical有限公司
这些重点不包括安全和有效使用PALYNZIQ需所有资料。请参阅PALYNZIQ 完整处方资料。
PALYNZIQ (pegvaliase-pqpz)注射液,为皮下使用
美国初次批准: 2018
 适应证和用途
适应证和用途
Palynziq是一种苯基丙氨酸[phenylalanine]-代谢酶适用减低血苯基丙氨酸浓度在成年患者有苯基丙氨酸尿患者有未控制的血苯基丙氨酸浓度大于600 µmol/L用存在处理。(1)
剂量和给药方法
剂量 (2.1)
● 治疗开始前得到基线血苯基丙氨酸浓度。
● 推荐的初始剂量为2.5 mg皮下每周一次共4周。
● 滴定调整剂量在逐步方式历时至少5周根据耐受性实现一个剂量20 mg皮下地每天一次。对滴定调整方案见完整处方资料。
● 评估患者耐受性,血苯基丙氨酸浓度,和膳食蛋白和苯基丙氨酸摄取至始至终治疗。
● 考虑增加剂量至最大40 mg皮下地每天一次在患者曽被用20 mg每天1次连续地共至少24周和患者未曽实现或一个20%减低在血苯基丙氨酸浓度从治疗前基线或一个血苯基丙氨酸浓度低于或等于600 µmol/L。
● 终止Palynziq在患者没有实现至少一个20%减低在血苯基丙氨酸浓度从治疗前基线或一个血 苯基丙氨酸浓度低于或等于600 µmol/L连续治疗的16周后 与最大剂量40 mg每天1次。
● 减低剂量和/或修饰膳食蛋白和苯基丙氨酸摄取,如需要时,以维持血苯基丙氨酸浓度一个临床上可接受的范围和高于30 µmol/L。血苯基丙氨酸监视和膳食(2.2)。
● 得到血苯基丙氨酸浓度每4周直至一个维持剂量被确定。
● 一个维持剂量被确定后,定期地监视血苯基丙氨酸浓度。
●与患者商讨监视膳食蛋白和苯基丙氨酸摄取,和由卫生保健提供者指导调整。y their 卫生保健提供者. 预先药物 (2.3,5.1,5.3)
● 考虑预先药物对超敏性反应. 给药指导 (2.4)
●。如对单次剂量需要一个以上注射旋转注射部位。
剂型和规格
注射液: 2.5 mg/0.5 mL,10 mg/0.5 mL,和20 mg/mL在一个单次-剂量预装注射器. (3)
禁忌证
无。(4)
警告和注意事项
超敏性反应,除了过敏反应: 处理应被根据反应的严重程度,复发,和临床判断,和可能包括剂量调整,短暂中断药物,或用抗组织胺,解热药,和/或皮质激素治疗。 (5.3)
不良反应
最常见不良反应(在任一治疗相至少20%)为: 注射部位反应,关节痛,超敏性反应,头痛,普遍性皮肤反应持续至少14天,瘙痒,恶心,腹痛,口咽痛,呕吐,咳嗽,腹泻,和疲乏. (6.1)
报告怀疑不良反应,联系BioMarin Pharmaceutical公司at 1-866- 6-906-6100, or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088或www.fda.gov/medwatch.
药物相互作用
Palynziq对其他PEG化产品的影响。监视对超敏性反应,包括过敏反应,与同时治疗。 (7.1)
在特殊人群中使用
妊娠: 可能致胎儿危害。(8.1)
完整处方资料


1 适应证和用途
Palynziq是适用为减低血苯基丙氨酸浓度在成年患者有苯基丙氨酸尿(PKU)患者有未控制的血苯基丙氨酸浓度大于600 µmol/L用存在处理。.
2 剂量和给药方法
2.1 剂量
● 用Palynziq治疗应被PKU中有经验的一个健康保健提供者
处理。
● 治疗开始前得到基线血苯基丙氨酸浓度。
诱导
对Palynziq推荐的初始诱导剂量为2.5 mg皮下每周一次共4周。在一位卫生保健提供者的监督下给予初始剂量[见剂量和给药方法(2.4)]。
滴定调整
滴定调整Palynziq剂量在逐步方式,根据耐受性,历时至少5周,实现一个剂量20 mg皮下地每天一次按照表1。
维持
治疗反应可能不实现直至患者被滴定调整至维持Palynziq维持有效剂量。使用Palynziq的最低有效和耐受剂量。
评估患者耐受性,血苯基丙氨酸浓度,和膳食蛋白和苯基丙氨酸摄取至始至终治疗。维持Palynziq剂量在20 mg皮下地每天一次共至少24周。考虑增加Palynziq剂量至最大40 mg皮下地每天一次在患者曽被连续地维持用20 mg每天1次共至少24周和患者没有实现或一个20%减低在血苯基丙氨酸浓度从治疗前基线或一个血苯基丙氨酸浓度低于或等于600 µmol/L。
终止
终止Palynziq在患者没有实现一个反应(至少一个20%减低在血苯基丙氨酸浓度从治疗前基线或一个血苯基丙氨酸浓度低于或等于 600 µmol/L)用最大剂量40 mg每天1次连续治疗16周后。


对低苯基丙氨酸浓度剂量减低
在滴定调整期间和Palynziq治疗的维持。患者可能经历血苯基丙氨酸浓度低于30 µmol/L。对血苯基丙氨酸浓度低于30 µmol/L,Palynziq的剂量可能被减低和/或膳食蛋白和苯基丙氨酸摄取可能被修饰至维持血苯基丙氨酸浓度在临床上可接受范围内和高于30 µmol/L[见剂量和给药方法(2.2)]。
过敏反应后再给药
如Palynziq后一个过敏反应发作做决定再给药,在装备处理过敏反应卫生保健提供者监督下在过敏反应发作后给予首次剂量和严密地观察患者共至少60分钟。随后应根据患者耐受性和治疗反应剂量滴定调整[见警告和注意事项(5.1)]。
缺失剂量
如一个剂量被缺失,指导患者如给药时间表服用下一剂和不要服用两剂量Palynziq组成缺失剂量。
2.2 血苯基丙氨酸监视和膳食
用Palynziq开始治疗后,得到血苯基丙氨酸浓度每4周直至一个维持剂量被确定。一个维持剂量被确定后,定期血苯基丙氨酸监视被推荐评估血苯基丙氨酸控制。
监视患者膳食蛋白和苯基丙氨酸摄取用Palynziq治疗至始至终和商讨它们如何调整他们的膳食摄入,当需要时,根据血苯基丙氨酸浓度。
2.3 预先药物
对超敏性反应,Palynziq给药前考虑用一种H1-受体拮抗剂,H2-受体拮抗剂,和/或解热药预先药物 根据个体患者耐受性[见警告和注意事项(5.1,5.3)]。
2.4 给药指导
● 每个Palynziq预装注射器是意向作为单次皮下注射使用。
● 给药前肉眼地观察Palynziq颗粒物质和变色。Palynziq是一种透明至略微不透明,无色至浅黄色溶液。如变色,云雾状,如存在颗粒物质遗弃。
● Palynziq的首次给药前,处方自动-可注射的肾上腺素,和指导患者和观察者(如合适)对如何识别过敏反应的体征和症状,如何适当给予自动-可注射的肾上腺素,和立即寻求医学医护它的使用。
● 进行初始给药和/或再给药在一个过敏反应发作后在一位装备处理过敏反应的卫生保健提供者 处理过敏反应,和注射后严密观察患者共至少60分钟[见警告和注意事项(5.1)]。自身-注射前确证患者胜任用自身-给药。
● 考虑有一位成年观察者对患者可能需要帮助在识别和处理过敏反应。Palynziq治疗期间如一为成年观察者是需要,观察者应被存在期间和每次Palynziq给药后共至少60分钟,应是能够给药自身-可注射的肾上腺素,和寻求紧急一项支持在使用时[见警告和注意事项(5.1)]。
● 对Palynziq推荐的注射部位为大腿前中部: 和腹部至少2英寸(5厘米)以外离开神经。如一位护理人员正在给予注射,臀顶部和上臂背部也适用注射部位。
● 不要注射Palynziq至耳廓,瘢痕,出生标记,瘀伤,皮疹,或区域皮肤是硬,触痛,红,受损,烧伤,炎症,或纹身。核查注射部位对发红,肿胀,或触痛。
● 对Palynziq的皮肤注射部位旋转。如一个以上注射是需要对单个剂量Palynziq ,注射部位应是彼此离开至少2寸。第二个注射部位可以是在机体相同部位或机体的不同部分。
3 剂型和规格
Palynziq 是一种透明至略微不透明,无色至浅黄色溶液可得到如下:
● 注射液: 2.5 mg/0.5 mL单次-剂量预装注射器
● 注射液: 10 mg/0.5 mL单次-剂量预装注射器
● 注射液: 20 mg/mL单次-剂量预装注射器
4 禁忌证
无。
5 警告和注意事项
5.1 过敏反应
Palynziq的临床试验中 有诱导/滴定调整/维持给药,26/285(9%)患者经受总共37次过敏反应发作[见不良反应(6.1,6.2)]。过敏反应的暴露-调整率为最高在诱导和滴定调整期时(0.15发作/人-年; 5% 的患者有至少一次发作)和在维持相中减低(0.04发作/人-年;6%的患者有至少一次发作)。Palynziq的临床试验中,被报道过敏反应体征和症状包括晕厥,低血压,缺氧,呼吸困难,喘息,胸部不适/胸部发紧,心动过速,血管水肿(颜面,唇,眼,舌肿胀),喉头发紧,皮肤充血,皮疹,荨麻疹,瘙痒。和胃肠道症状(呕吐,恶心,腹泻)。Palynziq的临床试验中,过敏反应一般地发生注射后在1小时内 (84%; 28/37发作);但是,延迟发作也发生至Palynziq给药 48小时后。过敏反应的大多数发作在给药第一年内(78%,29/37发作),但给药的一年后也发生病例和直至834天(2.3年)至治疗。在Palynziq临床试验过敏反应的处理包括:自身-可注射的肾上腺素的给药(54%; 20/37发作),皮质激素(54%; 20/37发作),抗组织胺(51%; 19/37发作),和/或氧(5%; 2/37发作)。18/26 (69%)经受过敏反应患者被用Palynziq再挑战和5/18被再调整患者(28%)有过敏反应的复发。所有过敏反应发作被解决无后遗。.
考虑有一个成年观察者对患者可能需要帮助在识别和处理过敏反应Palynziq治疗期间。如需要一个 成年观察者,Palynziq给药期间和后共至少60分钟观察者应是存在,应是能自身-可注射的肾上腺素给予,和需要紧急医学支持关于它的使用。
过敏反应需要用自身-可注射的肾上腺素立即治疗。处方自身-可注射的肾上腺素对所有患者接受Palynziq和指导患者携带自身-可注射的肾上腺素随他们在所有时间当Palynziq治疗。首次剂量前,指导患者和观察者(如合适)关于如何识别过敏反应的体征和症状,如何适当地给予自身-可注射的肾上腺素,和寻求立即医学医护关于它的使用。考虑伴随自身-可注射的肾上腺素使用的风险当处方Palynziq。对完整资料参考对自身-可注射的肾上腺素处方资料。
考虑在过敏反应发作后再给予Palynziq的风险和获益。如做出决定再给予,在一位装备仪器处理过敏反应的卫生保健提供者监督下给予首次剂量和给药后严密观察患者共至少60分钟。随后应是根据患者耐受性和治疗反应滴定调整Palynziq剂量[见剂量和给药方法(2.4)]。
Palynziq 给药前根据个体患者耐受性考虑用一种H1-受体拮抗剂,H2-受体拮抗剂,和/或解热药预先药物。 [见剂量和给药方法(2.3)].
Palynziq是只能通过一种受限制程序在REMS下得到[见警告和注意事项(5.2)]。
5.2 Palynziq REMS程序
仅能通过一个受限制程序在一个REMS下被称为Palynziq REM得到Palynziq。因为过敏反应的风险[见警告和注意事项(5.1)]。
Palynziq REMS的值得注意要求包括以下:
● 处方者用程序必须是合格通过参加程序和完成训练。
● 处方者必须处方用Palynziq自身-可注射的肾上腺素。
● 药房必须合格用程序和必须仅分发给被授权的患者接受Palynziq.
● 患者必须参加程序和被合格处方者教育关于过敏反应风险确保他们了解用Palynziq治疗风险和获益。
●在所有时间当服用Palynziq患者必须可得到自身-可注射的肾上腺素。
进一步资料,包括合格药房清单在以下网址可得到www.PALYNZIQREMS.com或电话1-855-758-REMS (1-855-758-7367).
5.3 其他超敏性反应
超敏性反应,除了过敏反应[见警告和注意事项(5.1),不良反应(6.1,6.2)],曽被报道在196/ 285 (69%)用Palynziq治疗患者。其他超敏性反应的暴露调整率是最高在诱导和滴定调整期时(4.5发作/人-年; 50%的患者有至少一次不良反应)和维持相中减低(1.5发作/人-年; 57%的患者有至少一次不良反应)。
Palynziq给药前根据个体患者的耐受性考虑预先用一种H1-受体拮抗剂,H2-受体拮抗剂,和/或解热药药物[见剂量和给药方法(2.3)]。超敏性反应的处理应是 根据反应的严重程度,反应的复发,和卫生保健提供者的临床判断,和可能包括剂量调整,短暂药物中断,或用抗组织胺,解热药,和/或皮质激素治疗。
6 不良反应
下面在说明书的其他节讨论以下严重的不良反应:
● 过敏反应[见警告和注意事项(5.1)]
● 其他超敏性反应[见警告和注意事项(5.3)]
6.1临床试验经验
因为临床试验是在广泛不同情况下进行,临床试验观察到不良反应率不能与另一种药临床试验发生率直接比较而且可能不反映在一般患者群观察到的发生率。
下面描述数据反映在285接受Palynziq患者一个总治疗暴露580患者-年。在一项诱导/滴定调整/维持方案在临床试验[见临床研究 (14)]。在285患者中,229患者被暴露至Palynziq共24周,209患者被暴露共一年,137患者被暴露共2年,和85患者被暴露共3年或更长。患者群为均匀地分布在男性和女性患者间,均数年龄为29岁(范围: 16至56岁),和98%的患者为白种人。
最常见不良反应(至少20%的患者在任一治疗期)为注射部位反应,关节痛,超敏性反应,头痛,普遍性皮肤反应持续至少14天,瘙痒,恶心,腹痛,口咽痛,呕吐,咳嗽,腹泻,和疲乏。
在临床试验中暴露至Palynziq的285患者用一项诱导/滴定调整/维持方案,31(11%)患者终止治疗 由于不良反应。最常见不良反应导致治疗终止为超敏性反应(6%的患者)包括过敏反应(3%的患者)和血管水肿(1%的患者),关节痛(4%的患者),普遍性皮肤反应持续至少14天(2%的患者),和注射部位反应(1%的患者)。
最常见不良反应导致剂量减低为关节痛(14%的患者),超敏性反应(9%的患者),注射部位反应(4%的患者),脱发(3%的患者),和普遍皮肤反应持续至少14天(2%的患者)。
最常见不良反应导致短暂药物中断为关节痛(13%的患者),超敏性反应(13%的患者),过敏反应(4%的患者),和注射部位反应(4%的患者)。
表2 列出被报道不良反应在至少15%的患者用Palynziq治疗在一项诱导/滴定调整/维持剂量方案,和显示不良反应率经历按治疗期时间。表3列出实验室异常被报道在至少10%的患者用Palynziq治疗在一项诱导/滴定调整/维持剂量方案在临床试验。
对这些分析,诱导/滴定调整期被定义为到达一个稳定剂量前时间(在相同剂量水平时完成一个8-周期)。一旦达到一个稳定剂量,患者被考虑其后将在维持期。对患者达到维持期的安全性数据被包括在或诱导/滴定调整或维持期依赖于不良反应的发作日期。对患者安全性数据没有达到维持期被包括在诱导/滴定调整期内。维持期包括数据对患者是以前用Palynziq和研究302的随机撤出阶段转至安慰剂[见临床研究(14)]。
不良反应率(对暴露时间调整)一般地随时间减低和对有些留在相对地稳定。在维持期,不良反应率(对暴露时间调整) 在患者达到维持期跨越被评价剂量是有可比性。在维持期和被报道不良反应率的类型在患者接受 20 mg每天一次和40 mg每天一次是相似。
实验室异常率(对暴露时间调整)随时间保留相对地稳定,除了对补体C4低于正常的低限(LLN)和hs-CRP高于0.287 mg/dL历时一个6个月阶段(两者随时间减低)和低苯基丙氨酸血症(血苯基丙氨酸浓度低于30 µmol/L) 在一个单次测量(随时间增加)。维持相期间报道的实验室异常的类型和速率(对暴露时间调整)在患者接受20 mg每天1次和40 mg每天1次是相似除hs-CRP高于0.287 mg/dL历时一个6月阶段(暴露-调整的事件率分别0.04和0.08在患者用20 mg每天1次和40 mg每天1次)。


