

Iluvien Implant 氟轻松玻璃体植入物




| 通用中文 | 氟轻松玻璃体植入物 | 通用外文 | fluocinolone ophthalmic |
| 品牌中文 | 伊洛维安植入剂 | 品牌外文 | Iluvien Implant |
| 其他名称 | |||
| 公司 | Psivida(Psivida) | 产地 | 美国(USA) |
| 含量 | 0.19mg | 包装 | 1支/盒 |
| 剂型给药 | 植入剂 | 储存 | 室温 |
| 适用范围 | 糖尿病性黄斑水肿的治疗 | ||
| 通用中文 | 氟轻松玻璃体植入物 |
| 通用外文 | fluocinolone ophthalmic |
| 品牌中文 | 伊洛维安植入剂 |
| 品牌外文 | Iluvien Implant |
| 其他名称 | |
| 公司 | Psivida(Psivida) |
| 产地 | 美国(USA) |
| 含量 | 0.19mg |
| 包装 | 1支/盒 |
| 剂型给药 | 植入剂 |
| 储存 | 室温 |
| 适用范围 | 糖尿病性黄斑水肿的治疗 |
公司:Psivida公司
糖尿病性黄斑水肿的治疗
伊洛维安(fluocinone acetonide)是一种玻璃体腔植入物,用于治疗糖尿病性黄斑水肿。
马萨诸塞州沃特敦讯(商业新闻)---在开发用于治疗眼疾的缓释药物递送产品方面处于领先地位的psivida公司今天宣布,美国食品和药物管理局(fda)已批准伊洛维安治疗糖尿病性黄斑水肿(dme)。它适用于以前接受过一个疗程皮质类固醇治疗且眼压(IOP)没有明显临床升高的患者。单次注射伊洛维恩微针可持续治疗二甲醚36个月。据估计,美国约有560000人在临床上有显著的DME,这是糖尿病患者最常见的视力丧失原因,也是发达国家中青年人致盲的主要原因。伊洛维恩预计将于2015年初在美国上市。
FDA批准伊洛维安后,Psivida有权从被许可方Alimera Sciences获得2500万美元的里程碑。普西维达还将有权获得伊鲁万在美国销售净利润的20%。
“FDA批准了我们的第三种经FDA批准的视网膜疾病产品——伊洛维恩,这为美国的二甲醚患者提供了一个重要的治疗选择,尽管其大部分二甲醚的抗血管内皮生长因子眼部注射频率高达每月一次,但并没有得到最佳的管理。伊洛维恩的临床试验表明,伊洛维恩实际上可以逆转许多二甲醚患者的视力下降。Iluvien对现有疗法的另一个优点是单次注射可以持续治疗三年,”Paul Ashton,Ph.D.,PSIVIDA总裁兼首席执行官说。
阿什顿博士补充道:“2500万美元的里程碑将有助于资助我们正在进行的产品开发计划,包括用于后葡萄膜炎的Medidur™和用于生物制剂持续交付的Tethadur™。”Psivida正在独立开发Medidur,一种与伊洛维恩相同设计、相同药物的可注射、缓释微植入物,用于治疗慢性后葡萄膜炎,作为美国第三大致盲原因,该公司计划在进行中的第三阶段临床试验的基础上,寻求fda对该产品的批准。本研究的注册预计在2015年第一季度末完成。
Iluvien已经在英国和德国商业化,并且已经收到或正在等待十七个欧盟国家的市场批准,用于治疗慢性DME患者对现有疗法的反应不足。阿什顿博士继续说:“我们非常高兴,FDA对伊洛维恩的批准并不像欧盟那样,仅限于慢性二甲醚患者、其他治疗失败的患者或白内障手术患者。”
伊洛维恩是一种可注射的微量插入物,通过连续36个月亚微克剂量的皮质激素氟辛醇酮乙酰奈德提供持续治疗。目前的护理治疗标准要求每月向眼睛注射抗血管内皮生长因子,研究表明,超过50%的患者没有得到最佳的治疗。fda的批准是基于临床试验数据,该数据显示,在24个月时,28.7%的患者在接受早期治疗糖尿病视网膜病变研究(etdrs)的15个字母或更多的眼图上,他们的最佳矫正视力比基线水平有改善。在试验结束后的36个月里,视力一直保持着这种改善。
关于伊洛维安
0.19mg的伊洛维恩(氟辛诺酮-丙酮胺玻璃体腔植入物)是美国批准的一种缓释玻璃体腔植入物,用于治疗先前接受过一个疗程皮质类固醇治疗且眼压没有明显升高的患者的二甲醚。每一个伊洛维恩植入物都被设计成释放亚微克水平的氟西诺酮丙酮胺(fac),一种持续36个月的皮质类固醇。
皮质类固醇在治疗眼病炎症方面有着有效的应用历史。使用25号针头的敷贴器将伊洛维恩注射到患者的眼睛后部,这样就可以实现伤口的自我封闭。在FAME™研究中,一项关于伊洛维恩的第3阶段临床研究中,最常见的药物不良反应包括白内障的发展和眼压升高。
伊鲁万重要安全信息