选定的不良反应的描述
关节痛
在临床试验中,235/285(83%)患者经受发作与关节痛一致(包括背痛,肌肉骨骼痛,肢体痛,和颈痛)。关节痛发作是更频在诱导/滴定调整相期间(7.6发作/患者-年)和随时间减低(1.5发作/患者-年在维持相)。39/285 (14%)患者有一次发作关节痛,32 (11%)患者有2次关节痛发作,18 (6%)有3次关节痛发作,和146(51%)有 4次或更多关节痛发作。关节痛发生早至Palynziq首次剂量后和发生在治疗期间任何时间。关节痛的均数时间为14天(中位数: 3添加,范围: 1天580天),和19%的关节痛发作有一个时间至少14天。严重关节痛(严重疼痛限制每天生活的自身-照顾活动)被报道至14 (5%)患者。除了关节痛,其他关节-相关被报道的为:关节肿胀(22患者; 8%),关节强直(22患者;8%),和肌肉关节强直(19患者; 7%)。关节痛发作被用药物处理(如,非甾体抗-炎症药物,糖皮质激素,和对乙酰氨基酚),Palynziq剂量减低(发作的4%),Palynziq中断(发作的4%),或Palynziq撤出(发作的0.6%)。关节痛发作的97%被报道为解决在末次观察时(直至随访的59月)。
注射部位反应
注射部位反应被报道早在治疗期间任何时间Palynziq的首次给药。注射部位反应是更频发在诱导/滴定调整相期间(21.9发作/患者-年)和随时间减低(在维持相4次发作/患者-年)。注射部位反应均数时间为8天(中位数: 2天,范围: 1至970天),和7%的注射部位反应有时间至少14天。99%的注射部位反应被报道为解决在末次观察时解决(至随访59月)。
三个注射部位反应与肉芽肿的皮肤病变一致被报道(各反应发生在一位患者): 肉芽肿性皮肤炎(发生 在Palynziq 治疗的464天后和持续16天),黄色肉芽肿(发生在Palynziq 治疗的378天后和持续638天)被用一个局部抗组织胺,皮质激素治疗,和Palynziq 治疗被终止,和糖尿病脂性渐进坏死[necrobiosis lipoidica diabeticorum](发生在Palynziq 治疗的281天后和持续281天)。糖尿病脂性渐进坏死被用甾体注射治疗和并发绿脓杆菌感染[Pseudomonas infection]。所有三个注射部位反应解决。
一例患者报道软组织感染(发生在Palynziq 治疗的196天和持续8天)伴随肠系膜蜂窝组织炎[mesenteric panniculitis]用抗菌素治疗,它导致治疗终止。
在临床试验中普遍性皮肤反应(不限于注射部位)持续至少14天,125/285(44%)用Palynziq治疗患者经受普遍性皮肤反应(不限于注射部位)持续至少14天。这些反应的均数时间为58天(中位数: 34天; 范围: 14至638天)。普遍性皮肤反应为更频在诱导/滴定调整相期间(0.7发作/患者-年),和随时间减少(0.3发作/患者年在维持相)。
从Palynziq的首次剂量至皮肤反应的发作均数时间为319天(中位数: 169天; 范围: 2 至1237天)。5%的这些反应持续至少180天,和85%的这些反应被报道为已解决在末次观察的时间(直至随访的 59月)。
血管水肿
在临床试验中,22/285(8%)患者经受血管水肿的45次发作(症状包括: 咽水肿,肿胀舌,唇肿胀,口肿胀,眼睑水肿和面水肿)发生与过敏反应无关。血管水肿(包括在表2超敏性下)为更频在诱导/滴定调整相期间(0.15发作/患者-年)和随时间减低(0.06发作/患者-年在维持相)。三例患者终止治疗。所有发作解决。血管水肿可能存在作为过敏反应的症状[见警告和注意事项(5.1)]。
血清病
在临床试验中,血清病被报道在7/285 (2%)患者。血清病发作为更频在诱导/滴定调整相期间(0.04发作/患者-年)和随时间减低(低于0.01发作/患者-年维持相期间)。所有血清病反应解决无后遗(血清病的时间范围从1至 8天)。经受血清病7患者中,5患者继续治疗无一例复发,和用药物中断,剂量减低和/或同时药物处理血清病。两例患者终止治疗。
6.2 免疫原性
如同所有治疗性蛋白,有对免疫原性潜能。空调形成的检测是高度依赖于分析的灵敏度和特异性。此外,在一项分析中抗体(包括纸盒抗体)阳性的观察发生率可能受几种因子影响,包括分析方法学,样品处置,采样时机,同时药物,和所患疾病。因为这些理由,在下面描述的研究中比较对Palynziq的抗体发生率与在其他研究或对其他产品抗体发生率 可能是误导。
所有用Palynziq治疗患者发生一个持续的总抗-药抗体(TAb)反应有一个患者的大多数(91%; N = 235/258)发生该反应在治疗的周4。Palynziq 开始后2周均数Tab滴度达峰和维持升高治疗至始至终(治疗开始后大于1年)。抗-苯基丙氨酸氨裂解酶(PAL)IgM抗体被检出在所有患者有患者的大多数(98%; N = 265/270)成为阳性对抗-PAL IgM至治疗开始后2月。抗-PAL IgG抗体被检出在几乎所有患者(N = 226/227)至治疗开始后4月。均数抗-PAL IgM和IgG滴度达峰在治疗开始后大约分别3和6月,和维持升高治疗至始至终(治疗开始后大于1年)。药物-诱导的抗-PEG IgM和IgG抗体被检出在患者的大多数(98%; N = 277/284对IgM;和278/284对IgG)有均数滴度对对两个峰在 治疗开始后1至 3月[见药物相互作用(7.1)]。中和抗体(NAb)能够抑制PAL酶活性被检出在至少一个测定在患者的大多数(88%; N = 249/284)随时间。均数Nab滴度达峰和达到一个平台在治疗的16至20周和然后维持存在治疗至始至终(治疗开始后大于 1年)。
25/26有过敏反应患者被测试对抗-pegvaliase-pqpz IgE抗体,它识别PEG化蛋白产品。在25被测试对抗-pegvaliase-pqpz IgE抗体患者中,24被测试患者阴性。一例患者对抗-pegvaliase-pqpz IgE抗体被测试阳性对用筛选测试没有足够样品确证IgE阳性。对抗-pegvaliase-pqpz IgE测试阴性患者 在过敏反应发作前和后常规访问(不在过敏反应时)。 Sixty-eight of在临床试验285患者的68例被测试对抗-PAL IgE抗体两者,它识别重组PAL蛋白,和对抗-pegvaliase-pqpz IgE抗体during常规研究访问期间(不在过敏反应发作时)或对超敏性反应附加访问期间。那些68 患者中,5 (7%)被测试阳性至少一次对抗-PAL IgE抗体但阴性对抗-pegvaliase-pqpz IgE抗体。
超敏性反应的最高频数(与一种类型III免疫复合物介导超敏性机制一致) 发生在Palynziq治疗的头6月内当均数循环免疫复合物(CIC)浓度为在它们的最高和均数补体C3和C4浓度是在它们的最低。 均数CIC浓度减低和补体水平增加随时间当超敏性反应暴露-调整率减低。IgG和IgM CIC浓度为高于正常上限分别在63% (N = 164/259)和41%的患者(N = 106/259),在Palynziq 治疗12周时。CIC阳性的发生率随时间减低。61%的患者(N = 110/180)有补体C3浓度低于正常低限(LLN)在治疗开始 6月后和38%的患者(N = 94/248)有补体C4浓度低于LLN在治疗开始后 3月时。 The 发生率 of 低补体C3和C4浓度随时间减低,但分别大约39% (N = 19/49)和12% (N = 6/49)的患者有低C3和C4浓度,在治疗开始后36月。
对所有抗体分析物较高抗体反应,包括NAb,被伴随有较低均数谷pegvaliase-pqpz浓度和有较高血苯基丙氨酸浓度。超敏性反应发生更频地在患者有较高抗体滴度对有些但不是所有抗体被分析物。患者有较高均数变化在IgG CIC浓度来自治疗前基线趋向有较高终止率比患者有较低均数变化在IgG CIC浓度。均数抗体滴度对抗-PAL IgG和IgM,Tab,和Nab依然相对稳定用长期治疗。
7 药物相互作用
7.1 Palynziq对其他PEG化产品的影响
在一项单次Palynziq剂量研究在成年患者有 苯基丙胺酸苯基丙胺酸尿(PKU),两例患者接受同时注射醋酸甲羟孕酮悬液(一种制剂含PEG 3350)经受超敏性反应。两例患者之一经受一个超敏性反应在天15后 一个单次 Palynziq 剂量0.67 mg内15分钟后醋酸甲羟孕酮可注射悬液,和皮下地经受过敏反应在天89醋酸甲羟孕酮可注射悬液的下一次剂量后30分钟内。其他经历一个超敏性反应在天40一个单次 Palynziq 剂量 0.08 mg内10分钟后醋酸甲羟孕酮可注射悬液。两患者有高抗-PEG IgG抗体滴度在或围绕超敏性反应的时间左右。
在Palynziq临床试验中,患者的大多数发生抗-PEG IgM和IgG抗体用Palynziq治疗后[见不良反应(6.2)]。不知道同时治疗用不同的PEG化产品的临床影响。 监视用Palynziq治疗患者和同时地用其他PEG化产品对超敏性反应包括过敏反应。
8 在特殊人群中使用
8.1 妊娠
风险总结
根据在妊娠动物无苯基丙胺酸苯基丙胺酸尿(PKU)用pegvaliase-pqpz治疗的研究中发现,Palynziq 可能致胎儿危害当给予至一位妊娠妇女。优先地可得到数据有pegvaliase-pqpz使用在妊娠妇女是不足以告知一个不良发育结局药物-关联风险。对胎儿伴随控制差的苯基丙氨酸浓度有风险在妇女有 PKU妊娠期间包括对流产,重大出生缺陷(包括头小畸形,重大心脏畸形),子宫内胎儿生长延迟,和未来智力的残疾与低IQ增加风险; 所以,苯基丙氨酸浓度应被严密地监视在妇女有PKU妊娠期间(见临床考虑和数据).
忠告妊娠妇女对胎儿潜在风险.
一项生殖研究在妊娠兔用pegvaliase-pqpz治疗显示一个高发生率的胎儿畸形遍及骨骼系统,和在肾,肺,和眼。胚胎-胎儿毒性(增加的再吸收和减低的胎儿体重)也被观察到。这些效应发生在7.5倍最大推荐的每天剂量和是伴随母体毒性的强体征,包括明显的减低体重增量和食物耗量,和死亡。一项生殖研究在妊娠大鼠中用pegvaliase-pqpz治疗显示一个增加在骨骼变异,与无畸形被观察到。在大鼠效应发生在4.2倍最大推荐的每天剂量。在一项围产期发育研究在大鼠中,哺乳期间pegvaliase-pqpz产生减低子代生存,减低幼畜体重和窝大小,和子代延迟性成熟当每天给予在19.4倍最大推荐的每天剂量。对大鼠胚胎-胎儿和产后新生儿发育效应是伴随母体毒性。
所有妊娠有一个重大出生缺陷的背景风险,妊娠丢失,或其他不良妊娠结局。在美国一般人群,重大出生缺陷和临床上认可妊娠流产的估算背景风险分别为2至4%和15至20%。
估算的背景风险的重大出生缺陷和流产在妊娠妇女有苯基丙胺酸苯基丙胺酸尿(PKU)患者维持血苯基丙氨酸浓度大于600 µmol/L妊娠期间是大于相应的背景风险对妊娠妇女无PKU。
有一个妊娠对Palynziq监视计划。如妊娠期间给予Palynziq,或如一位患者成为妊娠当接受Palynziq或末次剂量Palynziq后一个月内,卫生保健提供者应报告Palynziq暴露通过电话1-866-906-6100。
临床考虑
疾病-有关联的母体和/或胚胎-胎儿风险
妊娠前和期间胎儿风险未控制的血苯基丙氨酸浓度是 伴随有一种不良妊娠结局和胎儿不良效应的增加风险。为减低高苯基丙氨酸血症-诱导胎儿不良效应的风险,妊娠期间和受孕前3月期间血苯基丙氨酸浓度应被维持在120和360 µmol/L间[见剂量和给药方法(2.2)]。
妊娠期间和产后阶段剂量调整 苯基丙氨酸浓度低于30 µmol/L自妊娠妇女有 PKU用Palynziq治疗可能是伴随不良胎儿结局。妊娠期间监视血苯基丙氨酸浓度和调整Palynziq的剂量或修饰膳食蛋白和苯基丙氨酸 摄取避免血苯基丙氨酸浓度低于30 µmol/L[见剂量和给药方法(2.2)]。
数据
人数据
未控制的母体苯基丙胺酸苯基丙胺酸尿(PKU): 从母体苯基丙氨酸尿协作研究可得到数据对468妊娠和在有PKU妊娠妇女活出生331显示未控制苯基丙氨酸浓度高于600 µmol/L是伴随有一个对流产风险增加,重大出生缺陷(包括头小畸形,重大心脏畸形),子宫内胎儿生长延迟,和未来智力的残疾与低智商[IQ]。.
来自在妊娠妇女Palynziq 使用病例报告的有限数据是不足于确定一个药物-关联不良发育结局。
动物数据
所有发育毒性研究被进行在动物中(大鼠和兔)无PKU,在其中用pegvaliase-pqpz治疗产生一个剂量-依赖减低在母体血苯基丙氨酸浓度。在剂量产生母体毒性和/或影响对胚胎-胎儿发育,母体血浆苯基丙氨酸浓度与对照组比较是明显地减低。尚未评价母体苯基丙氨酸耗尽对胚胎-胎儿发育发生率的贡献。
皮下给予5 mg/kg/day pegvaliase-pqpz (7.5倍最大推荐的每天剂量根据体重[mg/kg])在妊娠兔器官形成阶段期间产生胚胎-致死性(增加再吸收),明显的减低在胎儿重量,和胎儿畸形。畸形包括头,机体和肢体的多种外部异常,多种软组织畸形(减低大小或肾缺乏,横隔疝,角膜混浊,变色或眼大小减低,和肺的减低大小)和颅面骨,脊椎,胸骨,肋骨,骨盆,肢体,和手指的多种骨骼畸形。在所有骨骼区域还观察到变异和延迟骨化一个增加。不良发育效应是伴随母体毒性,如被体重增量和食物耗量明显受损所示。死亡伴随体重丧失和流产发生在8%的妊娠兔用5 mg/kg/day pegvaliase-pqpz治疗。.
皮下给予2 mg/kg/day pegvaliase-pqpz(3倍最大推荐的每天剂量根据体重[mg/kg])在妊娠兔对胚胎-胎儿发育没有不良效应。对pegvaliase-pqpz 全身暴露被检测到在胎儿从兔用 2或5 mg/kg/day治疗。
Pegvaliase-pqpz增加胎儿改变当给予每天在妊娠大鼠在剂量8 mg/kg皮下地和更高(4.2倍人稳态 曲线下面积[AUC]在最大推荐的每天剂量)一个28-天交配前阶段期间,交配,和至器官形成阶段。胎儿改变是限于骨骼变异例如颈肋,腰椎裂和胸椎,和鳞状骨[squamosal bones],前额骨,腰椎弓,和肋骨的不完全骨化。每天给予20 mg/kg皮下地(19.4倍人稳态AUC在推荐的最大每天剂量)至妊娠大鼠产生减低窝大小和胎儿重量,它是伴随母体毒性(减低体重,卵巢重,和食物耗量)。在窝大小减少在20 mg/kg皮下地是继发于减低在黄体和植入。对pegvaliase-pqpz全身暴露被检测在胎儿从大鼠用20 mg/kg of pegvaliase-pqpz治疗(19.4倍人稳态AUC在 推荐的最大每天剂量)。皮下给予2 mg/kg/day pegvaliase-pqpz (低于人稳态AUC在最大推荐的每天剂量)在妊娠大鼠对胚胎-胎儿发育无不良影响。.
Pegvaliase-pqpz减低幼畜体重,窝大小,和子代的生存在哺乳期间,和延迟子代性成熟当给予每天在大鼠在20 mg/kg皮下地(19.4倍人稳态 AUC在推荐的最大每天剂量),用给药开始在交配前和继续至哺乳。效应在子代是伴随母体毒性。在子代未观察到效应在8 mg/kg/day皮下地(4.2倍人稳态 AUC 在推荐的最大每天剂量)。这项研究缺乏一个完全评价的身体和神经行为发育在子代; 但是,学习和记忆的测试中无pegvaliase-pqpz效应被注意到。.
8.2 哺乳
风险总结
关于在人乳汁中pegvaliase-pqpz的存在,对哺乳喂养婴儿影响,或对乳汁生产影响没有数据。一项在大鼠中围产期研究显示pegvaliase-pqpz是存在大鼠乳汁和哺乳期间给予pegvaliase-pqpz减低幼畜体重和生存[见在特殊人群中使用(8.1)]。但是,在大鼠幼畜中没有检测到pegvaliase-pqpz 全身吸收。Palynziq可能致低苯基丙氨酸浓度在人乳汁中。哺乳喂养的发育和健康获益应被考虑与对Palynziq 治疗临床需要和对哺乳喂养婴儿来自Palynziq或来自潜在情况任何潜在不良影响一并考虑(见临床考虑)。
临床考虑
在用Palynziq治疗哺乳喂养妇女监视血苯基丙氨酸浓度。
8.4 儿童使用
尚未确定在儿童患者中Palynziq的安全性和有效性。
8.5 老年人使用
Palynziq的临床研究没有包括患者年龄65岁和以上。
11 一般描述
Pegvaliase-pqpz是一种苯基丙氨酸-代谢酶是重组苯基丙氨酸胺裂解酶(rAvPAL)结合至N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS)-methoxypolyethylene glycol (PEG)组成。rAvPAL是在大肠杆菌细菌被制造,转化用一个质粒含苯基丙氨酸氨裂解酶(PAL)基因从念珠藻团[Anabaena] variabilis衍生。在rAvPAL制造过程期间,发酵携带营养介质含抗菌素卡那霉素。但是,卡那霉素在制造过程被清除和在最终产物中不能检测到。rAvPAL是一种四个相同亚基组成蛋白有一个分子量62 kD每个单体。为生产pegvaliase-pqpz,一个平均九个(9) 20 kD PEG分子被共价地结合(或结合)至每个单体rAvPAL. Pegvaliase-pqpz (rAvPAL-PEG)的总分子量接近1000 kD。
Palynziq (pegvaliase-pqpz)注射液,意向为皮下注射,是一个透明至略微不透明,无色至淡黄色,无菌,无防腐剂溶液和被制剂化在pH 6.6至7.4。
Palynziq在一个单次-剂量预装注射器提供和是可得到在三个剂量强度: 2.5 mg/0.5 mL,10 mg/0.5 mL,和20 mg/mL. 在表4中总结了各种剂量强度的Palynziq内容物。

12 临床药理学
12.1 作用机制
Pegvaliase-pqpz是一种PEG化的苯基丙氨酸氨裂解酶(PAL)转换苯基丙氨酸至氨和反式桂皮酸。它取代缺乏的苯基丙氨酸羟化酶(PAH)酶活性在患者有苯基丙胺酸苯基丙胺酸尿(PKU)和减低血苯基丙氨酸浓度。
12.2 药效动力学
Palynziq 治疗有 苯基丙胺酸苯基丙胺酸尿(PKU)成年患者导致血苯基丙氨酸浓度从治疗前基线的减低[见临床研究(14)]。血苯基丙氨酸浓度的减低减少与减低的pegvaliase-pqpz血浆浓度。
12.3 药代动力学
Pegvaliase-pqpz的药代动力学表现出高患者间和患者内变异性由于在有PKU成年患者免疫反应的异质性。较高抗体滴度与pegvaliase-pqpz的较高抗体滴度与较高表观清除率相关。在第一个八周的诱导和滴定调整治疗,血浆pegvaliase-pqpz浓度是低至不可测量的。用Palynziq 20 mg和40 mg皮下地每天一次维持治疗在稳态期间,均数 ± SD (范围)血浆谷pegvaliase-pqpz浓度分别为: 11.2 ± 9.0 (0.21 to 29.6) mg/L和10.4 ± 12.7 (0.18 to 43.1) mg/L。在成年患者有PKU用 Palynziq治疗在维持剂量20 mg每天1次和40 mg每天1次观察到药后药代动力学参数.
吸收
中位数Tmax为接近8小时。在稳态时均数 ± SD (范围)峰浓度(Cmax)分别为: 14.0 ± 16.3 (0.26至68.5) mg/L和16.7 ± 19.5 (0.24至63.8) mg/L。
分布
表观分布容积的均数 ± SD (范围)分别为26.4 ± 64.8 (1.8至 241) L和22.2 ± 19.7 (3.1至49.5) L。
消除
在稳态时表观清除率的均数± SD(范围)分别为0.39 ± 0.87(0.018至3.66)L/h和1.25 ± 2.46 L/h (0.034至8.88)。半衰期的均数±SD (范围)分别为47 ± 42 (14至132)小时和60 ± 45(14至127)小时。
代谢
苯基丙氨酸氨裂解酶的代谢被期望通过降解通路发生和被降解至小肽和氨基酸。.
排泄
在人中 Pegvaliase-pqpz的消除途径尚未研究。
13 非临床毒理学
13.1 癌发生,突变发生,生育率受损
未曽用pegvaliase-pqpz进行致癌性和遗传毒性研究。根据它的作用机制,pegvaliase-pqpz期望不是肿瘤生成。.
Pegvaliase-pqpz在雌性大鼠在产生受损的生育力在20 mg/kg/day 皮下地(19.4倍人稳态AUC 在最大推荐的每天剂量),如在黄体,植入,和窝大小中减低所示。这些效应是伴随毒性 (减低体重,卵巢重量,和食物消耗)。无效应对交配或生育力被观察到在雌性大鼠用8 mg/kg/day皮下地(4.2倍人稳态AUC在最大推荐的每天剂量)或在雄性大鼠用20 mg/kg/day皮下。
13.2 动物毒理学和/或药理学
在大鼠无苯基丙胺酸苯基丙胺酸尿(PKU)用pegvaliase-pqpz治疗的,剂量-依赖空泡在多个器官和组织被观察到在4-和26-周重复给药毒性研究在剂量8 mg/kg皮下地或更大给予2次每周(低于人稳态AUC在最大推荐的每天剂量)。空泡器官形成发生在肾小管细胞和在肝,脾,睾丸,肾上腺皮质,肠系膜淋巴结,和下颌淋巴结的组织细胞。受影响器官和组织的组织细胞中空泡形成持续在治疗停止后。在这些研究观察到空泡形成不伴随器官-相关毒性如测定被临床化学/尿分析和组织病理学检查。不知道这些发现的临床意义和功能性后果。
在39-周重复给药毒性研究在猴中,pegvaliase-pqpz 3 mg/kg皮下地2次每周(3倍人稳态AUC在最大推荐的每天剂量)产生全身动脉炎涉及小动脉和微动脉在一个广范围的器官和组织(肾,尿膀胱,胰腺,胆囊,食道,胃,十二指肠,空肠,回肠,盲肠,结肠,直肠,肺,心,坐骨神经,泪腺,下颌淋巴结,附睾,储精囊,卵巢,子宫,宫颈,和阴道)和在皮下注射部位。动脉炎是可能由于免疫介导的反应(如,免疫复合物沉积在血管)伴随一个外来蛋白慢性给药至动物。全身动脉炎的发生率和严重程度是剂量-依赖性。在这项研究观察到炎症是不伴随器官相关毒性如测定通过临床病理学参数(血液学,临床化学,和尿分析)和组织病理学检查。
未进行在大鼠和猴中用pegvaliase-pqpz的更长时间研究。
14 临床研究
研究301: 诱导/滴定调整/维持治疗
研究165-301 (被称为研究301,NCT01819727)是一项开放随机化,多中心研究有PKU成年评价在一个诱导/滴定调整/维持方案用一个目标维持剂量20 mg皮下地每天一次或40 mg皮下地每天一次Palynziq的自身-给药的安全性和耐受性。在Palynziq 治疗开始时,253患者显示不适当的血苯基丙氨酸控制(血苯基丙氨酸浓度大于600 µmol/L)用存在的处理,和8患者有血苯基丙氨酸浓度低于或等于600 µmol/L,存在处理选择包括 膳食苯基丙氨酸和蛋白摄取的以前和当前限制,和/或用二盐酸沙丙蝶呤[sapropterin dihydrochloride]以前治疗。患者以前用二盐酸沙丙蝶呤治疗被要求首次剂量前至终止使用至少14 天。
261被纳入患者为年龄16至55岁(均数: 29岁)和有一个基线均数(范围)血苯基丙氨酸的1,233 (285,2330) µmol/L。149/261(57%)患者为在基线时服用医疗食物和41/261患者(16%)在基线时用一种限制蛋白膳食(被定义为接受大于 75%的总蛋白摄取从医疗食物)。患者被随机化(1:1)至两种目标 维持剂量臂之一: 20 mg每天1次或40 mg每天1次。患者被滴定调整达到他们的随机化目标剂量的 20 mg每天1次或40 mg每天1次。滴定调整的时间在患者间变动和是根据患者耐受性。261被纳入患者,195 (75%)患者达到他们的随机化维持剂量(在20 mg每天1次臂103,在40 mg每天1次臂92).患者达到他们的随机维持剂量中,在20 mg每天1次随机化臂患者达到他们的维持剂量在一个中位数时间10周(范围: 9至29周)和在40 mg每天1次臂患者达到他们的维持剂量在一个中位数时间 11周(范围: 10至33周)。
被纳入在研究301261患者中,54 (21%)患者终止治疗研究301期间,4患者完成研究301和不继续至研究165-302 (被称为 研究302,NCT01889862),152患者继续至合格性阶段的研究302,和51患者继续直接地从研究301至研究302的长期治疗阶段。
研究302: 疗效评估
总共164成年有苯基丙胺酸苯基丙胺酸尿(PKU)患者患者是以前用Palynziq治疗过(152患者来自研究301和12患者来自其他Palynziq试验)被纳入在研究302和在研究302用Palynziq继续治疗共至13周评估对随机撤出阶段合格性。
随机撤出阶段
这个阶段后至附加Palynziq 治疗至13周在研究302,对纳入至该疗效评估阶段合格性(随机撤出阶段)被决定被是否一位患者实现至少一个20%减低在血苯基丙氨酸浓度从治疗前基线(当在以前研究)。86/164患者(52%)符合这个反应目标和继续进入随机撤出阶段。在双盲,安慰剂-对照,随机撤出阶段,患者被随机化在一个2:1比值至或继续他们的维持Palynziq剂量或接受匹配安慰剂共总共8周。治疗差别在最小平方(LS)均数变化在血苯基丙氨酸浓度从研究302随机化撤出基线至随机化撤出周8对各个随机化研究臂被显示在表5。均数血苯基丙氨酸浓度在治疗前基线(研究301或其他Palynziq试验)也被显示在表5。在研究302随机化撤出周8,Palynziq-被治疗患者(20 mg每天1次或40 mg每天1次)维持他们的血苯基丙氨酸浓度作为比较对他们的随机化撤出基线,而患者随机化至匹配安慰剂(20 mg每天1次或40 mg每天1次)返回至他们的治疗前基线血 苯基丙氨酸浓度(图1)。


图1: 观察的均数(SE)血苯基丙氨酸浓度随时间变化在成年患者有苯基丙胺酸苯基丙胺酸尿(PKU)在研究302
研究301和302连续治疗
118患者来自研究301有一个治疗前基线血苯基丙氨酸浓度大于600 µmol/L。患者被随机化至和接受至少一个剂量20 mg每天1次 Palynziq,108 患者,98 患者,和51患者分别被治疗共分别至少24周,48周,和96周。
118 患者中,53患者达到他们的首次反应(至少一个20%减低在血苯基丙氨酸浓度从治疗前基线或一个血苯基丙氨酸浓度低于或等于600 µmol/L)在治疗的 4周用20 mg每天1次和28患者达到他们的首次反应周 4和24间用20 mg每天1次。118 患者中,25患者递增他们的剂量从20 mg每天1次至40 mg每天1次达到一个首次反应前;那些25患者中,8患者达到他们的首次反应用4周治疗 用40 mg每天1次和6患者达到他们的首次反应在周 4和16间用40 mg每天1次。
16 如何供应/贮存和处置
如何供应
Palynziq (pegvaliase-pqpz)注射液被供应作为一个无防腐剂,无菌,透明至略微不透明,无色至浅黄色溶液。所有剂量强度的Palynziq被供应在一个1 mL玻璃注射器与一个26号,0.5英寸针头。
每纸盒含1或10碟有单次-剂量预装注射器(s),处方资料,用药指南,和使用指导。可得到以下包装规格。

贮存和处置
● 贮存在冰箱在36°F至46°F (2°C至8°C)在它的原始纸盒避光保护。.
● 不要冻结或摇晃。
● 对患者: 如需要时,贮存Palynziq在原始纸盒在室温68°F至77°F间(20°C至25°C)共至30天。. 在纸盒上记录从冰箱取出日期。一旦贮存在室温,不要将产品返回至冰箱。.
●贮存在室温共30天后储藏寿命过期,天,或产品纸盒上失效日期,看谁更早。.
17 患者咨询资料
建议患者阅读FDA-批准的患者说明书(用药指南和使用指导).
过敏反应和其他超敏性反应
● 忠告患者Palynziq可能致超敏性反应,包括过敏反应可能发生在任何时间。指导患者识别过敏反应的体征和症状[见警告和注意事项(5.1,5.3)]。
● 指导患者携带自身-可注射的肾上腺素与他们在Palynziq 治疗期间所有时间。指导患者和观察者(如合适)关于为过敏反应自身-可注射的肾上腺素的适当使用[见警告和注意事项(5.1)]。
● 指导患者经历过敏反应寻求立即医学医护,终止治疗,和恢复治疗仅在一位卫生保健提供者指导时[见警告和注意事项(5.1)]。
Palynziq REMS 程序
Palynziq仅通过一个受限制程序被称为 Palynziq REMS得到[见警告和注意事项(5.2)]。
告知患者以下值得注意要求:
●患者必须被纳入在Palynziq REMS。.
●患者必须被一位合格的处方者教育关于过敏反应风险确保他们了解用Palynziq治疗的风险和获益。.
●患者必须充填为自身-可注射的肾上腺素处方和在所有时间带着它。.
●患者将被给予一个Palynziq患者 钱包卡[Wallet Card]他们应在所有时间带着它。该卡描述症状 它如经受,应促使患者和观察者(如合适)立即寻求医疗护理。建议患者显示Palynziq Wallet卡至其他治疗卫生保健提供者。Palynziq是仅能从参加程序的合格的药房得到。所以,提供患者电话和网址对如何得到产品的信息。
给药
● 建议患者监视他们的膳食蛋白和苯基丙氨酸摄取用 Palynziq治疗至始至终,和调整摄取当他们的卫生保健提供者根据血苯基丙氨酸浓度的指导[见剂量和给药方法(2.2)]。
● 提供适当指导对自身-注射的方法,包括仔细复习 Palynziq用药指导和使用指导。指导患者无菌技术的使用当给予 Palynziq时[见剂量和给药方法(2.4)]。
● 告知患者一位卫生保健提供者将显示他们或他们的护理人员如何准备注射Palynziq在自身给药前。
● 忠告患者不要注射至痣,瘢痕,出生记号,瘀伤,皮疹,或区域处皮肤是硬,触痛,红,受损,烧伤,炎症,或纹身。
● 建议患者旋转注射与每次给药。建议患者核查注射部位对发红,肿胀,和触痛,和联系他们的卫生保健提供者如他们有一个皮肤反应和它不清除,或变坏。
● 建议患者遵循尖锐遗弃推荐[见使用指导]患者对安全遗弃步骤。
● 忠告患者储藏寿命过期在室温贮存共30天后或在产品纸盒上失效日期后,以先发生为准.
妊娠
● 建议妊娠妇女和生殖潜能女性对胎儿潜在风险。建议女性告知他们的卫生保健提供者一个已知或怀疑妊娠[见在特殊人群中使用(8.1)]。
● 建议妇女在被暴露至Palynziq妊娠期间或成为妊娠末次Palynziq剂量后一个月内有一个妊娠监视计划监视妊娠结局。鼓励这些患者报告她们的妊娠至BioMarin [见在特殊人群中使用(8.1)]。
使用说明书
新颖酶治疗为成年有PKU患者有未控制的血苯基丙按酸[苯基丙氨酸]浓度用当前治疗
2018年5月24日美国食品和药品监管局今天批准Palynziq(pegvaliase-pqpz)为成年有一种罕见和严重的遗传疾病被称为苯基丙胺酸苯基丙胺酸尿(PKU)。患者有PKU被出生有一种失能裂解苯基丙胺酸(Phe),一种氨基酸存在在含蛋白食物和高强度含蛋白食物和高-强度甜味剂被使用在各种食物和饮料。Palynziq是一种新颖酶治疗为成年PKU患者有未控制血Phe浓度用当前治疗。
FDA的药物评价和研究中心内药物评价III办公室主任Julie Beitz,M.D说:“这是一种新颖酶取代治疗帮助面对一种显著未满足需要在用当前治疗选择已不能控制他们的血Phe水平的PKU患者,” “这个新批准显示我们的承诺批准进展在治疗将给予有PKU患者对医护不同的选择。”
PKU影响约1在10,000至15,000在美国的人们。如未治疗,PKU可能致慢性智力的,神经发育和精神失能。苯基丙胺酸的通过膳食摄取终生受限是一种需要预防Palynziq 在体内的积蓄,它可能致中枢神经系统长期损伤。
在两项临床试验在成年患者有 苯基丙胺酸苯基丙胺酸尿(PKU)有血苯基丙胺酸浓度大于600 µmol/L 对存在的处理研究Palynziq的安全性和疗效。在Palynziq试验中大多数PKU患者在试验前和期间是用一种不受限制的膳食。第一个试验是一个随机化,开放试验在被治疗患者中用增加剂量的Palynziq 给予作为一个皮下注射至一个目标剂量的或20 mg每天一次或40 mg每天一次。第二个试验为一个8-周,安慰剂-对照,随机化撤出试验在患者以前用Palynziq治疗患者。患者用Palynziq治疗实现从他们的治疗前基线血Phe浓度在血苯基丙胺酸浓度统计上显著减低。
在 Palynziq试验中被报道的最常见不良事件包括注射部位反应,关节疼痛,超敏性反应,头痛,普遍性皮肤反应持续至少14天,瘙痒,恶心,眩晕,腹痛,喉痛,疲乏,呕吐,咳嗽和腹泻。在大多数患者中发生超敏性反应,可能地由于形成对产品的抗体。.
在Palynziq试验中最严重不良反应为过敏反应,它发生最频在治疗的头一年向上滴定调整剂量期间。因为这个严重的风险,对Palynziq说明书包括包括一个黑框警告和产品仅通过一个受限制的程序在一个风险评价和缓解策略(REMS)被称为Palynziq REMS程序才能得到。Palynziq REMS 程序的令人注目要求包括以下:
● 处方者必须合格通过纳入REMS 程序和完成训练
● 处方者必须处方自动-可注射的肾上腺素与 Palynziq
● 药房必须合格有程序和必须仅分发至患者被授权接受Palynziq
● 患者必须纳入程序和被合格处方者教育关于 过敏反应的风险处方者确保他们了解用Palynziq治疗的风险和获益
● 患者必须有自动-可注射的肾上腺素可得到在当采用Palynziq所有时间
FDA赋予Palynziq的批准给予BioMarin Pharmaceutical有限公司
这些重点不包括安全和有效使用PALYNZIQ需所有资料。请参阅PALYNZIQ 完整处方资料。
PALYNZIQ (pegvaliase-pqpz)注射液,为皮下使用
美国初次批准: 2018
 适应证和用途
适应证和用途
Palynziq是一种苯基丙氨酸[phenylalanine]-代谢酶适用减低血苯基丙氨酸浓度在成年患者有苯基丙氨酸尿患者有未控制的血苯基丙氨酸浓度大于600 µmol/L用存在处理。(1)
剂量和给药方法
剂量 (2.1)
● 治疗开始前得到基线血苯基丙氨酸浓度。
● 推荐的初始剂量为2.5 mg皮下每周一次共4周。
● 滴定调整剂量在逐步方式历时至少5周根据耐受性实现一个剂量20 mg皮下地每天一次。对滴定调整方案见完整处方资料。
● 评估患者耐受性,血苯基丙氨酸浓度,和膳食蛋白和苯基丙氨酸摄取至始至终治疗。
● 考虑增加剂量至最大40 mg皮下地每天一次在患者曽被用20 mg每天1次连续地共至少24周和患者未曽实现或一个20%减低在血苯基丙氨酸浓度从治疗前基线或一个血苯基丙氨酸浓度低于或等于600 µmol/L。
● 终止Palynziq在患者没有实现至少一个20%减低在血苯基丙氨酸浓度从治疗前基线或一个血 苯基丙氨酸浓度低于或等于600 µmol/L连续治疗的16周后 与最大剂量40 mg每天1次。
● 减低剂量和/或修饰膳食蛋白和苯基丙氨酸摄取,如需要时,以维持血苯基丙氨酸浓度一个临床上可接受的范围和高于30 µmol/L。血苯基丙氨酸监视和膳食(2.2)。
● 得到血苯基丙氨酸浓度每4周直至一个维持剂量被确定。
● 一个维持剂量被确定后,定期地监视血苯基丙氨酸浓度。
●与患者商讨监视膳食蛋白和苯基丙氨酸摄取,和由卫生保健提供者指导调整。y their 卫生保健提供者. 预先药物 (2.3,5.1,5.3)
● 考虑预先药物对超敏性反应. 给药指导 (2.4)
●。如对单次剂量需要一个以上注射旋转注射部位。
剂型和规格
注射液: 2.5 mg/0.5 mL,10 mg/0.5 mL,和20 mg/mL在一个单次-剂量预装注射器. (3)
禁忌证
无。(4)
警告和注意事项
超敏性反应,除了过敏反应: 处理应被根据反应的严重程度,复发,和临床判断,和可能包括剂量调整,短暂中断药物,或用抗组织胺,解热药,和/或皮质激素治疗。 (5.3)
不良反应
最常见不良反应(在任一治疗相至少20%)为: 注射部位反应,关节痛,超敏性反应,头痛,普遍性皮肤反应持续至少14天,瘙痒,恶心,腹痛,口咽痛,呕吐,咳嗽,腹泻,和疲乏. (6.1)
报告怀疑不良反应,联系BioMarin Pharmaceutical公司at 1-866- 6-906-6100, or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088或www.fda.gov/medwatch.
药物相互作用
Palynziq对其他PEG化产品的影响。监视对超敏性反应,包括过敏反应,与同时治疗。 (7.1)
在特殊人群中使用
妊娠: 可能致胎儿危害。(8.1)
完整处方资料


1 适应证和用途
Palynziq是适用为减低血苯基丙氨酸浓度在成年患者有苯基丙氨酸尿(PKU)患者有未控制的血苯基丙氨酸浓度大于600 µmol/L用存在处理。.
2 剂量和给药方法
2.1 剂量
● 用Palynziq治疗应被PKU中有经验的一个健康保健提供者
处理。
● 治疗开始前得到基线血苯基丙氨酸浓度。
诱导
对Palynziq推荐的初始诱导剂量为2.5 mg皮下每周一次共4周。在一位卫生保健提供者的监督下给予初始剂量[见剂量和给药方法(2.4)]。
滴定调整
滴定调整Palynziq剂量在逐步方式,根据耐受性,历时至少5周,实现一个剂量20 mg皮下地每天一次按照表1。
维持
治疗反应可能不实现直至患者被滴定调整至维持Palynziq维持有效剂量。使用Palynziq的最低有效和耐受剂量。
评估患者耐受性,血苯基丙氨酸浓度,和膳食蛋白和苯基丙氨酸摄取至始至终治疗。维持Palynziq剂量在20 mg皮下地每天一次共至少24周。考虑增加Palynziq剂量至最大40 mg皮下地每天一次在患者曽被连续地维持用20 mg每天1次共至少24周和患者没有实现或一个20%减低在血苯基丙氨酸浓度从治疗前基线或一个血苯基丙氨酸浓度低于或等于600 µmol/L。
终止
终止Palynziq在患者没有实现一个反应(至少一个20%减低在血苯基丙氨酸浓度从治疗前基线或一个血苯基丙氨酸浓度低于或等于 600 µmol/L)用最大剂量40 mg每天1次连续治疗16周后。


对低苯基丙氨酸浓度剂量减低
在滴定调整期间和Palynziq治疗的维持。患者可能经历血苯基丙氨酸浓度低于30 µmol/L。对血苯基丙氨酸浓度低于30 µmol/L,Palynziq的剂量可能被减低和/或膳食蛋白和苯基丙氨酸摄取可能被修饰至维持血苯基丙氨酸浓度在临床上可接受范围内和高于30 µmol/L[见剂量和给药方法(2.2)]。
过敏反应后再给药
如Palynziq后一个过敏反应发作做决定再给药,在装备处理过敏反应卫生保健提供者监督下在过敏反应发作后给予首次剂量和严密地观察患者共至少60分钟。随后应根据患者耐受性和治疗反应剂量滴定调整[见警告和注意事项(5.1)]。
缺失剂量
如一个剂量被缺失,指导患者如给药时间表服用下一剂和不要服用两剂量Palynziq组成缺失剂量。
2.2 血苯基丙氨酸监视和膳食
用Palynziq开始治疗后,得到血苯基丙氨酸浓度每4周直至一个维持剂量被确定。一个维持剂量被确定后,定期血苯基丙氨酸监视被推荐评估血苯基丙氨酸控制。
监视患者膳食蛋白和苯基丙氨酸摄取用Palynziq治疗至始至终和商讨它们如何调整他们的膳食摄入,当需要时,根据血苯基丙氨酸浓度。
2.3 预先药物
对超敏性反应,Palynziq给药前考虑用一种H1-受体拮抗剂,H2-受体拮抗剂,和/或解热药预先药物 根据个体患者耐受性[见警告和注意事项(5.1,5.3)]。
2.4 给药指导
● 每个Palynziq预装注射器是意向作为单次皮下注射使用。
● 给药前肉眼地观察Palynziq颗粒物质和变色。Palynziq是一种透明至略微不透明,无色至浅黄色溶液。如变色,云雾状,如存在颗粒物质遗弃。
● Palynziq的首次给药前,处方自动-可注射的肾上腺素,和指导患者和观察者(如合适)对如何识别过敏反应的体征和症状,如何适当给予自动-可注射的肾上腺素,和立即寻求医学医护它的使用。
● 进行初始给药和/或再给药在一个过敏反应发作后在一位装备处理过敏反应的卫生保健提供者 处理过敏反应,和注射后严密观察患者共至少60分钟[见警告和注意事项(5.1)]。自身-注射前确证患者胜任用自身-给药。
● 考虑有一位成年观察者对患者可能需要帮助在识别和处理过敏反应。Palynziq治疗期间如一为成年观察者是需要,观察者应被存在期间和每次Palynziq给药后共至少60分钟,应是能够给药自身-可注射的肾上腺素,和寻求紧急一项支持在使用时[见警告和注意事项(5.1)]。
● 对Palynziq推荐的注射部位为大腿前中部: 和腹部至少2英寸(5厘米)以外离开神经。如一位护理人员正在给予注射,臀顶部和上臂背部也适用注射部位。
● 不要注射Palynziq至耳廓,瘢痕,出生标记,瘀伤,皮疹,或区域皮肤是硬,触痛,红,受损,烧伤,炎症,或纹身。核查注射部位对发红,肿胀,或触痛。
● 对Palynziq的皮肤注射部位旋转。如一个以上注射是需要对单个剂量Palynziq ,注射部位应是彼此离开至少2寸。第二个注射部位可以是在机体相同部位或机体的不同部分。
3 剂型和规格
Palynziq 是一种透明至略微不透明,无色至浅黄色溶液可得到如下:
● 注射液: 2.5 mg/0.5 mL单次-剂量预装注射器
● 注射液: 10 mg/0.5 mL单次-剂量预装注射器
● 注射液: 20 mg/mL单次-剂量预装注射器
4 禁忌证
无。
5 警告和注意事项
5.1 过敏反应
Palynziq的临床试验中 有诱导/滴定调整/维持给药,26/285(9%)患者经受总共37次过敏反应发作[见不良反应(6.1,6.2)]。过敏反应的暴露-调整率为最高在诱导和滴定调整期时(0.15发作/人-年; 5% 的患者有至少一次发作)和在维持相中减低(0.04发作/人-年;6%的患者有至少一次发作)。Palynziq的临床试验中,被报道过敏反应体征和症状包括晕厥,低血压,缺氧,呼吸困难,喘息,胸部不适/胸部发紧,心动过速,血管水肿(颜面,唇,眼,舌肿胀),喉头发紧,皮肤充血,皮疹,荨麻疹,瘙痒。和胃肠道症状(呕吐,恶心,腹泻)。Palynziq的临床试验中,过敏反应一般地发生注射后在1小时内 (84%; 28/37发作);但是,延迟发作也发生至Palynziq给药 48小时后。过敏反应的大多数发作在给药第一年内(78%,29/37发作),但给药的一年后也发生病例和直至834天(2.3年)至治疗。在Palynziq临床试验过敏反应的处理包括:自身-可注射的肾上腺素的给药(54%; 20/37发作),皮质激素(54%; 20/37发作),抗组织胺(51%; 19/37发作),和/或氧(5%; 2/37发作)。18/26 (69%)经受过敏反应患者被用Palynziq再挑战和5/18被再调整患者(28%)有过敏反应的复发。所有过敏反应发作被解决无后遗。.
考虑有一个成年观察者对患者可能需要帮助在识别和处理过敏反应Palynziq治疗期间。如需要一个 成年观察者,Palynziq给药期间和后共至少60分钟观察者应是存在,应是能自身-可注射的肾上腺素给予,和需要紧急医学支持关于它的使用。
过敏反应需要用自身-可注射的肾上腺素立即治疗。处方自身-可注射的肾上腺素对所有患者接受Palynziq和指导患者携带自身-可注射的肾上腺素随他们在所有时间当Palynziq治疗。首次剂量前,指导患者和观察者(如合适)关于如何识别过敏反应的体征和症状,如何适当地给予自身-可注射的肾上腺素,和寻求立即医学医护关于它的使用。考虑伴随自身-可注射的肾上腺素使用的风险当处方Palynziq。对完整资料参考对自身-可注射的肾上腺素处方资料。
考虑在过敏反应发作后再给予Palynziq的风险和获益。如做出决定再给予,在一位装备仪器处理过敏反应的卫生保健提供者监督下给予首次剂量和给药后严密观察患者共至少60分钟。随后应是根据患者耐受性和治疗反应滴定调整Palynziq剂量[见剂量和给药方法(2.4)]。
Palynziq 给药前根据个体患者耐受性考虑用一种H1-受体拮抗剂,H2-受体拮抗剂,和/或解热药预先药物。 [见剂量和给药方法(2.3)].
Palynziq是只能通过一种受限制程序在REMS下得到[见警告和注意事项(5.2)]。
5.2 Palynziq REMS程序
仅能通过一个受限制程序在一个REMS下被称为Palynziq REM得到Palynziq。因为过敏反应的风险[见警告和注意事项(5.1)]。
Palynziq REMS的值得注意要求包括以下:
● 处方者用程序必须是合格通过参加程序和完成训练。
● 处方者必须处方用Palynziq自身-可注射的肾上腺素。
● 药房必须合格用程序和必须仅分发给被授权的患者接受Palynziq.
● 患者必须参加程序和被合格处方者教育关于过敏反应风险确保他们了解用Palynziq治疗风险和获益。
●在所有时间当服用Palynziq患者必须可得到自身-可注射的肾上腺素。
进一步资料,包括合格药房清单在以下网址可得到www.PALYNZIQREMS.com或电话1-855-758-REMS (1-855-758-7367).
5.3 其他超敏性反应
超敏性反应,除了过敏反应[见警告和注意事项(5.1),不良反应(6.1,6.2)],曽被报道在196/ 285 (69%)用Palynziq治疗患者。其他超敏性反应的暴露调整率是最高在诱导和滴定调整期时(4.5发作/人-年; 50%的患者有至少一次不良反应)和维持相中减低(1.5发作/人-年; 57%的患者有至少一次不良反应)。
Palynziq给药前根据个体患者的耐受性考虑预先用一种H1-受体拮抗剂,H2-受体拮抗剂,和/或解热药药物[见剂量和给药方法(2.3)]。超敏性反应的处理应是 根据反应的严重程度,反应的复发,和卫生保健提供者的临床判断,和可能包括剂量调整,短暂药物中断,或用抗组织胺,解热药,和/或皮质激素治疗。
6 不良反应
下面在说明书的其他节讨论以下严重的不良反应:
● 过敏反应[见警告和注意事项(5.1)]
● 其他超敏性反应[见警告和注意事项(5.3)]
6.1临床试验经验
因为临床试验是在广泛不同情况下进行,临床试验观察到不良反应率不能与另一种药临床试验发生率直接比较而且可能不反映在一般患者群观察到的发生率。
下面描述数据反映在285接受Palynziq患者一个总治疗暴露580患者-年。在一项诱导/滴定调整/维持方案在临床试验[见临床研究 (14)]。在285患者中,229患者被暴露至Palynziq共24周,209患者被暴露共一年,137患者被暴露共2年,和85患者被暴露共3年或更长。患者群为均匀地分布在男性和女性患者间,均数年龄为29岁(范围: 16至56岁),和98%的患者为白种人。
最常见不良反应(至少20%的患者在任一治疗期)为注射部位反应,关节痛,超敏性反应,头痛,普遍性皮肤反应持续至少14天,瘙痒,恶心,腹痛,口咽痛,呕吐,咳嗽,腹泻,和疲乏。
在临床试验中暴露至Palynziq的285患者用一项诱导/滴定调整/维持方案,31(11%)患者终止治疗 由于不良反应。最常见不良反应导致治疗终止为超敏性反应(6%的患者)包括过敏反应(3%的患者)和血管水肿(1%的患者),关节痛(4%的患者),普遍性皮肤反应持续至少14天(2%的患者),和注射部位反应(1%的患者)。
最常见不良反应导致剂量减低为关节痛(14%的患者),超敏性反应(9%的患者),注射部位反应(4%的患者),脱发(3%的患者),和普遍皮肤反应持续至少14天(2%的患者)。
最常见不良反应导致短暂药物中断为关节痛(13%的患者),超敏性反应(13%的患者),过敏反应(4%的患者),和注射部位反应(4%的患者)。
表2 列出被报道不良反应在至少15%的患者用Palynziq治疗在一项诱导/滴定调整/维持剂量方案,和显示不良反应率经历按治疗期时间。表3列出实验室异常被报道在至少10%的患者用Palynziq治疗在一项诱导/滴定调整/维持剂量方案在临床试验。
对这些分析,诱导/滴定调整期被定义为到达一个稳定剂量前时间(在相同剂量水平时完成一个8-周期)。一旦达到一个稳定剂量,患者被考虑其后将在维持期。对患者达到维持期的安全性数据被包括在或诱导/滴定调整或维持期依赖于不良反应的发作日期。对患者安全性数据没有达到维持期被包括在诱导/滴定调整期内。维持期包括数据对患者是以前用Palynziq和研究302的随机撤出阶段转至安慰剂[见临床研究(14)]。
不良反应率(对暴露时间调整)一般地随时间减低和对有些留在相对地稳定。在维持期,不良反应率(对暴露时间调整) 在患者达到维持期跨越被评价剂量是有可比性。在维持期和被报道不良反应率的类型在患者接受 20 mg每天一次和40 mg每天一次是相似。
实验室异常率(对暴露时间调整)随时间保留相对地稳定,除了对补体C4低于正常的低限(LLN)和hs-CRP高于0.287 mg/dL历时一个6个月阶段(两者随时间减低)和低苯基丙氨酸血症(血苯基丙氨酸浓度低于30 µmol/L) 在一个单次测量(随时间增加)。维持相期间报道的实验室异常的类型和速率(对暴露时间调整)在患者接受20 mg每天1次和40 mg每天1次是相似除hs-CRP高于0.287 mg/dL历时一个6月阶段(暴露-调整的事件率分别0.04和0.08在患者用20 mg每天1次和40 mg每天1次)。