伊洛维安含有一种皮质类固醇,用于治疗二甲醚的患者,这些患者以前接受过一个疗程的皮质类固醇治疗,但眼压没有明显的临床升高。
玻璃体腔注射与眼内炎、眼部炎症、眼压升高和视网膜脱离有关。注射后应监测病人。
使用皮质类固醇可导致后囊下白内障、眼压升高、青光眼,并可增强细菌、真菌或病毒引起的继发性眼部感染。
如果晶状体后囊不完整,植入物可能会迁移到前房。在对照研究中,最常见的不良反应是白内障的发展和眼压的升高。
关于二甲醚
糖尿病性黄斑水肿是糖尿病性视网膜病变引起视力下降的主要原因,是一种影响黄斑的疾病,黄斑是视网膜中负责中央视力的部分。当糖尿病视网膜病变的血管渗漏引起黄斑肿胀时,病情发展为二甲醚。二甲醚的发作是无痛的,在出现中心视力模糊或急性视力丧失之前,患者可能无法察觉。这种模糊的严重程度可能从轻微到严重的视力丧失不等。威斯康星糖尿病视网膜病变的流行病学研究发现,在10年的时间里,大约19%的糖尿病患者被诊断为DME。所有患有1型或2型糖尿病的人都有患二甲醚的危险。随着糖尿病患者人数的增加,诊断为二甲醚的年发病率预计也会增加。
糖尿病持续时间是视网膜病变增加的最大危险因素,与二甲醚患病率增加有关。视网膜病变的出现与血管内皮生长因子(vegf)的上调有关,血管通透性增加导致液体渗漏。随着视网膜病变的恶化,多种细胞因子(炎症因子)发生上调。皮质类固醇对持续存在的二甲醚相关的多种细胞因子的下调具有广泛的作用。
关于psivida公司。
Psivida公司总部位于马萨诸塞州沃特敦,是开发治疗眼疾的缓释药物递送产品的领导者。Psivida目前专注于利用其核心技术系统Durasert™和Bioslicon™治疗眼后慢性疾病,包括Tethadur™。psivida已经对其主要产品medidur™进行了关键的iii期临床试验,用于治疗慢性后葡萄膜炎。Medidur使用与Psivida的铅许可产品Iluvien®相同的可注射、缓释微插件,用于治疗二甲醚,许可给欧盟的Alimera Sciences,Inc.,Iluvien在英国和德国上市,并在十七欧盟接受或正在等待营销授权,认为治疗慢性DME对现有疗法没有足够的反应。在美国,伊洛维恩已被批准用于治疗二甲醚患者,这些患者先前已完成一个疗程的类固醇治疗,但没有出现临床上显著的眼压升高。psivida的fda批准的retisert®是一种为治疗后葡萄膜炎提供长期、持续药物递送的植入物,由bausch&lomb incorporated授权并出售。psivida的临床前研究主要集中在眼部和全身生物制剂的输送以及干湿性年龄相关性黄斑变性、骨关节炎和青光眼的治疗。
公司:Psivida公司
糖尿病性黄斑水肿的治疗
伊洛维安(fluocinone acetonide)是一种玻璃体腔植入物,用于治疗糖尿病性黄斑水肿。
马萨诸塞州沃特敦讯(商业新闻)---在开发用于治疗眼疾的缓释药物递送产品方面处于领先地位的psivida公司今天宣布,美国食品和药物管理局(fda)已批准伊洛维安治疗糖尿病性黄斑水肿(dme)。它适用于以前接受过一个疗程皮质类固醇治疗且眼压(IOP)没有明显临床升高的患者。单次注射伊洛维恩微针可持续治疗二甲醚36个月。据估计,美国约有560000人在临床上有显著的DME,这是糖尿病患者最常见的视力丧失原因,也是发达国家中青年人致盲的主要原因。伊洛维恩预计将于2015年初在美国上市。
FDA批准伊洛维安后,Psivida有权从被许可方Alimera Sciences获得2500万美元的里程碑。普西维达还将有权获得伊鲁万在美国销售净利润的20%。
“FDA批准了我们的第三种经FDA批准的视网膜疾病产品——伊洛维恩,这为美国的二甲醚患者提供了一个重要的治疗选择,尽管其大部分二甲醚的抗血管内皮生长因子眼部注射频率高达每月一次,但并没有得到最佳的管理。伊洛维恩的临床试验表明,伊洛维恩实际上可以逆转许多二甲醚患者的视力下降。Iluvien对现有疗法的另一个优点是单次注射可以持续治疗三年,”Paul Ashton,Ph.D.,PSIVIDA总裁兼首席执行官说。
阿什顿博士补充道:“2500万美元的里程碑将有助于资助我们正在进行的产品开发计划,包括用于后葡萄膜炎的Medidur™和用于生物制剂持续交付的Tethadur™。”Psivida正在独立开发Medidur,一种与伊洛维恩相同设计、相同药物的可注射、缓释微植入物,用于治疗慢性后葡萄膜炎,作为美国第三大致盲原因,该公司计划在进行中的第三阶段临床试验的基础上,寻求fda对该产品的批准。本研究的注册预计在2015年第一季度末完成。