选定的不良反应的描述
关节痛
在临床试验中,235/285(83%)患者经受发作与关节痛一致(包括背痛,肌肉骨骼痛,肢体痛,和颈痛)。关节痛发作是更频在诱导/滴定调整相期间(7.6发作/患者-年)和随时间减低(1.5发作/患者-年在维持相)。39/285 (14%)患者有一次发作关节痛,32 (11%)患者有2次关节痛发作,18 (6%)有3次关节痛发作,和146(51%)有 4次或更多关节痛发作。关节痛发生早至Palynziq首次剂量后和发生在治疗期间任何时间。关节痛的均数时间为14天(中位数: 3添加,范围: 1天580天),和19%的关节痛发作有一个时间至少14天。严重关节痛(严重疼痛限制每天生活的自身-照顾活动)被报道至14 (5%)患者。除了关节痛,其他关节-相关被报道的为:关节肿胀(22患者; 8%),关节强直(22患者;8%),和肌肉关节强直(19患者; 7%)。关节痛发作被用药物处理(如,非甾体抗-炎症药物,糖皮质激素,和对乙酰氨基酚),Palynziq剂量减低(发作的4%),Palynziq中断(发作的4%),或Palynziq撤出(发作的0.6%)。关节痛发作的97%被报道为解决在末次观察时(直至随访的59月)。
注射部位反应
注射部位反应被报道早在治疗期间任何时间Palynziq的首次给药。注射部位反应是更频发在诱导/滴定调整相期间(21.9发作/患者-年)和随时间减低(在维持相4次发作/患者-年)。注射部位反应均数时间为8天(中位数: 2天,范围: 1至970天),和7%的注射部位反应有时间至少14天。99%的注射部位反应被报道为解决在末次观察时解决(至随访59月)。
三个注射部位反应与肉芽肿的皮肤病变一致被报道(各反应发生在一位患者): 肉芽肿性皮肤炎(发生 在Palynziq 治疗的464天后和持续16天),黄色肉芽肿(发生在Palynziq 治疗的378天后和持续638天)被用一个局部抗组织胺,皮质激素治疗,和Palynziq 治疗被终止,和糖尿病脂性渐进坏死[necrobiosis lipoidica diabeticorum](发生在Palynziq 治疗的281天后和持续281天)。糖尿病脂性渐进坏死被用甾体注射治疗和并发绿脓杆菌感染[Pseudomonas infection]。所有三个注射部位反应解决。
一例患者报道软组织感染(发生在Palynziq 治疗的196天和持续8天)伴随肠系膜蜂窝组织炎[mesenteric panniculitis]用抗菌素治疗,它导致治疗终止。
在临床试验中普遍性皮肤反应(不限于注射部位)持续至少14天,125/285(44%)用Palynziq治疗患者经受普遍性皮肤反应(不限于注射部位)持续至少14天。这些反应的均数时间为58天(中位数: 34天; 范围: 14至638天)。普遍性皮肤反应为更频在诱导/滴定调整相期间(0.7发作/患者-年),和随时间减少(0.3发作/患者年在维持相)。
从Palynziq的首次剂量至皮肤反应的发作均数时间为319天(中位数: 169天; 范围: 2 至1237天)。5%的这些反应持续至少180天,和85%的这些反应被报道为已解决在末次观察的时间(直至随访的 59月)。
血管水肿
在临床试验中,22/285(8%)患者经受血管水肿的45次发作(症状包括: 咽水肿,肿胀舌,唇肿胀,口肿胀,眼睑水肿和面水肿)发生与过敏反应无关。血管水肿(包括在表2超敏性下)为更频在诱导/滴定调整相期间(0.15发作/患者-年)和随时间减低(0.06发作/患者-年在维持相)。三例患者终止治疗。所有发作解决。血管水肿可能存在作为过敏反应的症状[见警告和注意事项(5.1)]。
血清病
在临床试验中,血清病被报道在7/285 (2%)患者。血清病发作为更频在诱导/滴定调整相期间(0.04发作/患者-年)和随时间减低(低于0.01发作/患者-年维持相期间)。所有血清病反应解决无后遗(血清病的时间范围从1至 8天)。经受血清病7患者中,5患者继续治疗无一例复发,和用药物中断,剂量减低和/或同时药物处理血清病。两例患者终止治疗。
6.2 免疫原性
如同所有治疗性蛋白,有对免疫原性潜能。空调形成的检测是高度依赖于分析的灵敏度和特异性。此外,在一项分析中抗体(包括纸盒抗体)阳性的观察发生率可能受几种因子影响,包括分析方法学,样品处置,采样时机,同时药物,和所患疾病。因为这些理由,在下面描述的研究中比较对Palynziq的抗体发生率与在其他研究或对其他产品抗体发生率 可能是误导。
所有用Palynziq治疗患者发生一个持续的总抗-药抗体(TAb)反应有一个患者的大多数(91%; N = 235/258)发生该反应在治疗的周4。Palynziq 开始后2周均数Tab滴度达峰和维持升高治疗至始至终(治疗开始后大于1年)。抗-苯基丙氨酸氨裂解酶(PAL)IgM抗体被检出在所有患者有患者的大多数(98%; N = 265/270)成为阳性对抗-PAL IgM至治疗开始后2月。抗-PAL IgG抗体被检出在几乎所有患者(N = 226/227)至治疗开始后4月。均数抗-PAL IgM和IgG滴度达峰在治疗开始后大约分别3和6月,和维持升高治疗至始至终(治疗开始后大于1年)。药物-诱导的抗-PEG IgM和IgG抗体被检出在患者的大多数(98%; N = 277/284对IgM;和278/284对IgG)有均数滴度对对两个峰在 治疗开始后1至 3月[见药物相互作用(7.1)]。中和抗体(NAb)能够抑制PAL酶活性被检出在至少一个测定在患者的大多数(88%; N = 249/284)随时间。均数Nab滴度达峰和达到一个平台在治疗的16至20周和然后维持存在治疗至始至终(治疗开始后大于 1年)。
25/26有过敏反应患者被测试对抗-pegvaliase-pqpz IgE抗体,它识别PEG化蛋白产品。在25被测试对抗-pegvaliase-pqpz IgE抗体患者中,24被测试患者阴性。一例患者对抗-pegvaliase-pqpz IgE抗体被测试阳性对用筛选测试没有足够样品确证IgE阳性。对抗-pegvaliase-pqpz IgE测试阴性患者 在过敏反应发作前和后常规访问(不在过敏反应时)。 Sixty-eight of在临床试验285患者的68例被测试对抗-PAL IgE抗体两者,它识别重组PAL蛋白,和对抗-pegvaliase-pqpz IgE抗体during常规研究访问期间(不在过敏反应发作时)或对超敏性反应附加访问期间。那些68 患者中,5 (7%)被测试阳性至少一次对抗-PAL IgE抗体但阴性对抗-pegvaliase-pqpz IgE抗体。
超敏性反应的最高频数(与一种类型III免疫复合物介导超敏性机制一致) 发生在Palynziq治疗的头6月内当均数循环免疫复合物(CIC)浓度为在它们的最高和均数补体C3和C4浓度是在它们的最低。 均数CIC浓度减低和补体水平增加随时间当超敏性反应暴露-调整率减低。IgG和IgM CIC浓度为高于正常上限分别在63% (N = 164/259)和41%的患者(N = 106/259),在Palynziq 治疗12周时。CIC阳性的发生率随时间减低。61%的患者(N = 110/180)有补体C3浓度低于正常低限(LLN)在治疗开始 6月后和38%的患者(N = 94/248)有补体C4浓度低于LLN在治疗开始后 3月时。 The 发生率 of 低补体C3和C4浓度随时间减低,但分别大约39% (N = 19/49)和12% (N = 6/49)的患者有低C3和C4浓度,在治疗开始后36月。
对所有抗体分析物较高抗体反应,包括NAb,被伴随有较低均数谷pegvaliase-pqpz浓度和有较高血苯基丙氨酸浓度。超敏性反应发生更频地在患者有较高抗体滴度对有些但不是所有抗体被分析物。患者有较高均数变化在IgG CIC浓度来自治疗前基线趋向有较高终止率比患者有较低均数变化在IgG CIC浓度。均数抗体滴度对抗-PAL IgG和IgM,Tab,和Nab依然相对稳定用长期治疗。
7 药物相互作用
7.1 Palynziq对其他PEG化产品的影响
在一项单次Palynziq剂量研究在成年患者有 苯基丙胺酸苯基丙胺酸尿(PKU),两例患者接受同时注射醋酸甲羟孕酮悬液(一种制剂含PEG 3350)经受超敏性反应。两例患者之一经受一个超敏性反应在天15后 一个单次 Palynziq 剂量0.67 mg内15分钟后醋酸甲羟孕酮可注射悬液,和皮下地经受过敏反应在天89醋酸甲羟孕酮可注射悬液的下一次剂量后30分钟内。其他经历一个超敏性反应在天40一个单次 Palynziq 剂量 0.08 mg内10分钟后醋酸甲羟孕酮可注射悬液。两患者有高抗-PEG IgG抗体滴度在或围绕超敏性反应的时间左右。
在Palynziq临床试验中,患者的大多数发生抗-PEG IgM和IgG抗体用Palynziq治疗后[见不良反应(6.2)]。不知道同时治疗用不同的PEG化产品的临床影响。 监视用Palynziq治疗患者和同时地用其他PEG化产品对超敏性反应包括过敏反应。
8 在特殊人群中使用
8.1 妊娠
风险总结
根据在妊娠动物无苯基丙胺酸苯基丙胺酸尿(PKU)用pegvaliase-pqpz治疗的研究中发现,Palynziq 可能致胎儿危害当给予至一位妊娠妇女。优先地可得到数据有pegvaliase-pqpz使用在妊娠妇女是不足以告知一个不良发育结局药物-关联风险。对胎儿伴随控制差的苯基丙氨酸浓度有风险在妇女有 PKU妊娠期间包括对流产,重大出生缺陷(包括头小畸形,重大心脏畸形),子宫内胎儿生长延迟,和未来智力的残疾与低IQ增加风险; 所以,苯基丙氨酸浓度应被严密地监视在妇女有PKU妊娠期间(见临床考虑和数据).
忠告妊娠妇女对胎儿潜在风险.
一项生殖研究在妊娠兔用pegvaliase-pqpz治疗显示一个高发生率的胎儿畸形遍及骨骼系统,和在肾,肺,和眼。胚胎-胎儿毒性(增加的再吸收和减低的胎儿体重)也被观察到。这些效应发生在7.5倍最大推荐的每天剂量和是伴随母体毒性的强体征,包括明显的减低体重增量和食物耗量,和死亡。一项生殖研究在妊娠大鼠中用pegvaliase-pqpz治疗显示一个增加在骨骼变异,与无畸形被观察到。在大鼠效应发生在4.2倍最大推荐的每天剂量。在一项围产期发育研究在大鼠中,哺乳期间pegvaliase-pqpz产生减低子代生存,减低幼畜体重和窝大小,和子代延迟性成熟当每天给予在19.4倍最大推荐的每天剂量。对大鼠胚胎-胎儿和产后新生儿发育效应是伴随母体毒性。
所有妊娠有一个重大出生缺陷的背景风险,妊娠丢失,或其他不良妊娠结局。在美国一般人群,重大出生缺陷和临床上认可妊娠流产的估算背景风险分别为2至4%和15至20%。
估算的背景风险的重大出生缺陷和流产在妊娠妇女有苯基丙胺酸苯基丙胺酸尿(PKU)患者维持血苯基丙氨酸浓度大于600 µmol/L妊娠期间是大于相应的背景风险对妊娠妇女无PKU。
有一个妊娠对Palynziq监视计划。如妊娠期间给予Palynziq,或如一位患者成为妊娠当接受Palynziq或末次剂量Palynziq后一个月内,卫生保健提供者应报告Palynziq暴露通过电话1-866-906-6100。
临床考虑
疾病-有关联的母体和/或胚胎-胎儿风险
妊娠前和期间胎儿风险未控制的血苯基丙氨酸浓度是 伴随有一种不良妊娠结局和胎儿不良效应的增加风险。为减低高苯基丙氨酸血症-诱导胎儿不良效应的风险,妊娠期间和受孕前3月期间血苯基丙氨酸浓度应被维持在120和360 µmol/L间[见剂量和给药方法(2.2)]。
妊娠期间和产后阶段剂量调整 苯基丙氨酸浓度低于30 µmol/L自妊娠妇女有 PKU用Palynziq治疗可能是伴随不良胎儿结局。妊娠期间监视血苯基丙氨酸浓度和调整Palynziq的剂量或修饰膳食蛋白和苯基丙氨酸 摄取避免血苯基丙氨酸浓度低于30 µmol/L[见剂量和给药方法(2.2)]。
数据
人数据
未控制的母体苯基丙胺酸苯基丙胺酸尿(PKU): 从母体苯基丙氨酸尿协作研究可得到数据对468妊娠和在有PKU妊娠妇女活出生331显示未控制苯基丙氨酸浓度高于600 µmol/L是伴随有一个对流产风险增加,重大出生缺陷(包括头小畸形,重大心脏畸形),子宫内胎儿生长延迟,和未来智力的残疾与低智商[IQ]。.
来自在妊娠妇女Palynziq 使用病例报告的有限数据是不足于确定一个药物-关联不良发育结局。
动物数据
所有发育毒性研究被进行在动物中(大鼠和兔)无PKU,在其中用pegvaliase-pqpz治疗产生一个剂量-依赖减低在母体血苯基丙氨酸浓度。在剂量产生母体毒性和/或影响对胚胎-胎儿发育,母体血浆苯基丙氨酸浓度与对照组比较是明显地减低。尚未评价母体苯基丙氨酸耗尽对胚胎-胎儿发育发生率的贡献。
皮下给予5 mg/kg/day pegvaliase-pqpz (7.5倍最大推荐的每天剂量根据体重[mg/kg])在妊娠兔器官形成阶段期间产生胚胎-致死性(增加再吸收),明显的减低在胎儿重量,和胎儿畸形。畸形包括头,机体和肢体的多种外部异常,多种软组织畸形(减低大小或肾缺乏,横隔疝,角膜混浊,变色或眼大小减低,和肺的减低大小)和颅面骨,脊椎,胸骨,肋骨,骨盆,肢体,和手指的多种骨骼畸形。在所有骨骼区域还观察到变异和延迟骨化一个增加。不良发育效应是伴随母体毒性,如被体重增量和食物耗量明显受损所示。死亡伴随体重丧失和流产发生在8%的妊娠兔用5 mg/kg/day pegvaliase-pqpz治疗。.
皮下给予2 mg/kg/day pegvaliase-pqpz(3倍最大推荐的每天剂量根据体重[mg/kg])在妊娠兔对胚胎-胎儿发育没有不良效应。对pegvaliase-pqpz 全身暴露被检测到在胎儿从兔用 2或5 mg/kg/day治疗。
Pegvaliase-pqpz增加胎儿改变当给予每天在妊娠大鼠在剂量8 mg/kg皮下地和更高(4.2倍人稳态 曲线下面积[AUC]在最大推荐的每天剂量)一个28-天交配前阶段期间,交配,和至器官形成阶段。胎儿改变是限于骨骼变异例如颈肋,腰椎裂和胸椎,和鳞状骨[squamosal bones],前额骨,腰椎弓,和肋骨的不完全骨化。每天给予20 mg/kg皮下地(19.4倍人稳态AUC在推荐的最大每天剂量)至妊娠大鼠产生减低窝大小和胎儿重量,它是伴随母体毒性(减低体重,卵巢重,和食物耗量)。在窝大小减少在20 mg/kg皮下地是继发于减低在黄体和植入。对pegvaliase-pqpz全身暴露被检测在胎儿从大鼠用20 mg/kg of pegvaliase-pqpz治疗(19.4倍人稳态AUC在 推荐的最大每天剂量)。皮下给予2 mg/kg/day pegvaliase-pqpz (低于人稳态AUC在最大推荐的每天剂量)在妊娠大鼠对胚胎-胎儿发育无不良影响。.
Pegvaliase-pqpz减低幼畜体重,窝大小,和子代的生存在哺乳期间,和延迟子代性成熟当给予每天在大鼠在20 mg/kg皮下地(19.4倍人稳态 AUC在推荐的最大每天剂量),用给药开始在交配前和继续至哺乳。效应在子代是伴随母体毒性。在子代未观察到效应在8 mg/kg/day皮下地(4.2倍人稳态 AUC 在推荐的最大每天剂量)。这项研究缺乏一个完全评价的身体和神经行为发育在子代; 但是,学习和记忆的测试中无pegvaliase-pqpz效应被注意到。.
8.2 哺乳
风险总结
关于在人乳汁中pegvaliase-pqpz的存在,对哺乳喂养婴儿影响,或对乳汁生产影响没有数据。一项在大鼠中围产期研究显示pegvaliase-pqpz是存在大鼠乳汁和哺乳期间给予pegvaliase-pqpz减低幼畜体重和生存[见在特殊人群中使用(8.1)]。但是,在大鼠幼畜中没有检测到pegvaliase-pqpz 全身吸收。Palynziq可能致低苯基丙氨酸浓度在人乳汁中。哺乳喂养的发育和健康获益应被考虑与对Palynziq 治疗临床需要和对哺乳喂养婴儿来自Palynziq或来自潜在情况任何潜在不良影响一并考虑(见临床考虑)。
临床考虑
在用Palynziq治疗哺乳喂养妇女监视血苯基丙氨酸浓度。
8.4 儿童使用
尚未确定在儿童患者中Palynziq的安全性和有效性。
8.5 老年人使用
Palynziq的临床研究没有包括患者年龄65岁和以上。
11 一般描述
Pegvaliase-pqpz是一种苯基丙氨酸-代谢酶是重组苯基丙氨酸胺裂解酶(rAvPAL)结合至N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS)-methoxypolyethylene glycol (PEG)组成。rAvPAL是在大肠杆菌细菌被制造,转化用一个质粒含苯基丙氨酸氨裂解酶(PAL)基因从念珠藻团[Anabaena] variabilis衍生。在rAvPAL制造过程期间,发酵携带营养介质含抗菌素卡那霉素。但是,卡那霉素在制造过程被清除和在最终产物中不能检测到。rAvPAL是一种四个相同亚基组成蛋白有一个分子量62 kD每个单体。为生产pegvaliase-pqpz,一个平均九个(9) 20 kD PEG分子被共价地结合(或结合)至每个单体rAvPAL. Pegvaliase-pqpz (rAvPAL-PEG)的总分子量接近1000 kD。
Palynziq (pegvaliase-pqpz)注射液,意向为皮下注射,是一个透明至略微不透明,无色至淡黄色,无菌,无防腐剂溶液和被制剂化在pH 6.6至7.4。
Palynziq在一个单次-剂量预装注射器提供和是可得到在三个剂量强度: 2.5 mg/0.5 mL,10 mg/0.5 mL,和20 mg/mL. 在表4中总结了各种剂量强度的Palynziq内容物。

12 临床药理学
12.1 作用机制
Pegvaliase-pqpz是一种PEG化的苯基丙氨酸氨裂解酶(PAL)转换苯基丙氨酸至氨和反式桂皮酸。它取代缺乏的苯基丙氨酸羟化酶(PAH)酶活性在患者有苯基丙胺酸苯基丙胺酸尿(PKU)和减低血苯基丙氨酸浓度。
12.2 药效动力学
Palynziq 治疗有 苯基丙胺酸苯基丙胺酸尿(PKU)成年患者导致血苯基丙氨酸浓度从治疗前基线的减低[见临床研究(14)]。血苯基丙氨酸浓度的减低减少与减低的pegvaliase-pqpz血浆浓度。
12.3 药代动力学
Pegvaliase-pqpz的药代动力学表现出高患者间和患者内变异性由于在有PKU成年患者免疫反应的异质性。较高抗体滴度与pegvaliase-pqpz的较高抗体滴度与较高表观清除率相关。在第一个八周的诱导和滴定调整治疗,血浆pegvaliase-pqpz浓度是低至不可测量的。用Palynziq 20 mg和40 mg皮下地每天一次维持治疗在稳态期间,均数 ± SD (范围)血浆谷pegvaliase-pqpz浓度分别为: 11.2 ± 9.0 (0.21 to 29.6) mg/L和10.4 ± 12.7 (0.18 to 43.1) mg/L。在成年患者有PKU用 Palynziq治疗在维持剂量20 mg每天1次和40 mg每天1次观察到药后药代动力学参数.
吸收
中位数Tmax为接近8小时。在稳态时均数 ± SD (范围)峰浓度(Cmax)分别为: 14.0 ± 16.3 (0.26至68.5) mg/L和16.7 ± 19.5 (0.24至63.8) mg/L。
分布
表观分布容积的均数 ± SD (范围)分别为26.4 ± 64.8 (1.8至 241) L和22.2 ± 19.7 (3.1至49.5) L。
消除
在稳态时表观清除率的均数± SD(范围)分别为0.39 ± 0.87(0.018至3.66)L/h和1.25 ± 2.46 L/h (0.034至8.88)。半衰期的均数±SD (范围)分别为47 ± 42 (14至132)小时和60 ± 45(14至127)小时。
代谢
苯基丙氨酸氨裂解酶的代谢被期望通过降解通路发生和被降解至小肽和氨基酸。.
排泄
在人中 Pegvaliase-pqpz的消除途径尚未研究。
13 非临床毒理学
13.1 癌发生,突变发生,生育率受损
未曽用pegvaliase-pqpz进行致癌性和遗传毒性研究。根据它的作用机制,pegvaliase-pqpz期望不是肿瘤生成。.
Pegvaliase-pqpz在雌性大鼠在产生受损的生育力在20 mg/kg/day 皮下地(19.4倍人稳态AUC 在最大推荐的每天剂量),如在黄体,植入,和窝大小中减低所示。这些效应是伴随毒性 (减低体重,卵巢重量,和食物消耗)。无效应对交配或生育力被观察到在雌性大鼠用8 mg/kg/day皮下地(4.2倍人稳态AUC在最大推荐的每天剂量)或在雄性大鼠用20 mg/kg/day皮下。
13.2 动物毒理学和/或药理学
在大鼠无苯基丙胺酸苯基丙胺酸尿(PKU)用pegvaliase-pqpz治疗的,剂量-依赖空泡在多个器官和组织被观察到在4-和26-周重复给药毒性研究在剂量8 mg/kg皮下地或更大给予2次每周(低于人稳态AUC在最大推荐的每天剂量)。空泡器官形成发生在肾小管细胞和在肝,脾,睾丸,肾上腺皮质,肠系膜淋巴结,和下颌淋巴结的组织细胞。受影响器官和组织的组织细胞中空泡形成持续在治疗停止后。在这些研究观察到空泡形成不伴随器官-相关毒性如测定被临床化学/尿分析和组织病理学检查。不知道这些发现的临床意义和功能性后果。
在39-周重复给药毒性研究在猴中,pegvaliase-pqpz 3 mg/kg皮下地2次每周(3倍人稳态AUC在最大推荐的每天剂量)产生全身动脉炎涉及小动脉和微动脉在一个广范围的器官和组织(肾,尿膀胱,胰腺,胆囊,食道,胃,十二指肠,空肠,回肠,盲肠,结肠,直肠,肺,心,坐骨神经,泪腺,下颌淋巴结,附睾,储精囊,卵巢,子宫,宫颈,和阴道)和在皮下注射部位。动脉炎是可能由于免疫介导的反应(如,免疫复合物沉积在血管)伴随一个外来蛋白慢性给药至动物。全身动脉炎的发生率和严重程度是剂量-依赖性。在这项研究观察到炎症是不伴随器官相关毒性如测定通过临床病理学参数(血液学,临床化学,和尿分析)和组织病理学检查。
未进行在大鼠和猴中用pegvaliase-pqpz的更长时间研究。
14 临床研究
研究301: 诱导/滴定调整/维持治疗
研究165-301 (被称为研究301,NCT01819727)是一项开放随机化,多中心研究有PKU成年评价在一个诱导/滴定调整/维持方案用一个目标维持剂量20 mg皮下地每天一次或40 mg皮下地每天一次Palynziq的自身-给药的安全性和耐受性。在Palynziq 治疗开始时,253患者显示不适当的血苯基丙氨酸控制(血苯基丙氨酸浓度大于600 µmol/L)用存在的处理,和8患者有血苯基丙氨酸浓度低于或等于600 µmol/L,存在处理选择包括 膳食苯基丙氨酸和蛋白摄取的以前和当前限制,和/或用二盐酸沙丙蝶呤[sapropterin dihydrochloride]以前治疗。患者以前用二盐酸沙丙蝶呤治疗被要求首次剂量前至终止使用至少14 天。
261被纳入患者为年龄16至55岁(均数: 29岁)和有一个基线均数(范围)血苯基丙氨酸的1,233 (285,2330) µmol/L。149/261(57%)患者为在基线时服用医疗食物和41/261患者(16%)在基线时用一种限制蛋白膳食(被定义为接受大于 75%的总蛋白摄取从医疗食物)。患者被随机化(1:1)至两种目标 维持剂量臂之一: 20 mg每天1次或40 mg每天1次。患者被滴定调整达到他们的随机化目标剂量的 20 mg每天1次或40 mg每天1次。滴定调整的时间在患者间变动和是根据患者耐受性。261被纳入患者,195 (75%)患者达到他们的随机化维持剂量(在20 mg每天1次臂103,在40 mg每天1次臂92).患者达到他们的随机维持剂量中,在20 mg每天1次随机化臂患者达到他们的维持剂量在一个中位数时间10周(范围: 9至29周)和在40 mg每天1次臂患者达到他们的维持剂量在一个中位数时间 11周(范围: 10至33周)。
被纳入在研究301261患者中,54 (21%)患者终止治疗研究301期间,4患者完成研究301和不继续至研究165-302 (被称为 研究302,NCT01889862),152患者继续至合格性阶段的研究302,和51患者继续直接地从研究301至研究302的长期治疗阶段。
研究302: 疗效评估
总共164成年有苯基丙胺酸苯基丙胺酸尿(PKU)患者患者是以前用Palynziq治疗过(152患者来自研究301和12患者来自其他Palynziq试验)被纳入在研究302和在研究302用Palynziq继续治疗共至13周评估对随机撤出阶段合格性。
随机撤出阶段
这个阶段后至附加Palynziq 治疗至13周在研究302,对纳入至该疗效评估阶段合格性(随机撤出阶段)被决定被是否一位患者实现至少一个20%减低在血苯基丙氨酸浓度从治疗前基线(当在以前研究)。86/164患者(52%)符合这个反应目标和继续进入随机撤出阶段。在双盲,安慰剂-对照,随机撤出阶段,患者被随机化在一个2:1比值至或继续他们的维持Palynziq剂量或接受匹配安慰剂共总共8周。治疗差别在最小平方(LS)均数变化在血苯基丙氨酸浓度从研究302随机化撤出基线至随机化撤出周8对各个随机化研究臂被显示在表5。均数血苯基丙氨酸浓度在治疗前基线(研究301或其他Palynziq试验)也被显示在表5。在研究302随机化撤出周8,Palynziq-被治疗患者(20 mg每天1次或40 mg每天1次)维持他们的血苯基丙氨酸浓度作为比较对他们的随机化撤出基线,而患者随机化至匹配安慰剂(20 mg每天1次或40 mg每天1次)返回至他们的治疗前基线血 苯基丙氨酸浓度(图1)。


图1: 观察的均数(SE)血苯基丙氨酸浓度随时间变化在成年患者有苯基丙胺酸苯基丙胺酸尿(PKU)在研究302
研究301和302连续治疗
118患者来自研究301有一个治疗前基线血苯基丙氨酸浓度大于600 µmol/L。患者被随机化至和接受至少一个剂量20 mg每天1次 Palynziq,108 患者,98 患者,和51患者分别被治疗共分别至少24周,48周,和96周。
118 患者中,53患者达到他们的首次反应(至少一个20%减低在血苯基丙氨酸浓度从治疗前基线或一个血苯基丙氨酸浓度低于或等于600 µmol/L)在治疗的 4周用20 mg每天1次和28患者达到他们的首次反应周 4和24间用20 mg每天1次。118 患者中,25患者递增他们的剂量从20 mg每天1次至40 mg每天1次达到一个首次反应前;那些25患者中,8患者达到他们的首次反应用4周治疗 用40 mg每天1次和6患者达到他们的首次反应在周 4和16间用40 mg每天1次。
16 如何供应/贮存和处置
如何供应
Palynziq (pegvaliase-pqpz)注射液被供应作为一个无防腐剂,无菌,透明至略微不透明,无色至浅黄色溶液。所有剂量强度的Palynziq被供应在一个1 mL玻璃注射器与一个26号,0.5英寸针头。
每纸盒含1或10碟有单次-剂量预装注射器(s),处方资料,用药指南,和使用指导。可得到以下包装规格。

贮存和处置
● 贮存在冰箱在36°F至46°F (2°C至8°C)在它的原始纸盒避光保护。.
● 不要冻结或摇晃。
● 对患者: 如需要时,贮存Palynziq在原始纸盒在室温68°F至77°F间(20°C至25°C)共至30天。. 在纸盒上记录从冰箱取出日期。一旦贮存在室温,不要将产品返回至冰箱。.
●贮存在室温共30天后储藏寿命过期,天,或产品纸盒上失效日期,看谁更早。.
17 患者咨询资料
建议患者阅读FDA-批准的患者说明书(用药指南和使用指导).
过敏反应和其他超敏性反应
● 忠告患者Palynziq可能致超敏性反应,包括过敏反应可能发生在任何时间。指导患者识别过敏反应的体征和症状[见警告和注意事项(5.1,5.3)]。
● 指导患者携带自身-可注射的肾上腺素与他们在Palynziq 治疗期间所有时间。指导患者和观察者(如合适)关于为过敏反应自身-可注射的肾上腺素的适当使用[见警告和注意事项(5.1)]。
● 指导患者经历过敏反应寻求立即医学医护,终止治疗,和恢复治疗仅在一位卫生保健提供者指导时[见警告和注意事项(5.1)]。
Palynziq REMS 程序
Palynziq仅通过一个受限制程序被称为 Palynziq REMS得到[见警告和注意事项(5.2)]。
告知患者以下值得注意要求:
●患者必须被纳入在Palynziq REMS。.
●患者必须被一位合格的处方者教育关于过敏反应风险确保他们了解用Palynziq治疗的风险和获益。.
●患者必须充填为自身-可注射的肾上腺素处方和在所有时间带着它。.
●患者将被给予一个Palynziq患者 钱包卡[Wallet Card]他们应在所有时间带着它。该卡描述症状 它如经受,应促使患者和观察者(如合适)立即寻求医疗护理。建议患者显示Palynziq Wallet卡至其他治疗卫生保健提供者。Palynziq是仅能从参加程序的合格的药房得到。所以,提供患者电话和网址对如何得到产品的信息。
给药
● 建议患者监视他们的膳食蛋白和苯基丙氨酸摄取用 Palynziq治疗至始至终,和调整摄取当他们的卫生保健提供者根据血苯基丙氨酸浓度的指导[见剂量和给药方法(2.2)]。
● 提供适当指导对自身-注射的方法,包括仔细复习 Palynziq用药指导和使用指导。指导患者无菌技术的使用当给予 Palynziq时[见剂量和给药方法(2.4)]。
● 告知患者一位卫生保健提供者将显示他们或他们的护理人员如何准备注射Palynziq在自身给药前。
● 忠告患者不要注射至痣,瘢痕,出生记号,瘀伤,皮疹,或区域处皮肤是硬,触痛,红,受损,烧伤,炎症,或纹身。
● 建议患者旋转注射与每次给药。建议患者核查注射部位对发红,肿胀,和触痛,和联系他们的卫生保健提供者如他们有一个皮肤反应和它不清除,或变坏。
● 建议患者遵循尖锐遗弃推荐[见使用指导]患者对安全遗弃步骤。
● 忠告患者储藏寿命过期在室温贮存共30天后或在产品纸盒上失效日期后,以先发生为准.
妊娠
● 建议妊娠妇女和生殖潜能女性对胎儿潜在风险。建议女性告知他们的卫生保健提供者一个已知或怀疑妊娠[见在特殊人群中使用(8.1)]。
● 建议妇女在被暴露至Palynziq妊娠期间或成为妊娠末次Palynziq剂量后一个月内有一个妊娠监视计划监视妊娠结局。鼓励这些患者报告她们的妊娠至BioMarin [见在特殊人群中使用(8.1)]。
Anaphylaxis has been reported after administration of Palynziq and may occur at any time during treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Administer the initial dose of Palynziq under the supervision of a healthcare provider equipped to manage anaphylaxis, and closely observe patients for at least 60 minutes following injection. Prior to self‑injection, confirm patient competency with self‑administration, and patient’s and observer’s (if applicable) ability to recognize signs and symptoms of anaphylaxis and administer auto‑injectable epinephrine, if needed [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
Consider having an adult observer for patients who may need assistance in recognizing and managing anaphylaxis during Palynziq treatment. If an adult observer is needed, the observer should be present during and for at least 60 minutes after Palynziq administration, should be able to administer auto‑injectable epinephrine, and call for emergency medical support upon its use [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Prescribe auto‑injectable epinephrine to all patients treated with Palynziq. Prior to the first dose, instruct the patient and observer (if applicable) how to recognize the signs and symptoms of anaphylaxis, how to properly administer auto‑injectable epinephrine, and to seek immediate medical care upon its use. Instruct patients to carry auto‑injectable epinephrine with them at all times during treatment with Palynziq [see Dosage and Administration (2.4), Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Consider the risks and benefits of readministering Palynziq following an episode of anaphylaxis. If the decision is made to readminister Palynziq, readminister the first dose under the supervision of a healthcare provider equipped to manage anaphylaxis and closely observe the patient for at least 60 minutes following the dose [see Dosage and Administration (2.4), Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Because of the risk of anaphylaxis, Palynziq is available only through a restricted program under a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) called the Palynziq REMS [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Palynziq is indicated to reduce blood phenylalanine concentrations in adult patients with phenylketonuria (PKU) who have uncontrolled blood phenylalanine concentrations greater than 600 micromol/L on existing management.