Iluvien已经在英国和德国商业化,并且已经收到或正在等待十七个欧盟国家的市场批准,用于治疗慢性DME患者对现有疗法的反应不足。阿什顿博士继续说:“我们非常高兴,FDA对伊洛维恩的批准并不像欧盟那样,仅限于慢性二甲醚患者、其他治疗失败的患者或白内障手术患者。”
伊洛维恩是一种可注射的微量插入物,通过连续36个月亚微克剂量的皮质激素氟辛醇酮乙酰奈德提供持续治疗。目前的护理治疗标准要求每月向眼睛注射抗血管内皮生长因子,研究表明,超过50%的患者没有得到最佳的治疗。fda的批准是基于临床试验数据,该数据显示,在24个月时,28.7%的患者在接受早期治疗糖尿病视网膜病变研究(etdrs)的15个字母或更多的眼图上,他们的最佳矫正视力比基线水平有改善。在试验结束后的36个月里,视力一直保持着这种改善。
关于伊洛维安
0.19mg的伊洛维恩(氟辛诺酮-丙酮胺玻璃体腔植入物)是美国批准的一种缓释玻璃体腔植入物,用于治疗先前接受过一个疗程皮质类固醇治疗且眼压没有明显升高的患者的二甲醚。每一个伊洛维恩植入物都被设计成释放亚微克水平的氟西诺酮丙酮胺(fac),一种持续36个月的皮质类固醇。
皮质类固醇在治疗眼病炎症方面有着有效的应用历史。使用25号针头的敷贴器将伊洛维恩注射到患者的眼睛后部,这样就可以实现伤口的自我封闭。在FAME™研究中,一项关于伊洛维恩的第3阶段临床研究中,最常见的药物不良反应包括白内障的发展和眼压升高。
伊鲁万重要安全信息
伊洛维安含有一种皮质类固醇,用于治疗二甲醚的患者,这些患者以前接受过一个疗程的皮质类固醇治疗,但眼压没有明显的临床升高。
玻璃体腔注射与眼内炎、眼部炎症、眼压升高和视网膜脱离有关。注射后应监测病人。
使用皮质类固醇可导致后囊下白内障、眼压升高、青光眼,并可增强细菌、真菌或病毒引起的继发性眼部感染。
如果晶状体后囊不完整,植入物可能会迁移到前房。在对照研究中,最常见的不良反应是白内障的发展和眼压的升高。
关于二甲醚
糖尿病性黄斑水肿是糖尿病性视网膜病变引起视力下降的主要原因,是一种影响黄斑的疾病,黄斑是视网膜中负责中央视力的部分。当糖尿病视网膜病变的血管渗漏引起黄斑肿胀时,病情发展为二甲醚。二甲醚的发作是无痛的,在出现中心视力模糊或急性视力丧失之前,患者可能无法察觉。这种模糊的严重程度可能从轻微到严重的视力丧失不等。威斯康星糖尿病视网膜病变的流行病学研究发现,在10年的时间里,大约19%的糖尿病患者被诊断为DME。所有患有1型或2型糖尿病的人都有患二甲醚的危险。随着糖尿病患者人数的增加,诊断为二甲醚的年发病率预计也会增加。
糖尿病持续时间是视网膜病变增加的最大危险因素,与二甲醚患病率增加有关。视网膜病变的出现与血管内皮生长因子(vegf)的上调有关,血管通透性增加导致液体渗漏。随着视网膜病变的恶化,多种细胞因子(炎症因子)发生上调。皮质类固醇对持续存在的二甲醚相关的多种细胞因子的下调具有广泛的作用。
关于psivida公司。
Psivida公司总部位于马萨诸塞州沃特敦,是开发治疗眼疾的缓释药物递送产品的领导者。Psivida目前专注于利用其核心技术系统Durasert™和Bioslicon™治疗眼后慢性疾病,包括Tethadur™。psivida已经对其主要产品medidur™进行了关键的iii期临床试验,用于治疗慢性后葡萄膜炎。Medidur使用与Psivida的铅许可产品Iluvien®相同的可注射、缓释微插件,用于治疗二甲醚,许可给欧盟的Alimera Sciences,Inc.,Iluvien在英国和德国上市,并在十七欧盟接受或正在等待营销授权,认为治疗慢性DME对现有疗法没有足够的反应。在美国,伊洛维恩已被批准用于治疗二甲醚患者,这些患者先前已完成一个疗程的类固醇治疗,但没有出现临床上显著的眼压升高。psivida的fda批准的retisert®是一种为治疗后葡萄膜炎提供长期、持续药物递送的植入物,由bausch&lomb incorporated授权并出售。psivida的临床前研究主要集中在眼部和全身生物制剂的输送以及干湿性年龄相关性黄斑变性、骨关节炎和青光眼的治疗。
Generic Name: fluocinolone acetonide
Dosage Form: implant
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Sep 1, 2019.