Treatment with Palynziq should be managed by a healthcare provider experienced in the management of PKU.
Obtain baseline blood phenylalanine concentration before initiating treatment.
Induction
The recommended initial induction dosage for Palynziq is 2.5 mg subcutaneously once weekly for 4 weeks. Administer the initial dose under the supervision of a healthcare provider [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
Titration
Titrate the Palynziq dosage in a step-wise manner, based on tolerability, over at least 5 weeks, to achieve a dosage of 20 mg subcutaneously once daily according to Table 1.
Maintenance
Therapeutic response may not be achieved until the patient is titrated to an effective maintenance dosage of Palynziq. Use the lowest effective and tolerated dosage of Palynziq.
Assess patient tolerability, blood phenylalanine concentrations, and dietary protein and phenylalanine intake throughout treatment. Maintain the Palynziq dosage at 20 mg subcutaneously once daily for at least 24 weeks. Consider increasing the Palynziq dosage to a maximum of 40 mg subcutaneously once daily in patients who have been maintained continuously on 20 mg once daily for at least 24 weeks and who have not achieved either a 20% reduction in blood phenylalanine concentration from pre-treatment baseline or a blood phenylalanine concentration less than or equal to 600 micromol/L.
Discontinuation
Discontinue Palynziq in patients who have not achieved a response (at least a 20% reduction in blood phenylalanine concentration from pre-treatment baseline or a blood phenylalanine concentration less than or equal to 600 micromol/L) after 16 weeks of continuous treatment with the maximum dosage of 40 mg once daily.
|
*Additional time may be required prior to each dosage escalation based on patient tolerability.†Individualize treatment to the lowest effective and tolerated dosage. Consider increasing to a maximum of 40 mg once daily in patients who have not achieved a response with 20 mg once daily continuous treatment for at least 24 weeks [see Clinical Studies (14)].‡Discontinue Palynziq treatment in patients who have not achieved a response after 16 weeks of continuous treatment with the maximum dosage of 40 mg once daily. |
||
| Treatment | Palynziq Dosage | Duration* |
| Induction | 2.5 mg once weekly | 4 weeks |
| Titration | 2.5 mg twice weekly | 1 week |
| 10 mg once weekly | 1 week | |
| 10 mg twice weekly | 1 week | |
| 10 mg four times per week | 1 week | |
| 10 mg once daily | 1 week | |
| Maintenance | 20 mg once daily | 24 weeks |
| Maximum† | 40 mg once daily | 16 weeks‡ |
Dose Reduction for Low Phenylalanine Concentrations
During titration and maintenance of Palynziq treatment, patients may experience blood phenylalanine concentrations below 30 micromol/L. For blood phenylalanine concentrations below 30 micromol/L, the dosage of Palynziq may be reduced and/or dietary protein and phenylalanine intake may be modified to maintain blood phenylalanine concentrations within a clinically acceptable range and above 30 micromol/L [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Readministration Following Anaphylaxis
If the decision is made to readminister Palynziq after an anaphylaxis episode, administer the first dose following the anaphylaxis episode under the supervision of a healthcare provider equipped to manage anaphylaxis and closely observe the patient for at least 60 minutes following the dose. Subsequent dose titration should be based on patient tolerability and therapeutic response [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Missed Dose
If a dose is missed, instruct patients to take their next dose as scheduled and to not take two doses of Palynziq to make up for the missed dose.
Blood Phenylalanine Monitoring and DietAfter initiating treatment with Palynziq, obtain blood phenylalanine concentrations every 4 weeks until a maintenance dosage is established. After a maintenance dosage is established, periodic blood phenylalanine monitoring is recommended to assess blood phenylalanine control.
Monitor patients’ dietary protein and phenylalanine intake throughout treatment with Palynziq and counsel them on how to adjust their dietary intake, as needed, based on blood phenylalanine concentrations.
PremedicationFor hypersensitivity reactions, consider premedication with an H1‑receptor antagonist, H2‑receptor antagonist, and/or antipyretic prior to Palynziq administration based upon individual patient tolerability [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.3)].
Administration InstructionsEach prefilled syringe of Palynziq is intended for use as a single subcutaneous injection.Palynziq is a clear to slightly opalescent, colorless to pale yellow solution available as follows:
Injection: 2.5 mg/0.5 mL single-dose prefilled syringeInjection: 10 mg/0.5 mL single-dose prefilled syringeInjection: 20 mg/mL single-dose prefilled syringeContraindicationsNone.
Warnings and PrecautionsAnaphylaxisIn clinical trials of Palynziq with induction/titration/maintenance dosing, 26 out of 285 (9%) patients experienced a total of 37 anaphylaxis episodes [see Adverse Reactions (6.1, 6.2)]. The exposure-adjusted rate of anaphylaxis was highest during the induction and titration phases (0.15 episodes/person‑years; 5% of patients with at least one episode) and decreased in the maintenance phase (0.04 episodes/person‑years; 6% of patients with at least one episode). Signs and symptoms of anaphylaxis reported in clinical trials of Palynziq included syncope, hypotension, hypoxia, dyspnea, wheezing, chest discomfort/chest tightness, tachycardia, angioedema (swelling of face, lips, eyes, tongue), throat tightness, skin flushing, rash, urticaria, pruritus, and gastrointestinal symptoms (vomiting, nausea, diarrhea). In clinical trials of Palynziq, anaphylaxis generally occurred within 1 hour after injection (84%; 28/37 episodes); however, delayed episodes also occurred up to 48 hours after Palynziq administration. Most episodes of anaphylaxis occurred within the first year of dosing (78%, 29/37 episodes), but cases also occurred after one year of dosing and up to 834 days (2.3 years) into treatment. Management of anaphylaxis in Palynziq clinical trials included: administration of auto-injectable epinephrine (54%; 20/37 episodes), corticosteroids (54%; 20/37 episodes), antihistamines (51%; 19/37 episodes), and/or oxygen (5%; 2/37 episodes). Eighteen out of the 26 (69%) patients who experienced anaphylaxis were rechallenged with Palynziq and 5 out of the 18 patients who were rechallenged (28%) had recurrence of anaphylaxis. All anaphylaxis episodes resolved without sequelae.
Consider having an adult observer for patients who may need assistance in recognizing and managing anaphylaxis during Palynziq treatment. If an adult observer is needed, the observer should be present during and for at least 60 minutes after Palynziq administration, should be able to administer auto‑injectable epinephrine, and to call for emergency medical support upon its use.
Anaphylaxis requires immediate treatment with auto-injectable epinephrine. Prescribe auto‑injectable epinephrine to all patients receiving Palynziq and instruct patients to carry auto‑injectable epinephrine with them at all times during Palynziq treatment. Prior to the first dose, instruct the patient and observer (if applicable) on how to recognize the signs and symptoms of anaphylaxis, how to properly administer auto‑injectable epinephrine, and to seek immediate medical care upon its use. Consider the risks associated with auto-injectable epinephrine use when prescribing Palynziq. Refer to the auto‑injectable epinephrine prescribing information for complete information.
Consider the risks and benefits of readministering Palynziq following an episode of anaphylaxis. If the decision is made to readminister Palynziq, administer the first dose under the supervision of a healthcare provider equipped to manage anaphylaxis and closely observe the patient for at least 60 minutes following the dose. Subsequent Palynziq dose titration should be based on patient tolerability and therapeutic response [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
Consider premedication with an H1-receptor antagonist, H2-receptor antagonist, and/or antipyretic prior to Palynziq administration based upon individual patient tolerability [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
Palynziq is available only through a restricted program under a REMS [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Palynziq REMS ProgramPalynziq is available only through a restricted program under a REMS called the Palynziq REMS, because of the risk of anaphylaxis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Notable requirements of the Palynziq REMS include the following:
Prescribers must be certified with the program by enrolling in the program and completing training.Prescribers must prescribe auto‑injectable epinephrine with Palynziq.Pharmacies must be certified with the program and must dispense only to patients who are authorized to receive Palynziq.Patients must enroll in the program and be educated about the risk of anaphylaxis by a certified prescriber to ensure they understand the risks and benefits of treatment with Palynziq.Patients must have auto‑injectable epinephrine available at all times while taking Palynziq.Further information, including a list of qualified pharmacies, is available at www.PalynziqREMS.com or by telephone 1‑855‑758‑REMS (1‑855‑758‑7367).
Other Hypersensitivity ReactionsHypersensitivity reactions, other than anaphylaxis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Adverse Reactions (6.1, 6.2)], have been reported in 196 out of 285 (69%) patients treated with Palynziq. The exposure adjusted rate of other hypersensitivity reactions was highest during the induction and titration phases (4.5 episodes/person-year; 50% of patients with at least one adverse reaction) and decreased in the maintenance phase (1.5 episodes/person-year; 57% of patients with at least one adverse reaction).
Consider premedication with an H1‑receptor antagonist, H2‑receptor antagonist, and/or antipyretic prior to Palynziq administration based upon individual patient tolerability [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. Management of hypersensitivity reactions should be based on the severity of the reaction, recurrence of the reaction, and the clinical judgement of the healthcare provider, and may include dosage adjustment, temporary drug interruption, or treatment with antihistamines, antipyretics, and/or corticosteroids.
Adverse ReactionsThe following serious adverse reactions are discussed below and in other sections of labeling:
Anaphylaxis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]Other Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]Clinical Trials ExperienceBecause clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The data described below reflect a total treatment exposure of 580 patient-years in 285 patients who received Palynziq in an induction/titration/maintenance regimen in clinical trials [see Clinical Studies (14)]. Of the 285 patients, 229 patients were exposed to Palynziq for 24 weeks, 209 patients were exposed for 1 year, 137 patients were exposed for 2 years, and 85 patients were exposed for 3 years or longer. The patient population was evenly distributed between male and female patients, the mean age was 29 years (range: 16 to 56 years), and 98% of patients were White.
The most common adverse reactions (at least 20% of patients in either treatment phase) were injection site reactions, arthralgia, hypersensitivity reactions, headache, generalized skin reactions lasting at least 14 days, pruritus, nausea, abdominal pain, oropharyngeal pain, vomiting, cough, diarrhea, and fatigue.
Of the 285 patients exposed to Palynziq in an induction/titration/maintenance regimen in clinical trials, 31 (11%) patients discontinued treatment due to adverse reactions. The most common adverse reactions leading to treatment discontinuation were hypersensitivity reactions (6% of patients) including anaphylaxis (3% of patients) and angioedema (1% of patients), arthralgia (4% of patients), generalized skin reactions lasting at least 14 days (2% of patients), and injection site reactions (1% of patients).
The most common adverse reactions leading to dosage reduction were arthralgia (14% of patients), hypersensitivity reactions (9% of patients), injection site reactions (4% of patients), alopecia (3% of patients), and generalized skin reactions lasting at least 14 days (2% of patients).
The most common adverse reactions leading to temporary drug interruption were arthralgia (13% of patients), hypersensitivity reactions (13% of patients), anaphylaxis (4% of patients), and injection site reactions (4% of patients).
Table 2 lists adverse reactions reported in at least 15% of patients treated with Palynziq in an induction/titration/maintenance dosage regimen in clinical trials, and illustrates the adverse reaction rates over time by treatment phase. Table 3 lists laboratory abnormalities reported in at least 10% of patients treated with Palynziq in an induction/titration/maintenance dosage regimen in clinical trials.
For these analyses, the induction/titration phase was defined as the time prior to reaching a stable dose (completing an 8‑week phase at the same dose level). Once a stable dosage was reached, patients were considered to be in the maintenance phase thereafter. Safety data for patients who reached the maintenance phase are included within either the induction/titration or maintenance phases depending on the onset date of the adverse reaction. Safety data for patients who did not reach the maintenance phase are included within the induction/titration phase. The maintenance phase includes data for patients who were previously on Palynziq and transitioned to placebo during the randomized withdrawal period of Study 302 [see Clinical Studies (14)].
Rates of adverse reactions (adjusted for duration of exposure) generally decreased over time and for some stayed relatively stable. In the maintenance phase, the rate of adverse reactions (adjusted for duration of exposure) in patients who reached the maintenance phase was comparable across dosages evaluated. The types and rate of adverse reactions reported during the maintenance phase in patients who received 20 mg once daily and 40 mg once daily were similar.
Rates of laboratory abnormalities (adjusted for duration of exposure) stayed relatively stable over time, except for complement C4 below lower limit of normal (LLN) and hs-CRP above 0.287 mg/dL over a 6 month period (both decreased over time) and hypophenylalaninemia (blood phenylalanine concentration below 30 micromol/L) on a single measurement (increased over time). The types and rates of laboratory abnormalities (adjusted for duration of exposure) reported during the maintenance phase in patients receiving 20 mg once daily and 40 mg once daily were similar with the exception of hs‑CRP above 0.287 mg/dL over a 6 month period (exposure‑adjusted event rates 0.04 and 0.08 in patients on 20 mg once daily and 40 mg once daily, respectively).
|
*≥ 15% incidence in either treatment phase†N (%) = Number of patients with at least 1 Adverse Reaction (%); Rate = Exposure-Adjusted Rate of Adverse Reactions (Adverse Reactions/Person‑Years)‡Includes Injection site: reaction, erythema, pruritus, pain, bruising, rash, swelling, urticaria, induration, hemorrhage, edema, mass, inflammation, nodule, discoloration, warmth, hematoma, irritation, vesicles, hypersensitivity, papule, discomfort, scar, paresthesia, hypertrophy, extravasation, and dryness§
Includes arthralgia, pain in extremity, back pain, musculoskeletal pain, neck pain ¶Includes rash, urticaria, anaphylaxis, rash generalized, hypersensitivity, rash erythematous, rash maculo-papular, rash pruritic, serum sickness, swelling face, dermatitis contact, swollen tongue, lip swelling, rash macular, pharyngeal edema, injection site hypersensitivity, eczema, drug eruption, dermatitis allergic, dermatitis, tongue edema, palatal edema, edema mouth, multiple allergies, lip edema, eye edema, exfoliative rash, drug hypersensitivity, dermatitis atopic, dermatitis acneiform, pruritus allergic, mouth swelling, implant site rash, gingival swelling, face edema, eyelid edema, eye swelling, dermatitis psoriasiform, dermatitis infected, conjunctivitis allergic, bronchospasm, angioedema, allergic sinusitis, allergic cough#Includes headache, migraine, sinus headache ÞIncludes pruritus, rash, urticaria, dry skin, rash erythematous, erythema, cellulitis, rash macular, pruritus generalized, petechiae, dermatitis allergic, skin infection, skin induration, rash maculo-papular, rash generalized, pharyngeal edema, macule, granulomatous dermatitis, exfoliative rash, drug eruption, dermatitis atopic, dermatitis, xanthogranuloma, skin plaque, skin mass, skin lesion, skin hypopigmentation, skin hypertrophy, skin hyperpigmentation, skin exfoliation, septal panniculitis, scleroderma, scar, rash pruritic, rash papular, psoriatic arthropathy, pruritus allergic, papule, necrobiosis lipoidica diabeticorum, furuncle, eczema, ecchymosis, dermatitis psoriasiform, dermatitis infected, blisterßIncludes abdominal pain, abdominal pain upper, abdominal discomfort |
||||
|
Treatment Phase Treatment Duration |
Induction/Titration Phase (N = 285) 135 person-years Mean: 178 days Median: 116 days Range: 1 to 1607 days |
Maintenance Phase (N = 223) 444 person-years Mean: 739 days Median: 697 days Range: 5 to 1561 days |
||
| Adverse Reaction | N (%)† |
Episodes (Rate)† |
N (%)† |
Episodes (Rate)† |
| Injection site reactions‡ | 252 (88%) | 2964 (21.9) | 161 (72%) | 1754 (4) |
| Arthralgia§ | 210 (74%) | 1035 (7.6) | 137 (61%) | 661 (1.5) |
| Hypersensitivity reactions¶ | 152 (53%) | 633 (4.7) | 135 (61%) | 663 (1.5) |
| Headache# | 100 (35%) | 211 (1.6) | 111 (50%) | 778 (1.8) |
| Generalized skin reaction lasting at least 14 daysÞ | 61 (21%) | 95 (0.7) | 82 (37%) | 133 (0.3) |
| Pruritus | 58 (20%) | 100 (0.7) | 53 (24%) | 402 (0.9) |
| Nausea | 51 (18%) | 66 (0.5) | 57 (26%) | 106 (0.2) |
| Dizziness | 46 (16%) | 64 (0.5) | 38 (17%) | 72 (0.2) |
| Abdominal painß | 39 (14%) | 53 (0.4) | 55 (25%) | 128 (0.3) |
| Oropharyngeal pain | 38 (13%) | 43 (0.3) | 51 (23%) | 70 (0.2) |
| Fatigue | 37 (13%) | 81 (0.6) | 48 (22%) | 86 (0.2) |
| Vomiting | 36 (13%) | 53 (0.4) | 58 (26%) | 100 (0.2) |
| Cough | 27 (9%) | 33 (0.2) | 50 (22%) | 65 (0.2) |
| Diarrhea | 25 (9%) | 31 (0.2) | 50 (22%) | 91 (0.2) |
| Anxiety | 14 (5%) | 23 (0.2) | 41 (18%) | 79 (0.2) |
| Alopecia | 13 (5%) | 14 (0.1) | 39 (17%) | 50 (0.1) |
| Nasal congestion | 12 (4%) | 15 (0.1) | 41 (18%) | 50 (0.1) |
|
*N (%) = Number of patients with at least 1 laboratory abnormality (%); Rate = Exposure-Adjusted Rate of Laboratory Abnormalities (Laboratory Abnormalities/Person‑Years) †Blood phenylalanine concentration below 30 micromol/L |
||||
|
Treatment Phase
Treatment Duration |
Induction/Titration Phase (N = 285) 135 person‑years Mean: 178 days Median: 116 days Range: 1 to 1607 days |
Maintenance Phase (N = 223) 444 person‑years Mean: 739 days Median: 697 days Range: 5 to 1561 days |
||
| Laboratory Measurement | N (%)* |
Episodes (Rate)* |
N (%)* |
Episodes (Rate)* |
| Complement factor C3 below LLN | 195 (68%) | 446 (3.3) | 188 (84%) | 1719 (3.9) |
| C-reactive protein (CRP) above ULN | 182 (64%) | 358 (2.6) | 151 (68%) | 947 (2.1) |
| Complement factor C4 below LLN | 177 (62%) | 318 (2.4) | 108 (48%) | 604 (1.4) |
| Hypophenylalaninemia† on a single measurement | 53 (19%) | 204 (1.5) | 137 (61%) | 1128 (2.5) |
| Blood creatine phosphokinase (CPK) above ULN | 50 (18%) | 87 (0.6) | 96 (43%) | 277 (0.6) |
| Hypophenylalaninemia† on 2 or more consecutive measurements | 45 (16%) | 60 (0.4) | 93 (42%) | 140 (0.3) |
| Hs-CRP above 0.287 mg/dL over a 6 month period | 34 (12%) | 34 (0.4) | 23 (10%) | 26 (0.06) |
LLN – lower limit of normal
ULN – upper limit of normal
Hs – high sensitivity
Description of Selected Adverse Reactions
Arthralgia
In clinical trials, 235 out of 285 (83%) patients experienced episodes consistent with arthralgia (includes back pain, musculoskeletal pain, pain in extremity, and neck pain). Arthralgia episodes were more frequent during the induction/titration phase (7.6 episodes/patient-year) and decreased over time (1.5 episodes/patient-year in the maintenance phase). Thirty-nine out of 285 (14%) patients had one episode of arthralgia, 32 (11%) patients had 2 episodes of arthralgia, 18 (6%) had 3 episodes of arthralgia, and 146 (51%) had 4 or more episodes of arthralgia. Arthralgia occurred as early as after the first dose of Palynziq and occurred at any time during treatment. The mean duration of arthralgia was 14 days (median: 3 days, range: 1 to 580 days), and 19% of arthralgia episodes had a duration of at least 14 days. Severe arthralgia (severe pain limiting self-care activities of daily living) was reported by 14 (5%) patients. In addition to arthralgia, other joint-related signs and symptoms reported were: joint swelling (22 patients; 8%), joint stiffness (22 patients; 8%), and musculoskeletal stiffness (19 patients; 7%). Arthralgia episodes were managed with medications (e.g., nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, glucocorticoids, and acetaminophen), Palynziq dosage reduction (4% of episodes), Palynziq interruption (4% of episodes), or Palynziq withdrawal (0.6% of episodes). 97% of arthralgia episodes were reported as resolved at the time of last observation (up to 59 months of follow‑up).
Injection Site Reactions
Injection site reactions were reported as early as after the first dose of Palynziq and occurred at any time during treatment. Injection site reactions were more frequent during the induction/titration phase (21.9 episodes/patient-years) and decreased over time (4 episodes/patient‑years in the maintenance phase). The mean duration of injection site reaction was 8 days (median: 2 days, range: 1 to 970 days), and 7% of injection site reactions had a duration of at least 14 days. 99% of injection site reactions were reported as resolved at the time of last observation (up to 59 months of follow‑up).
Three injection site reactions consistent with granulomatous skin lesions were reported (each reaction occurring in one patient): granulomatous dermatitis (occurred after 464 days of Palynziq treatment and lasted 16 days), xanthogranuloma (occurred after 378 days of Palynziq treatment and lasted 638 days) was treated with a topical antihistamine, corticosteroid, and Palynziq treatment was discontinued, and necrobiosis lipoidica diabeticorum (occurred after 281 days of Palynziq treatment and lasted 281 days). Necrobiosis lipoidica diabeticorum was treated with steroid injections and complicated by Pseudomonas infection. All three injection site reactions resolved.
One patient reported soft tissue infection (occurred after 196 days of Palynziq treatment and lasted 8 days) associated with mesenteric panniculitis treated with antibiotics, which resulted in treatment discontinuation.
Generalized Skin Reactions (not limited to the injection site) Lasting at Least 14 Days
In clinical trials, 125 out of 285 (44%) patients treated with Palynziq experienced generalized skin reactions (not limited to the injection site) lasting at least 14 days. Mean duration of these reactions was 58 days (median: 34 days; range: 14 to 638 days). Generalized skin reactions were more frequent during the induction/titration phase (0.7 episodes/patient‑years), and decreased over time (0.3 episodes/patient-years in the maintenance phase).
The mean time from first dose of Palynziq to onset of skin reactions was 319 days (median: 169 days; range: 2 to 1237 days). 5% of these reactions persisted at least 180 days, and 85% of these reactions were reported as resolved at the time of last observation (up to 59 months of follow‑up).
Angioedema
In clinical trials, 22 out of 285 (8%) patients experienced 45 episodes of angioedema (symptoms included: pharyngeal edema, swollen tongue, lip swelling, mouth swelling, eyelid edema and face edema) occurring independent of anaphylaxis. Angioedema (included under Hypersensitivity in Table 2) was more frequent during the induction/titration phase (0.15 episodes/patient-year) and decreased over time (0.06 episodes/patient-year in the maintenance phase). Three patients discontinued treatment. All episodes resolved. Angioedema can present as a symptom of anaphylaxis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Serum Sickness
In clinical trials, serum sickness was reported in 7 out of 285 (2%) patients. Serum sickness episodes were more frequent during the induction/titration phase (0.04 episodes/patient-year) and decreased over time (less than 0.01 episodes/patient-year during the maintenance phase). All serum sickness reactions resolved without sequelae (duration of serum sickness ranged from 1 to 8 days). Out of the 7 patients who experienced serum sickness, 5 patients continued treatment without a recurrence, and managed serum sickness with drug interruption, dosage reduction and/or concomitant medication. Two patients discontinued treatment.
ImmunogenicityAs with all therapeutic proteins, there is potential for immunogenicity. The detection of antibody formation is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Additionally, the observed incidence of antibody (including neutralizing antibody) positivity in an assay may be influenced by several factors, including assay methodology, sample handling, timing of sample collection, concomitant medications, and underlying disease. For these reasons, comparison of the incidence of antibodies to Palynziq in the studies described below with the incidence of antibodies in other studies or to other products may be misleading.
All patients treated with Palynziq developed a sustained total anti-drug antibody (TAb) response with a majority of patients (91%; N = 235/258) developing that response by Week 4 of treatment. Mean TAb titers peaked 2 weeks after Palynziq initiation and remained elevated throughout treatment (greater than 1 year after treatment initiation). Anti-phenylalanine ammonia lyase (PAL) IgM antibodies were detected in all patients with a majority of patients (98%; N = 265/270) becoming positive for anti-PAL IgM by 2 months after treatment initiation. Anti‑PAL IgG antibodies were detected in almost all patients (N = 226/227) by 4 months after treatment initiation. Mean anti-PAL IgM and IgG titers peaked at approximately 3 and 6 months, respectively, after treatment initiation and remained elevated throughout treatment (greater than 1 year after treatment initiation). Drug-induced anti-PEG IgM and IgG antibodies were detected in the majority of patients (98%; N = 277/284 for IgM; and 278/284 for IgG) with mean titers for both peaking at 1 to 3 months after treatment initiation [see Drug Interactions (7.1)]. Neutralizing antibodies (NAb) capable of inhibiting PAL enzyme activity were detected on at least one measurement in the majority of patients (88%; N = 249/284) over time. Mean NAb titers peaked and reached a plateau at 16 to 20 weeks of treatment and then remained present throughout treatment (greater than 1 year after treatment initiation).
Twenty-five of 26 patients who had anaphylaxis were tested for anti‑pegvaliase‑pqpz IgE antibodies, which recognize the PEGylated protein product. Of the 25 patients tested for anti‑pegvaliase‑pqpz IgE antibodies, 24 patients tested negative. The one patient who tested positive for anti‑pegvaliase‑pqpz IgE antibodies on the screening test did not have sufficient sample to confirm IgE positivity. This patient tested negative for anti‑pegvaliase‑pqpz IgE at routine visits prior to and after the anaphylaxis episode (not at times of anaphylaxis). Sixty‑eight of 285 patients in clinical trials were tested for both anti‑PAL IgE antibodies, which recognize the recombinant PAL protein, and for anti‑pegvaliase‑pqpz IgE antibodies during routine study visits (not at times of anaphylaxis episodes) or during additional visits for hypersensitivity reactions. Of those 68 patients, 5 (7%) tested positive at least once for anti‑PAL IgE antibodies but negative for anti‑pegvaliase‑pqpz IgE antibodies.
The highest frequency of hypersensitivity reactions (consistent with a Type III immune complex-mediated hypersensitivity mechanism) occurred within the first 6 months of Palynziq treatment when the mean circulating immune complex (CIC) concentrations were at their highest and mean complement C3 and C4 concentrations were at their lowest. Mean CIC concentrations decreased and complement levels increased over time as the exposure-adjusted rate of hypersensitivity reactions decreased. IgG and IgM CIC concentrations were above the upper limit of normal in 63% (N = 164/259) and 41% of patients (N = 106/259), respectively, at 12 weeks of Palynziq treatment. The incidence of CIC positivity decreased over time. 61% of patients (N = 110/180) had complement C3 concentrations less than lower limit of normal (LLN) at 6 months after treatment initiation and 38% of patients (N = 94/248) had complement C4 concentrations less than LLN at 3 months after treatment initiation. The incidence of low complement C3 and C4 concentrations decreased over time, but approximately 39% (N = 19/49) and 12% (N = 6/49) of patients had low C3 and C4 concentrations, respectively, at 36 months after treatment initiation.
Higher antibody responses for all antibody analytes, including NAb, were associated with lower mean trough pegvaliase‑pqpz concentrations and with higher blood phenylalanine concentrations. Hypersensitivity reactions occurred more frequently in patients with higher antibody titers for some but not all antibody analytes. Patients with higher mean change in IgG CIC concentrations from pre-treatment baseline tended to have higher discontinuation rates than patients with lower mean change in IgG CIC concentrations. Mean antibody titers for anti‑PAL IgG and IgM, TAb, and NAb remained relatively stable with long-term treatment.
Drug InteractionsEffect of Palynziq on Other PEGylated ProductsIn a single dose study of Palynziq in adult patients with PKU, two patients receiving concomitant injections of medroxyprogesterone acetate suspension (a formulation containing PEG 3350) experienced hypersensitivity reactions. One of the two patients experienced a hypersensitivity reaction on day 15 after a single Palynziq dosage of 0.67 mg within 15 minutes following medroxyprogesterone acetate injectable suspension, and subsequently experienced anaphylaxis on day 89 within 30 minutes after the next dose of medroxyprogesterone acetate injectable suspension. The other patient experienced a hypersensitivity reaction on day 40 after a single Palynziq dosage of 0.08 mg within 10 minutes following medroxyprogesterone acetate injectable suspension. Both patients had high anti‑PEG IgG antibody titers at or around the time of the hypersensitivity reactions.
In Palynziq clinical trials, the majority of patients developed anti‑PEG IgM and IgG antibodies after treatment with Palynziq [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)]. The clinical effects of concomitant treatment with different PEGylated products is unknown. Monitor patients treated with Palynziq and concomitantly with other PEGylated products for hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONSPregnancyRisk Summary
Based on findings in studies of pregnant animals without PKU treated with pegvaliase-pqpz, Palynziq may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Limited available data with pegvaliase-pqpz use in pregnant women are insufficient to inform a drug-associated risk of adverse developmental outcomes. There are risks to the fetus associated with poorly controlled phenylalanine concentrations in women with PKU during pregnancy including increased risk for miscarriage, major birth defects (including microcephaly, major cardiac malformations), intrauterine fetal growth retardation, and future intellectual disability with low IQ; therefore, phenylalanine concentrations should be closely monitored in women with PKU during pregnancy (see Clinical Considerations and Data). Advise pregnant women of the potential risks to the fetus.
A reproduction study in pregnant rabbits treated with pegvaliase‑pqpz demonstrated a high incidence of fetal malformations throughout the skeletal system, and in kidneys, lungs, and eyes. Embryo-fetal toxicity (increased resorptions and reduced fetal weight) was also observed. These effects occurred at 7.5 times the maximum recommended daily dose and were associated with strong signs of maternal toxicity, including marked reductions in weight gain and food consumption, and death. A reproduction study in pregnant rats treated with pegvaliase-pqpz demonstrated an increase in skeletal variations, with no malformations observed. The effects in rats occurred at 4.2 times the maximum recommended daily dose. In a pre-/post-natal development study in rats, pegvaliase‑pqpz produced reduced survival of offspring during lactation, decreases in pup weight and litter size, and delayed sexual maturation of offspring when administered daily at 19.4 times the maximum recommended daily dose. The effects on rat embryo‑fetal and post-natal development were associated with maternal toxicity.
All pregnancies have a background risk of major birth defects, pregnancy loss, or other adverse pregnancy outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively. The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in pregnant women with PKU who maintain blood phenylalanine concentrations greater than 600 micromol/L during pregnancy is greater than the corresponding background risk for pregnant women without PKU.
There is a pregnancy surveillance program for Palynziq. If Palynziq is administered during pregnancy, or if a patient becomes pregnant while receiving Palynziq or within one month following the last dose of Palynziq, healthcare providers should report Palynziq exposure by calling 1-866-906-6100.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-Associated Maternal and/or Embryo-Fetal Risk
Uncontrolled blood phenylalanine concentrations before and during pregnancy are associated with an increased risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes and fetal adverse effects. To reduce the risk of hyperphenylalaninemia-induced fetal adverse effects, blood phenylalanine concentrations should be maintained between 120 and 360 micromol/L during pregnancy and during the 3 months before conception [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Dose Adjustments During Pregnancy and the Postpartum Period
Phenylalanine concentrations below 30 micromol/L in pregnant women with PKU treated with Palynziq may be associated with adverse fetal outcomes. Monitor blood phenylalanine concentrations during pregnancy and adjust the dosage of Palynziq or modify dietary protein and phenylalanine intake to avoid blood phenylalanine concentrations below 30 micromol/L [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Data
Human Data
Uncontrolled Maternal PKU: Available data from the Maternal Phenylketonuria Collaborative Study on 468 pregnancies and 331 live births in pregnant women with PKU demonstrated that uncontrolled phenylalanine concentrations above 600 micromol/L are associated with an increased risk for miscarriage, major birth defects (including microcephaly, major cardiac malformations), intrauterine fetal growth retardation, and future intellectual disability with low IQ.
Limited data from case reports of Palynziq use in pregnant women are insufficient to determine a drug‑associated risk of adverse developmental outcomes.
Animal Data
All developmental toxicity studies were conducted in animals (rats and rabbits) without PKU, in which treatment with pegvaliase-pqpz produced a dose-dependent reduction in maternal blood phenylalanine concentrations. At doses that produced maternal toxicity and/or effects on embryo-fetal development, the maternal plasma phenylalanine concentrations were markedly reduced compared to the control group. The contribution of maternal phenylalanine depletion to the incidence of embryo‑fetal developmental effects was not evaluated.
Subcutaneous administration of 5 mg/kg/day pegvaliase-pqpz (7.5 times the maximum recommended daily dose based on bodyweight [mg/kg]) in pregnant rabbits during the period of organogenesis produced embryo-lethality (increased resorptions), marked reduction in fetal weight, and fetal malformations. The malformations included multiple external abnormalities of the head, body and limbs, multiple soft tissue malformations (reduced size or absence of kidneys, diaphragmatic hernia, corneal opacity, discoloration or reduced size of eyes, and reduced size of lungs) and multiple skeletal malformations of the craniofacial bones, vertebrae, sternebrae, ribs, pelvis, limbs, and digits. An increase in variations and delayed ossification was also observed in all skeletal regions. The adverse developmental effects were associated with maternal toxicity, as indicated by marked impairment of weight gain and food consumption. Deaths associated with weight loss and abortion occurred in 8% of the pregnant rabbits treated with 5 mg/kg/day pegvaliase-pqpz.
Subcutaneous administration of 2 mg/kg/day pegvaliase‑pqpz (3 times the maximum recommended daily dose based on bodyweight [mg/kg]) in pregnant rabbits had no adverse effects on embryo-fetal development. Systemic exposure to pegvaliase‑pqpz was detected in fetuses from rabbits treated with 2 or 5 mg/kg/day.
Pegvaliase-pqpz increased fetal alterations when administered daily in pregnant rats at doses of 8 mg/kg subcutaneously and higher (4.2 times the human steady-state area under the curve [AUC] at the maximum recommended daily dose) during a 28‑day premating period, mating, and through the period of organogenesis. The fetal alterations were limited to skeletal variations such as cervical ribs, bifid centra of lumbar and thoracic vertebrae, and incomplete ossification of squamosal bones, frontal bones, lumbar vertebra arch, and ribs. Daily administration of 20 mg/kg subcutaneously (19.4 times the human steady-state AUC at the recommended maximum daily dose) to pregnant rats produced reductions in litter sizes and fetal weights, which was associated with maternal toxicity (decreased body weight, ovarian weight, and food consumption). The decrease in litter sizes at 20 mg/kg subcutaneously was secondary to reductions in corpora lutea and implantations. Systemic exposure to pegvaliase-pqpz was detected in fetuses from rats treated with 20 mg/kg of pegvaliase-pqpz (19.4 times the human steady-state AUC at the recommended maximum daily dose). Subcutaneous administration of 2 mg/kg/day pegvaliase-pqpz (less than the human steady state AUC at the maximum recommended daily dose) in pregnant rats had no adverse effects on embryo‑fetal development.
Pegvaliase-pqpz decreased pup weight, litter size, and survival of offspring during lactation, and delayed sexual maturation of offspring when administered daily in rats at 20 mg/kg subcutaneously (19.4 times the human steady‑state AUC at the recommended maximum daily dose), with dosing starting before mating and continuing through lactation. The effects in offspring were associated with maternal toxicity. No effects in offspring were observed at 8 mg/kg/day subcutaneously (4.2 times the human steady-state AUC at the recommended maximum daily dose). This study lacked a complete evaluation of physical and neurobehavioral development in offspring; however, no effects of pegvaliase‑pqpz were noted in tests of learning and memory.
LactationRisk Summary
There are no data on the presence of pegvaliase-pqpz in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. A pre-/post-natal study in rats showed that pegvaliase-pqpz is present in rat milk and that administration of pegvaliase-pqpz during lactation decreased pup weight and survival [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)]. However, systemic absorption of pegvaliase-pqpz was not detected in the rat pups. Palynziq may cause low phenylalanine concentrations in human milk.The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the clinical need for Palynziq treatment and any potential adverse effect on the breastfed infant from Palynziq or from the underlying condition (see Clinical Considerations).
Clinical Considerations
Monitor blood phenylalanine concentrations in breastfeeding women treated with Palynziq.
Pediatric UseThe safety and effectiveness of Palynziq in pediatric patients have not been established.
Geriatric UseClinical studies of Palynziq did not include patients aged 65 years and older.
Palynziq DescriptionPegvaliase-pqpz is a phenylalanine-metabolizing enzyme that is composed of recombinant phenylalanine ammonia lyase (rAvPAL) conjugated to N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS)-methoxypolyethylene glycol (PEG). rAvPAL is manufactured in Escherichia coli bacteria transformed with a plasmid containing the phenylalanine ammonia lyase (PAL) gene derived from Anabaena variabilis. During the rAvPAL manufacturing process, fermentation is carried out in nutrient medium containing the antibiotic kanamycin. However, kanamycin is cleared in the manufacturing process and is not detectable in the final product. rAvPAL is a homotetrameric protein with a molecular weight of 62 kD per monomer. To produce pegvaliase-pqpz, an average of nine (9) 20 kD PEG molecules are covalently bound (or conjugated) to each monomer of rAvPAL. The total molecular weight of pegvaliase‑pqpz (rAvPAL‑PEG) is approximately 1000 kD.
Palynziq (pegvaliase‑pqpz) injection, intended for subcutaneous injection, is a clear to slightly opalescent, colorless to pale yellow, sterile, preservative-free solution and is formulated at pH 6.6 to 7.4.
Palynziq is provided in a single-dose prefilled syringe and is available in three dosage strengths: 2.5 mg/0.5 mL, 10 mg/0.5 mL, and 20 mg/mL. Palynziq contents for each dosage strength are summarized in Table 4.
|
Strength |
Total Contents per Prefilled Syringe |
|
Palynziq 2.5 mg/0.5 mL prefilled syringe |
2.5 mg pegvaliase-pqpz (expressed as the amount of rAvPAL conjugated to 7.25 mg of 20 kD PEG in 0.5 mL Water for Injection, USP and contains the following inactive ingredients: sodium chloride (for tonicity adjustment), trans-cinnamic acid (0.07 mg), and tromethamine and tromethamine hydrochloride (for pH adjustment). |
|
Palynziq 10 mg/0.5 mL prefilled syringe |
10 mg pegvaliase-pqpz (expressed as the amount of rAvPAL conjugated to 29 mg of 20 kD PEG in 0.5 mL Water for Injection, USP and contains the following inactive ingredients: sodium chloride (for tonicity adjustment), trans-cinnamic acid (0.07 mg), and tromethamine and tromethamine hydrochloride (for pH adjustment). |
|
Palynziq 20 mg/mL prefilled syringe |
20 mg pegvaliase-pqpz (expressed as the amount of rAvPAL conjugated to 58 mg of 20 kD PEG in 1 mL Water for Injection, USP and contains the following inactive ingredients: sodium chloride (for tonicity adjustment), trans-cinnamic acid (0.15 mg), and tromethamine and tromethamine hydrochloride (for pH adjustment). |
Pegvaliase-pqpz is a PEGylated phenylalanine ammonia lyase (PAL) enzyme that converts phenylalanine to ammonia and trans‑cinnamic acid. It substitutes for the deficient phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) enzyme activity in patients with PKU and reduces blood phenylalanine concentrations.
PharmacodynamicsPalynziq treatment of adult patients with PKU resulted in the reduction of blood phenylalanine concentrations from pre-treatment baseline [see Clinical Studies (14)]. The reduction of blood phenylalanine concentrations diminished with decreased pegvaliase‑pqpz plasma concentrations.
PharmacokineticsThe pharmacokinetics of pegvaliase‑pqpz exhibit high inter-patient and intra-patient variability due to the heterogeneity of the immune response in adult patients with PKU. Higher antibody titers correlated with higher apparent clearance of pegvaliase‑pqpz. In the first eight weeks of induction and titration treatment, plasma pegvaliase‑pqpz concentrations were low to not measurable. At steady state during maintenance treatment with Palynziq 20 mg and 40 mg subcutaneously once daily, the mean ± SD (range) plasma trough pegvaliase‑pqpz concentrations were: 11.2 ± 9.0 (0.21 to 29.6) mg/L and 10.4 ± 12.7 (0.18 to 43.1) mg/L, respectively. The following pharmacokinetic parameters were observed in adult patients with PKU treated with Palynziq at maintenance dosages of 20 mg once daily and 40 mg once daily.
Absorption
The median Tmax was approximately 8 hours. The mean ± SD (range) peak concentration (Cmax) at steady state was: 14.0 ± 16.3 (0.26 to 68.5) mg/L and 16.7 ± 19.5 (0.24 to 63.8) mg/L, respectively.
Distribution
The mean ± SD (range) apparent volume of distribution was 26.4 ± 64.8 (1.8 to 241) L and 22.2 ± 19.7 (3.1 to 49.5) L, respectively.
Elimination
The mean ± SD (range) apparent clearance at steady state was 0.39 ± 0.87 (0.018 to 3.66) L/h and 1.25 ± 2.46 L/h (0.034 to 8.88), respectively. The mean ± SD (range) half-life was 47 ± 42 (14 to 132) hours and 60 ± 45 (14 to 127) hours, respectively.
Metabolism
The metabolism of phenylalanine ammonia lyase is expected to occur via catabolic pathways and be degraded into small peptides and amino acids.
Excretion
The route of elimination of pegvaliase‑pqpz has not been studied in humans.
Nonclinical ToxicologyCarcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of FertilityCarcinogenicity and genotoxicity studies have not been performed with pegvaliase‑pqpz. Based on its mechanism of action, pegvaliase‑pqpz is not expected to be tumorigenic.
Pegvaliase-pqpz produced impaired fertility in female rats at 20 mg/kg/day subcutaneously (19.4 times the human steady‑state AUC at the maximum recommended daily dose), as indicated by decreases in corpora lutea, implantations, and litter size. These effects were associated with toxicity (decreased body weight, ovarian weight, and food consumption). No effects on mating or fertility were observed in female rats with 8 mg/kg/day subcutaneously (4.2 times the human steady‑state AUC at the maximum recommended daily dose) or in male rats with 20 mg/kg/day subcutaneously.
Animal Toxicology and/or PharmacologyIn rats without PKU treated with pegvaliase-pqpz, dose-dependent vacuolation in multiple organs and tissues was observed in the 4‑ and 26‑week repeat dose toxicity studies at doses of 8 mg/kg subcutaneously or greater administered twice weekly (less than the human steady state AUC at the maximum recommended daily dose). Vacuolation occurred in renal tubule cells and in histiocytic cells of the liver, spleen, testes, adrenal cortex, mesenteric lymph node, and mandibular lymph node. Vacuolation in histiocytes of the affected organs and tissues persisted after cessation of treatment. The vacuolation observed in these studies was not associated with organ‑related toxicities as determined by clinical chemistry/urinalysis and histopathological examination. The clinical significance of these findings and functional consequences are unknown.
In the 39‑week repeat dose toxicity study in monkeys, pegvaliase-pqpz 3 mg/kg subcutaneously twice weekly (3 times the human steady state AUC at the maximum recommended daily dose) produced systemic arteritis involving small arteries and arterioles in a wide range of organs and tissues (kidney, urinary bladder, pancreas, gallbladder, esophagus, stomach, duodenum, jejunum, ileum, cecum, colon, rectum, lung, heart, sciatic nerve, lacrimal gland, mandibular lymph node, epididymis, seminal vesicle, ovary, uterus, cervix, and vagina) and in subcutaneous injection sites. Arteritis was likely due to the immune-mediated response (e.g., immune complex deposition in blood vessels) associated with chronic administration of a foreign protein to the animals. The incidence and severity of systemic arteritis was dose-dependent. The vascular inflammation observed in this study was not associated with organ related toxicities as determined by clinical pathology parameters (hematology, clinical chemistry, and urinalysis) and histopathological examination.
Studies of longer duration in rats and monkeys treated with pegvaliase‑pqpz have not been conducted.
Clinical StudiesStudy 301: Induction/Titration/Maintenance Treatment
Study 165‑301 (referred to as Study 301, NCT01819727) was an open-label randomized, multi-center study of adults with PKU to assess safety and tolerability of self-administered Palynziq in an induction/titration/maintenance regimen with a target maintenance dose of 20 mg subcutaneously once daily or 40 mg subcutaneously once daily. At Palynziq treatment initiation, 253 patients demonstrated inadequate blood phenylalanine control (blood phenylalanine concentration greater than 600 micromol/L) on existing management, and 8 patients had blood phenylalanine concentrations less than or equal to 600 micromol/L. Existing management options included prior or current restriction of dietary phenylalanine and protein intake, and/or prior treatment with sapropterin dihydrochloride. Patients previously treated with sapropterin dihydrochloride were required to discontinue use at least 14 days prior to the first dose.
The 261 enrolled patients were aged 16 to 55 years (mean: 29 years) and had a baseline mean (range) blood phenylalanine of 1,233 (285, 2330) micromol/L. One hundred forty nine out of 261 (57%) patients were taking medical food at baseline and 41 out of 261 patients (16%) were on a protein-restricted diet at baseline (defined as receiving greater than 75% of total protein intake from medical food). Patients were randomized (1:1) to one of two target maintenance dosage arms: 20 mg once daily or 40 mg once daily. Patients were titrated to reach their randomized target dosage of 20 mg once daily or 40 mg once daily. The duration of titration varied among patients and was based on patient tolerability. Of the 261 enrolled patients, 195 (75%) patients reached their randomized maintenance dosage (103 in the 20 mg once daily arm, 92 in the 40 mg once daily arm). Among the patients who reached their randomized maintenance dosage, patients in the 20 mg once daily randomized arm reached their maintenance dosage at a median time of 10 weeks (range: 9 to 29 weeks) and patients in the 40 mg once daily arm reached their maintenance dosage at a median time of 11 weeks (range: 10 to 33 weeks).
Of the 261 patients who enrolled in Study 301, 54 (21%) patients discontinued treatment during Study 301, 4 patients completed Study 301 and did not continue to Study 165‑302 (referred to as Study 302, NCT01889862), 152 patients continued to the eligibility period of Study 302, and 51 patients continued directly from Study 301 into the long‑term treatment period of Study 302.
Study 302: Efficacy Assessment
A total of 164 adult patients with PKU who were previously-treated with Palynziq (152 patients from Study 301 and 12 patients from other Palynziq trials) enrolled in Study 302 and continued treatment with Palynziq in Study 302 for up to 13 weeks to assess eligibility for randomized withdrawal period.
Randomized Withdrawal Period
Following this period of up to 13 weeks of additional Palynziq treatment in Study 302, eligibility for entry into the efficacy assessment period (randomized withdrawal period) was determined by whether a patient achieved at least a 20% reduction in blood phenylalanine concentration from pre-treatment baseline (when in previous studies). Eighty‑six out of 164 patients (52%) met this response target and continued into the randomized withdrawal period. In the double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized withdrawal period, patients were randomized in a 2:1 ratio to either continue their maintenance Palynziq dosage or to receive matching placebo for a total of 8 weeks. The treatment difference in least squares (LS) mean change in blood phenylalanine concentration from the Study 302 randomized withdrawal baseline to randomized withdrawal Week 8 for each randomized study arm is shown in Table 5. Mean blood phenylalanine concentrations at pre-treatment baseline (Study 301 or other Palynziq trials) are also shown in Table 5. At Study 302 randomized withdrawal Week 8, Palynziq‑treated patients (20 mg once daily or 40 mg once daily) maintained their blood phenylalanine concentrations as compared to their randomized withdrawal baseline, whereas patients randomized to matching placebo (20 mg once daily or 40 mg once daily) returned to their pretreatment baseline blood phenylalanine concentrations (Figure 1).
|
*Based on the mixed model repeated measures (MMRM) method, with treatment arm, visit, and treatment arm-by-visit interaction as factors adjusting for baseline blood phenylalanine concentration. †Patients who did not complete phenylalanine assessment within the window for Week 8 (Day 43 to 56) were excluded. |
|||||
| Randomized Study Arm | Blood Phenylalanine Concentration (micromol/L) Mean (SD) |
LS Mean Change from Study 302 Randomized Withdrawal Baseline to Week 8 (95% CI) |
Treatment Difference in LS Mean Change (95% CI) P‑value* | ||
| Pre‑treatmentBaseline | Study 302 Randomized Withdrawal Baseline | Study 302 Randomized Withdrawal Week 8 | |||
|
Palynziq 20 mg once daily |
1450.2 (310.5) n = 29 |
596.8 (582.8) n = 29 |
553.0 (582.4) n = 26† |
-23.3 (-156.2, 109.7) |
-973.0 (‑1204.2, ‑741.9) p < 0.0001 |
|
Placebo 20 mg once daily |
1459.1 (354.7) n = 14 |
563.9 (504.6) n = 14 |
1509.0 (372.6) n = 13† |
949.8 (760.4, 1139.1) |
|
|
Palynziq 40 mg once daily |
1185.8 (344.0) n = 29 |
410.9 (440.0) n = 29 |
566.3 (567.5) n = 23† |
76.3 (-60.2, 212.8) |
-588.5
(-830.1, -346.9) p < 0.0001 |
|
Placebo 40 mg once daily |
1108.9 (266.8) n = 14 |
508.2 (363.7) n = 14 |
1164.4 (343.3) n = 10† |
664.8 (465.5, 864.1) |
|
Figure 1: Observed Mean (SE) Blood Phenylalanine Concentrations Over Time in Adult Patients with PKU in Study 302
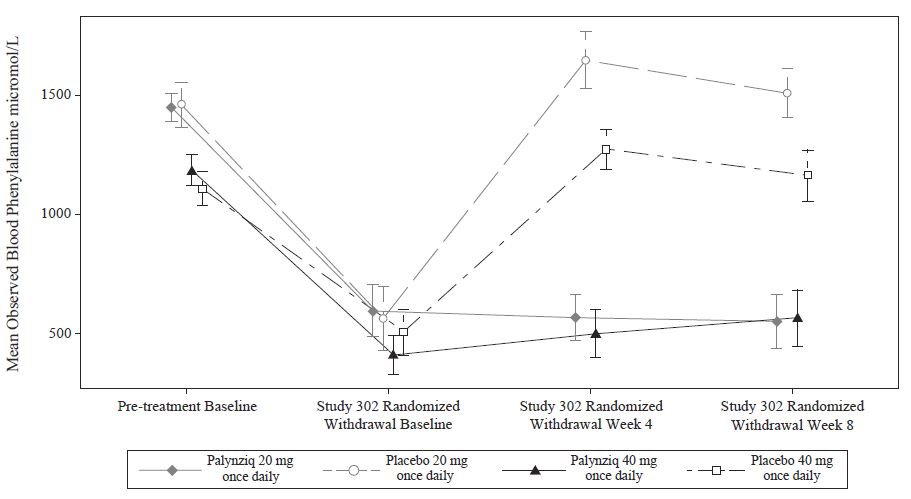
Study 301 and 302 Continuous Treatment
Of 118 patients from Study 301 with a pre‑treatment baseline blood phenylalanine concentration greater than 600 micromol/L who were randomized to and received at least one dose of 20 mg once daily Palynziq, 108 patients, 98 patients, and 51 patients were treated for at least 24 weeks, 48 weeks, and 96 weeks, respectively.
Of the 118 patients, 53 patients reached their first response (at least a 20% reduction in blood phenylalanine concentration from pre-treatment baseline or a blood phenylalanine concentration less than or equal to 600 micromol/L) by 4 weeks of treatment with 20 mg once daily and 28 patients reached their first response between Weeks 4 and 24 with 20 mg once daily. Of the 118 patients, 25 patients escalated their dosage from 20 mg once daily to 40 mg once daily before reaching a first response; of those 25 patients, 8 patients reached their first response by 4 weeks of treatment with 40 mg once daily and 6 patients reached their first response between Weeks 4 and 16 with 40 mg once daily.
How Supplied/Storage and HandlingHow Supplied
Palynziq (pegvaliase-pqpz) injection is supplied as a preservative-free, sterile, clear to slightly opalescent, colorless to pale yellow solution. All dosage strengths of Palynziq are provided in a 1 mL glass syringe with a 26 gauge, 0.5 inch needle.
Each carton contains 1 or 10 trays with single-dose prefilled syringe(s), Prescribing Information, Medication Guide, and Instructions for Use. The following packaging configurations are available.
|
Pegvaliase‑pqpz 2.5 mg/0.5 mL
|
1 syringe/carton |
NDC 68135‑058‑90 |
| Pegvaliase‑pqpz 10 mg/0.5 mL |
1 syringe/carton
|
NDC 68135‑756‑20 |
| Pegvaliase‑pqpz 20 mg/mL |
1 syringe/carton 10 syringes/carton |
NDC 68135‑673‑40 NDC 68135‑673‑45 |
Storage and Handling
Store in refrigerator at 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C) in its original carton to protect from light.Do not freeze or shake.For patients: If needed, store Palynziq in the original carton at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C) for up to 30 days. Record the date removed from refrigeration on the carton. Once stored at room temperature, do not return the product to the refrigerator.The shelf-life expires after storage at room temperature for 30 days, or after the expiration date on the product carton, whichever is earlier.Patient Counseling InformationAdvise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide and Instructions for Use).
Anaphylaxis and Other Hypersensitivity Reactions
Advise patients that Palynziq may cause hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis that can occur at any time. Instruct patients to recognize the signs and symptoms of anaphylaxis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.3)].Instruct patients to carry auto-injectable epinephrine with them at all times during Palynziq treatment. Instruct the patient and observer (if applicable) on the appropriate use of auto‑injectable epinephrine for anaphylaxis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].Instruct patients who experience anaphylaxis to seek immediate medical care, discontinue therapy, and resume treatment only at the instruction of a healthcare provider [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].Palynziq REMS Program
Palynziq is available only through a restricted program called the Palynziq REMS [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. Inform the patient of the following notable requirements:
Patients must be enrolled in the Palynziq REMS.Patients must be educated about the risk of anaphylaxis by a certified prescriber to ensure they understand the risks and benefits of treatment with Palynziq.Patients must fill a prescription for auto-injectable epinephrine and carry it with them at all times.Patients will be given a Palynziq Patient Wallet Card that they should carry with them at all times. This card describes symptoms which, if experienced, should prompt the patient and observer (if applicable) to immediately seek medical care. Advise the patient to show the Palynziq Wallet Card to other treating healthcare providers.Palynziq is available only from certified pharmacies participating in the program. Therefore, provide patients with the telephone number and website for information on how to obtain the product.
Administration
Advise patients to monitor their dietary protein and phenylalanine intake throughout treatment with Palynziq, and adjust intake as directed by their healthcare provider based on blood phenylalanine concentrations [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].Provide appropriate instruction for methods of self-injection, including careful review of the Palynziq Medication Guide and Instructions for Use. Instruct patients in the use of aseptic technique when administering Palynziq [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].Inform patients that a healthcare provider will show them or their caregiver how to prepare to inject Palynziq before self-administering.Advise patients not to inject into moles, scars, birthmarks, bruises, rashes, or areas where the skin is hard, tender, red, damaged, burned, inflamed, or tattooed.Advise patients to rotate areas of injection with each dose. Advise patients to check the injection site for redness, swelling, and tenderness, and to contact their healthcare provider if they have a skin reaction and it does not clear up, or worsens.Advise patients to follow sharps disposal recommendations [see Instructions for Use] patients on safe disposal procedures.Advise patients that the shelf‑life expires after storage at room temperature for 30 days or after the expiration date on the product carton, whichever is earlier.Pregnancy
Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females to inform their healthcare provider of a known or suspected pregnancy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].Advise women who are exposed to Palynziq during pregnancy or who become pregnant within one month following the last dose of Palynziq that there is a pregnancy surveillance program that monitors pregnancy outcomes. Encourage these patients to report their pregnancy to BioMarin (1‑866‑906‑6100) [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].Manufactured by:
BioMarin Pharmaceutical Inc.
Novato, CA 94949
US License No. 1649
MEDICATION GUIDE|
Medication Guide Palynziq™ (Pal-lin-zeek) (pegvaliase-pqpz) injection |
|
|
What is the most important information I should know about Palynziq?
Palynziq can cause a severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis) that may be life-threatening and can happen any time during treatment with Palynziq. Severe allergic reactions are a serious but common side effect of Palynziq. You will receive your first injection of Palynziq in a healthcare setting where you will be closely watched for at least 1 hour after your injection for a severe allergic reaction.If you have a severe allergic reaction during treatment with Palynziq, you will need to receive an auto-injection of epinephrine immediately and get emergency medical help right away.Your healthcare provider will decide if you (or your caregiver) are able to give the Palynziq injections, recognize the signs and symptoms of a severe allergic reaction, give an injection of epinephrine and call for emergency medical help, if needed.Your healthcare provider may recommend that an adult observer (or your caregiver) be with you when you give your Palynziq injection, and for at least 1 hour after your injection to watch you for signs and symptoms of a severe allergic reaction and, if needed, give you an injection of epinephrine and call for emergency medical help.Stop injecting Palynziq and get emergency medical care right away if you have any of the following symptoms of a severe allergic reaction during treatment with Palynziq: |
|
| fainting (passing out)dizziness or lightheadednesssudden confusiontrouble breathing or wheezingchest discomfort or chest tightnessfast heart rate | swelling of your face, lips, eyes, or tonguethroat tightnessflushed skinskin rash, itching, or raised bumps on skinnausea, vomiting, or diarrhealosing control of urine or stools |
|
Your healthcare provider will prescribe an auto-injectable epinephrine for you and will teach you (or your caregiver) and your observer, if needed, when and how to use it if you have a severe allergic reaction. Keep the auto-injectable epinephrine with you at all times during treatment with Palynziq. Read the Patient Information that comes with the auto-injectable epinephrine that your healthcare provider prescribes for you for more information.If you have a severe allergic reaction, do not continue to take Palynziq until you talk with your healthcare provider. Tell your healthcare provider that you had a severe allergic reaction. Your healthcare provider will tell you if you can continue treatment with Palynziq.Your healthcare provider may prescribe other medicines to take before your Palynziq injection that may help reduce the symptoms of an allergic reaction.If your healthcare provider decides that you can continue treatment with Palynziq after a severe allergic reaction, you will receive your next injection of Palynziq in a healthcare setting where you will be closely watched for at least 1 hour after your injection for a severe allergic reaction.Your healthcare provider will give you a Palynziq Patient Wallet Card that describes symptoms that you (or your caregiver), or your observer, should know that require you to get emergency medical care right away. Carry this card with you at all times during treatment with Palynziq. It is important to show your Palynziq Patient Wallet Card to any other healthcare provider who treats you.
Palynziq is only available through a restricted program called the Palynziq Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) Program. Before you can receive Palynziq, you must: enroll in this program.receive education about the risk of a severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis) by a healthcare provider certified in the Palynziq REMS to be sure that you understand the risks and benefits of treatment with Palynziq.fill the prescription your healthcare provider gives you for the auto-injectable epinephrine and carry it with you at all times during treatment with Palynziq.carry the Palynziq Patient Wallet Card with you at all times.Talk to your healthcare provider for more information about the Palynziq REMS and how to enroll. |
|
|
What is Palynziq?
Palynziq is a prescription medicine used to lower blood levels of phenylalanine in adults with PKU (phenylketonuria) who have uncontrolled blood phenylalanine levels above 600 micromol/L (10 mg/dL) on their current treatment. It is not known if Palynziq is safe and effective in children. |
|
|
Before injecting Palynziq, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you: cannot or are not willing to use auto-injectable epinephrine to treat a severe allergic reaction.are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. Palynziq may harm your unborn baby. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you become pregnant or think you might be pregnant while taking Palynziq.If your phenylalanine levels are too high or too low during pregnancy, this may also affect your unborn baby. You and your healthcare provider can decide the best way for you to manage your blood phenylalanine levels and discuss the risks and benefits of taking Palynziq during pregnancy to you and your unborn baby. It is very important to keep your phenylalanine levels at the levels your healthcare provider recommends during pregnancy.Pregnancy Surveillance Program. There is a pregnancy surveillance program for females who take Palynziq during pregnancy, or who become pregnant while receiving Palynziq or within 1 month after their last dose of Palynziq. The purpose of this program is to collect information about the health of you and your baby while taking Palynziq. Talk to your healthcare provider about how you can take part in this program or call BioMarin at 1-866-906-6100.are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if Palynziq passes into your breast milk. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby if you take Palynziq.Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription or over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, or herbal supplements. |
|
|
How should I take Palynziq? Your healthcare provider will give you the Palynziq injection until they decide that you (or your caregiver) can give it. See “What is the most important information I should know about Palynziq?”Your healthcare provider may prescribe medicine for you to take before your Palynziq injection to help reduce the symptoms of an allergic reaction.If your healthcare provider decides that you (or your caregiver) can give your Palynziq injections, you (or your caregiver) will be shown how to prepare and give your Palynziq injections. See the “Instructions for Use” for detailed instructions on how to prepare and give an injection of Palynziq.Use Palynziq exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to. Your healthcare provider will tell you how much Palynziq to inject and when to inject it. Palynziq comes in prefilled syringes with 3 different strengths (2.5 mg, 10 mg, or 20 mg). You may need more than 1 Palynziq prefilled syringe for your prescribed dose.Monitor the amount of protein and phenylalanine that you eat or drink. Your healthcare provider may change the amount of protein and phenylalanine you should have in your diet during treatment with Palynziq, depending on the levels of phenylalanine in your blood. Follow your healthcare provider’s instructions about the amount of protein and phenylalanine you should have in your diet.If you miss a dose, take your next dose at the regular time. Do not take two doses of Palynziq to make up for a missed dose. |
|
|
What are the possible side effects of Palynziq?
Palynziq may cause serious side effects, including: See “What is the most important information I should know about Palynziq?”Other allergic reactions to Palynziq can happen during treatment with Palynziq. Contact your healthcare provider right away if you have any of the following symptoms of an allergic reaction including: rash, itching, or swelling of the face, lips, eyes, or tongue. Your healthcare provider may change your dose of Palynziq, stop your treatment with Palynziq for a period of time, or prescribe medicine for you to take before your Palynziq injection to help reduce the symptoms of an allergic reaction.The most common side effects of Palynziq include: |
|
|
injection site reactions, such as redness, itching, pain, bruising, rash, swelling, tendernessjoint painheadacheskin reactions that spread on your skin and last at least 14 days, such as itching, rash, rednessitchingnausea |
stomach painmouth and throat painvomitingcoughdiarrheafeel very tiredlow levels of phenylalanine in your blood |
| These are not all the possible side effects of Palynziq. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. | |
|
How should I store Palynziq? Store Palynziq in the refrigerator at 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C).If needed, you may store Palynziq at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C) for up to 30 days.Write the date that you remove Palynziq from the refrigerator on the carton.If stored at room temperature, do not put Palynziq back in the refrigerator.Keep Palynziq in the original carton to protect from light.Do not freeze or shake Palynziq.Throw away Palynziq if it has been kept at room temperature for 30 days and has not been used, or after the expiration date on the carton, whichever comes first.Keep Palynziq and all medicines out of the reach of children. |
|
|
General Information about the safe and effective use of Palynziq. Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use Palynziq for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Palynziq to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about Palynziq that is written for health professionals. |
|
|
What are the ingredients in Palynziq?
Active ingredients: pegvaliase-pqpz Inactive ingredients: sodium chloride, trans-cinnamic acid, tromethamine, and tromethamine hydrochloride |
|
|
Manufactured by: BioMarin Pharmaceutical Inc. Novato, CA 94949 US License No. 1649 For more information, go to http://www.Palynziq.com/ or call 1-866-906-6100. |
|
| This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. | |
| Issued: May 2018 | |
Instructions for Use
Palynziq (Pal-lin-zeek)
(pegvaliase-pqpz)
injection
prefilled syringe
Read this Instructions for Use before you start using the Palynziq prefilled syringe and each time you get a new prescription. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your medical condition or your treatment.
Follow these instructions carefully while you are using Palynziq. If your healthcare provider decides that you (or your caregiver) can give the injections of Palynziq at home, your healthcare provider will show you (or your caregiver) how to inject Palynziq the right way. Your healthcare provider should watch you (or your caregiver) give the first Palynziq injection and monitor you for signs and symptoms of a severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis). Do not inject Palynziq until your healthcare provider shows you (or your caregiver) how to inject Palynziq the right way and has watched you (or your caregiver) give your injection.
Talk to your healthcare provider if you (or your caregiver) have any questions about how to inject Palynziq the right way.
Do not share your prefilled syringes with anyone else. You may give an infection to them or get an infection from them.
Store your Palynziq prefilled syringe(s) in its original carton in the refrigerator. See “Storage of Palynziq” at the end of this Instructions for Use.
Supplies you will need for each injection of Palynziq (See Figure A):
Palynziq prefilled syringe(s) in sealed tray(s). Each tray contains 1 prefilled syringe. You may need more than 1 prefilled syringe for your prescribed dose.
1 gauze pad or cotton ball
1 alcohol pad
1 bandage
1 puncture resistant or sharps disposal container. See “Dispose of the used prefilled syringes” at the end of this Instructions for Use.
Figure A