OverviewSide EffectsDosageProfessionalInteractionsPregnancyMoreILUVIEN® (fluocinolone acetonide intravitreal implant) 0.19 mg is indicated for the treatment of diabetic macular edema (DME) in patients who have been previously treated with a course of corticosteroids and did not have a clinically significant rise in intraocular pressure.
Iluvien Implant Dosage and AdministrationGeneral Dosing InformationFor ophthalmic intravitreal injection.
AdministrationThe intravitreal injection procedure should be carried out under aseptic conditions, which include use of sterile gloves, a sterile drape, a sterile caliper, and a sterile eyelid speculum (or equivalent). Adequate anesthesia and a broad-spectrum microbicide should be given prior to the injection.
The injection procedure for ILUVIEN is as follows:
The exterior of the tray should not be considered sterile. An assistant (non-sterile) should remove the tray from the carton and examine the tray and lid for damage. If damaged, do not use unit.Following the injection, patients should be monitored for elevation in intraocular pressure and for endophthalmitis. Monitoring may consist of a check for perfusion of the optic nerve head immediately after the injection, tonometry within 30 minutes following the injection, and biomicroscopy between two and seven days following the injection. Patients should be instructed to report without delay any symptoms suggestive of endophthalmitis.
Dosage Forms and StrengthsILUVIEN is a non-bioerodable intravitreal implant in a drug delivery system containing 0.19 mg fluocinolone acetonide, designed to release fluocinolone acetonide at an initial rate of 0.25 μg/day and lasting 36 months.
ContraindicationsOcular or Periocular InfectionsILUVIEN is contraindicated in patients with active or suspected ocular or periocular infections including most viral disease of the cornea and conjunctiva including active epithelial herpes simplex keratitis (dendritic keratitis), vaccinia, varicella, mycobacterial infections and fungal diseases.