Important things to know about using your Palynziq prefilled syringe:
Inject only 1 time with each Palynziq prefilled syringe. Do not use a Palynziq syringe more than 1 time.
Do not pull back on the plunger at any time.
Do not remove the needle cap until you are ready to inject.
Figure B below shows what the prefilled syringe looks like before use.
Figure B
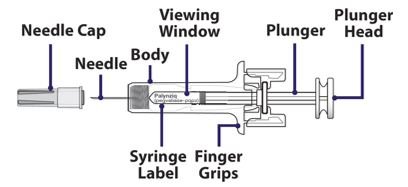
Select the correct Palynziq prefilled syringe(s) for your dose. You may need more than 1 prefilled syringe for your prescribed dose. Your healthcare provider will tell you which syringe(s) to use. Ask your healthcare provider if you have any questions.
When you receive your Palynziq prefilled syringe(s), check that the name “Palynziq" appears on the carton(s).
Palynziq prefilled syringes come in 3 different strengths (See Figure C).
Before you inject Palynziq, check each carton and syringe to make sure you have the right prefilled syringe for your prescribed dose.
Figure C

Set up your injection
Step 1: Gather your supplies for the injection(s) (See Figure A) and place them on a clean flat surface.
Take out the number of cartons needed for your prescribed dose from the refrigerator.
Check the expiration date on the carton(s) (See Figure D).
If the expiration date has passed, do not use the prefilled syringe(s) in that carton. Call BioMarin at 1‑866‑906‑6100 or your healthcare provider for help with Palynziq.Figure D
Step 2: Open the carton(s) and take out the sealed tray(s) that you need for your prescribed dose (See Figure E). You may need more than 1 prefilled syringe for your prescribed dose.
Place the sealed tray(s) on a clean, flat surface out of reach of children and pets.
Put the carton with any remaining trays back in the refrigerator.
Figure E

Step 3: Let the sealed tray(s) sit at room temperature for at least 30 minutes. Injecting Palynziq when cold can make the injection feel uncomfortable.
Do not warm up the prefilled syringe in any other way other than letting it sit at room temperature. Do not warm in a microwave and do not place in hot water.| Let the sealed tray(s) sit at room temperature for at least 30 minutes before opening. |
Step 4: Peel off the cover from the tray (See Figure F).
Figure F
Step 5: Hold the middle of the prefilled syringe body and remove the prefilled syringe from the tray (See Figure G).
Throw away the prefilled syringe if it looks damaged or used, and use a new prefilled syringe for your injection. See “Dispose of the used prefilled syringes” at the end of this Instructions for Use. Call BioMarin at 1‑866‑906‑6100 or your healthcare provider for help with Palynziq.Do not remove the needle cap from the prefilled syringe until Step 12.Do not shake or roll the syringe in your hands.Figure G
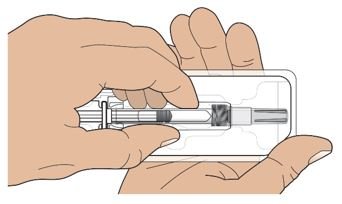
Step 6: Check the prefilled syringe label to make sure you have the correct strength for your prescribed dose.
| Check the prefilled syringe label to make sure you have the correct strength. |
Step 7: Look at the liquid through the viewing window (See Figure H).
It is normal to see air bubbles. Do not flick or try to push the bubbles out.The liquid should look clear and colorless to pale yellow. Throw away the prefilled syringe if the liquid is cloudy, discolored, or has particles in it and use a new prefilled syringe for your injection. See “Dispose of the used prefilled syringes” at the end of this Instructions for Use. Call BioMarin at 1‑866‑906‑6100 or your healthcare provider for help with Palynziq.
Figure H
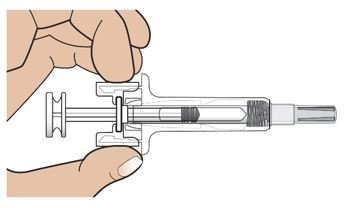
Choose and prepare injection site
Step 8: Choose your injection site.
The recommended injection sites are:
Front middle of the thighs.The abdomen except for the 2 inch (5 centimeter) area directly around the belly button (navel).Figure I
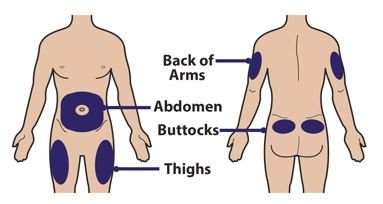
If a caregiver is giving the injection, the top of the buttocks and the back of the upper arms may also be used (See Figure I).
Do not inject into moles, scars, birthmarks, bruises, rashes, or areas where the skin is hard, tender, red, damaged, burned, inflamed, or tattooed.If you need more than 1 injection for your dose, the injection sites should be at least 2 inches away from each other. The second injection site can be on the same part of the body or a different part of the body (See Figures I and J).For each injection, change (rotate) your injection sites. Choose an injection site that is at least 2 inches away from the injection site that you used for the last injection. It can be on the same part of the body or a different part of the body (See Figures I and J).Figure J
Inject at least 2 inches apart
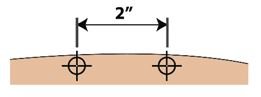
Step 9: Wash your hands well with soap and water before injecting Palynziq (See Figure K).
Figure K
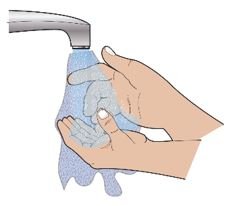
Step 10: Clean the chosen site with an alcohol pad. Let the skin air dry for at least 10 seconds before injecting Palynziq (See Figure L).
Do not touch the cleaned injection site.Do not remove the needle cap until you are ready to inject Palynziq.Figure L
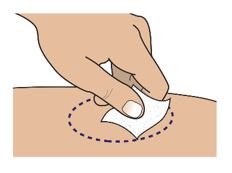
Inject Palynziq
Step 11: Hold the body of the prefilled syringe with one hand with the needle facing away from you (See Figure M).
Do not use the prefilled syringe if it is dropped. Throw away the prefilled syringe if it is dropped and use a new prefilled syringe for your injection. See “Dispose of the used prefilled syringes” at the end of this Instructions for Use. Call BioMarin at 1‑866‑906‑6100 or your healthcare provider for help with Palynziq.Figure M
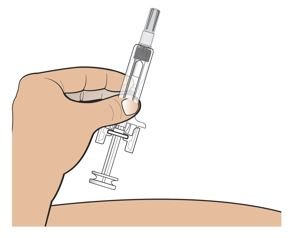
Step 12: Pull the needle cap straight off the needle (See Figure N).
Do not twist the needle cap during removal.Do not hold the prefilled syringe by the plunger or plunger head while taking the needle cap off.Before injecting Palynziq, check to make sure that the needle is not damaged or bent. Throw away the prefilled syringe if the needle is damaged or bent and use a new prefilled syringe for your injection. See “Dispose of the used prefilled syringes” at the end of this Instructions for Use. Call BioMarin at 1‑866‑906‑6100 or your healthcare provider for help with Palynziq.You may see a drop of liquid on the tip of the needle. This is normal. Do not wipe it away. Throw the needle cap away in a puncture resistant or sharps disposal container.
Figure N
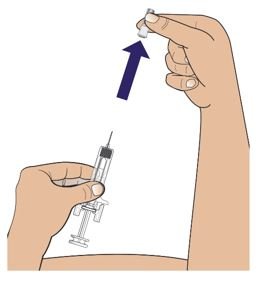
Step 13: Hold the body of the prefilled syringe in 1 hand between your thumb and index finger. Use your other hand to pinch up the skin around the injection site. Hold the skin firmly (See Figure O).
Do not touch the plunger head while inserting the needle into the skin.Figure O
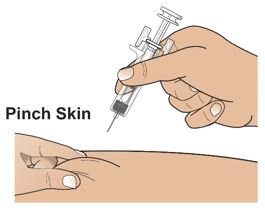
Step 14: Use a quick motion to fully insert the needle into the pinched skin at a 45 to 90 degree angle (See Figure P).
Release the pinch of skin. Use that hand to hold the bottom of the prefilled syringe steady. Place the thumb of your other hand on the plunger head and place your index and middle fingers under the finger grips (See Figure P).
Figure P
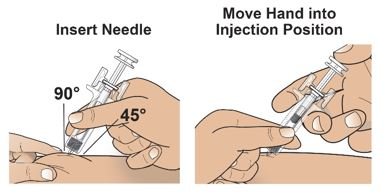
Step 15: Use your thumb to push in the plunger slowly and steadily as far as it will go to inject all the medicine (See Figure Q). More pressure on the plunger may be needed to inject all the medicine for the 10 mg and 20 mg strength prefilled syringes.
Figure Q
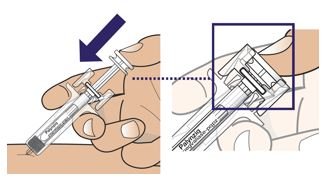
Step 16: Slowly move your thumb up to release the plunger. The needle will automatically be covered by the prefilled syringe body (See Figure R).
Figure R
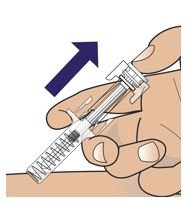
Treat injection site
Step 17: Treat injection site (if needed).
If you see drops of blood at the injection site, press a cotton ball or gauze over the injection site and hold for about 10 seconds. You may cover the injection site with a small adhesive bandage if needed.
If more than 1 prefilled syringe is needed for your prescribed dose:
Step 18: If your healthcare provider tells you to use more than one prefilled syringe for your prescribed dose, repeat Steps 4 to 17 listed above for each prefilled syringe that you use.
Note: Do not give the injection in the same spot. The injection sites should be at least 2 inches away from each other. See Step 8 for information on choosing an injection site.| If you need to use more than 1 prefilled syringe for your prescribed dose, repeat Steps 4 to 17 right away for each prefilled syringe you use. |
Dispose of the used prefilled syringes
Step 19: Put your used prefilled syringes in a puncture resistant container, such as an FDA‑cleared sharps disposal container immediately after use (See Figure S).
Do not throw away (dispose of) prefilled syringes in your household trash.
If you do not have an FDA-cleared sharps disposal container, you may use a household container that is:
made of a heavy-duty plastic,can be closed with a tight-fitting, puncture-resistant lid, without sharps being able to come out,upright and stable during use,leak-resistant, andproperly labeled to warn of hazardous waste inside the container.When your sharps disposal container is almost full, you will need to follow your community guidelines for the right way to dispose of your sharps disposal container. There may be state or local laws about how you should throw away used needles and syringes. For more information about safe sharps disposal and for specific information about sharps disposal in the state that you live in, go to the FDA’s website at: http://www.fda.gov/safesharpsdisposal
Do not dispose of your used sharps disposal container in your household trash unless your community guidelines permit this. Do not recycle your used sharps disposal container.
Note: Keep sharps disposal container out of the reach of children and pets.
Figure S
Storage of Palynziq
Figure T
Keep Palynziq and all medicines out of the reach of children.
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Manufactured by:
BioMarin Pharmaceutical Inc.
Novato, CA 94949
U.S. License No. 1649
Issued: 05/2018
Palynziq - 2.5 MG/0.5 MLNDC 68135-058-90 Rx only
PalynziqTM
(pegvaliase-pqpz)
Injection
2.5 mg/0.5 mL
For Subcutaneous Use Only
Contains one x 2.5 mg/0.5 mL single-dose prefilled syringe.
Discard after use.
ATTENTION: Dispense the enclosed Medication Guide to each patient.



NDC 68135-756-20 Rx only
PalynziqTM
(pegvaliase-pqpz)
Injection
10 mg/0.5 mL
For Subcutaneous Use Only
Contains one x 10 mg/0.5 mL single-dose prefilled syringe.
Discard after use.
ATTENTION: Dispense the enclosed Medication Guide to each patient.
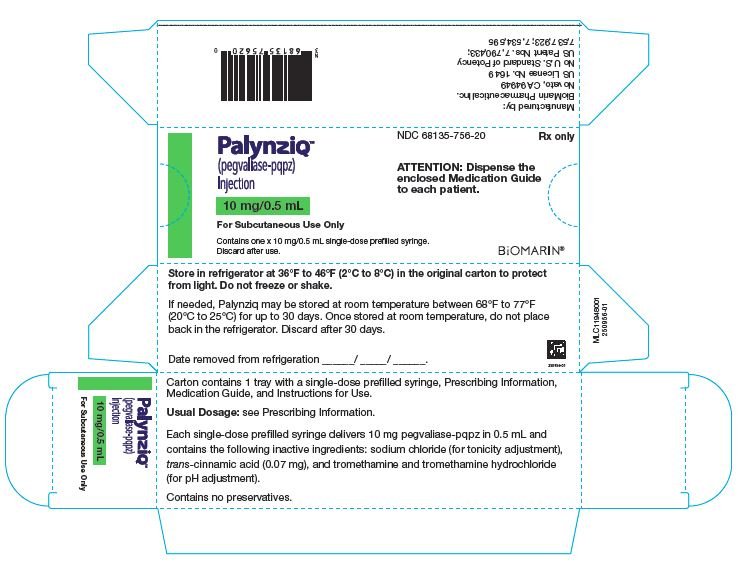


NDC 68135-673-40 Rx only
PalynziqTM
(pegvaliase-pqpz)
Injection
20 mg/mL
For Subcutaneous Use Only
Contains one x 20 mg/mL single-dose prefilled syringe.
Discard after use.
ATTENTION: Dispense the enclosed Medication Guide to each patient.
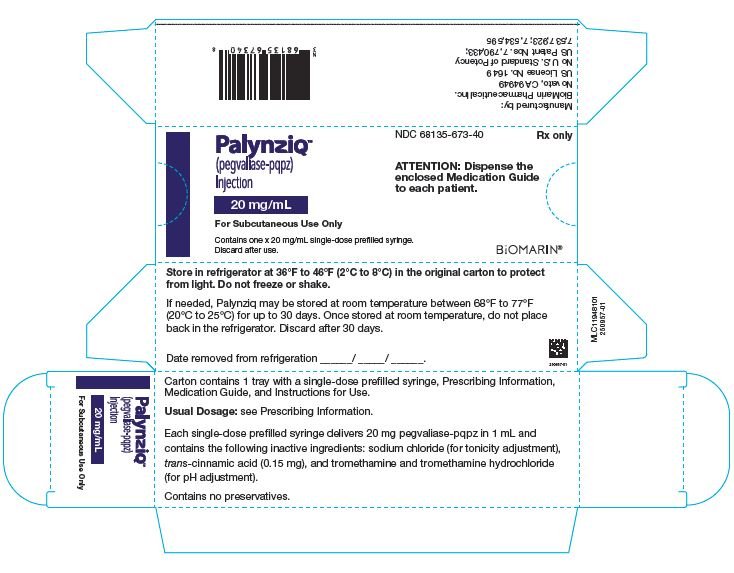


NDC 68135-673-45 Rx only
PalynziqTM
(pegvaliase-pqpz)
Injection
20 mg/mL
For Subcutaneous Use Only
Contains ten 20 mg/mL single-dose prefilled syringes.
Discard after use.
ATTENTION: Dispense the enclosed Medication Guide to each patient.