GlaucomaILUVIEN is contraindicated in patients with glaucoma, who have cup to disc ratios of greater than 0.8.
HypersensitivityILUVIEN is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to any components of this product.
Warnings and PrecautionsIntravitreal Injection-related EffectsIntravitreal injections, including those with ILUVIEN, have been associated with endophthalmitis, eye inflammation, increased intraocular pressure, and retinal detachments. Patients should be monitored following the intravitreal injection [see Patient Counseling Information (17)].
Steroid-related Effects
Use of corticosteroids including ILUVIEN may produce posterior subcapsular cataracts, increased intraocular pressure and glaucoma.
Use of corticosteroids may enhance the establishment of secondary ocular infections due to bacteria, fungi, or viruses.
Corticosteroids are not recommended to be used in patients with a history of ocular herpes simplex because of the potential for reactivation of the viral infection.
Risk of Implant MigrationPatients in whom the posterior capsule of the lens is absent or has a tear are at risk of implant migration into the anterior chamber.
Adverse ReactionsClinical Studies ExperienceBecause clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Adverse reactions associated with ophthalmic steroids including ILUVIEN include cataract formation and subsequent cataract surgery, elevated intraocular pressure, which may be associated with optic nerve damage, visual acuity and field defects, secondary ocular infection from pathogens including herpes simplex, and perforation of the globe where there is thinning of the cornea or sclera.
ILUVIEN was studied in two multicenter, randomized, sham-controlled, masked trials in which patients with diabetic macular edema (DME) were treated with either ILUVIEN (n=375) or sham (n=185).
Table 1 summarizes safety data available when the last subject completed the last 36 month follow up visit for the two primary ILUVIEN trials. In these trials, subjects were eligible for retreatment no earlier than 12 months after study entry. Over the three year follow up period, approximately 75% of the ILUVIEN treated subjects received only one ILUVIEN implant.
The most common ocular (study eye) and non-ocular adverse reactions are shown in Tables 1 and 2:
| 1 Includes cataract, cataract nuclear, cataract subcapsular, cataract cortical and cataract diabetic in patients who were phakic at baseline. Among these patients, 80% of ILUVIEN subjects vs. 27% of sham-controlled subjects underwent cataract surgery. | ||||
| 2 235 of the 375 ILUVIEN subjects were phakic at baseline; 121 of 185 sham-controlled subjects were phakic at baseline. | ||||
| Adverse Reactions |
ILUVIEN (N=375) n (%) |
Sham (N=185) n (%) |
||
| Ocular | ||||
| Cataract1 | 192/2352 (82%) | 61/1212 (50%) | ||
| Myodesopsia | 80 (21%) | 17 (9%) | ||
| Eye pain | 57 (15%) | 25 (14%) | ||
| Conjunctival haemorrhage | 50 (13%) | 21 (11%) | ||
| Posterior capsule opacification | 35 (9%) | 6 (3%) | ||
| Eye irritation | 30 (8%) | 11 (6%) | ||
| Vitreous detachment | 26 (7%) | 12 (7%) | ||
| Conjunctivitis | 14 (4%) | 5 (3%) | ||
| Corneal oedema | 13 (4%) | 3 (2%) | ||
| Foreign body sensation in eyes | 12 (3%) | 4 (2%) | ||
| Eye pruritus | 10 (3%) | 3 (2%) | ||
| Ocular hyperaemia | 10 (3%) | 3 (2%) | ||
| Optic atrophy | 9 (2%) | 2 (1%) | ||
| Ocular discomfort | 8 (2%) | 1 (1%) | ||
| Photophobia | 7 (2%) | 2 (1%) | ||
| Retinal exudates | 7 (2%) | 0 (0%) | ||
| Anterior chamber cell | 6 (2%) | 1 (1%) | ||
| Eye discharge | 6 (2%) | 1 (1%) | ||
| Non-ocular | ||||
| Anemia | 40 (11%) | 10 (5%) | ||
| Headache | 33 (9%) | 11 (6%) | ||
| Renal Failure | 32 (9%) | 10 (5%) | ||
| Pneumonia | 28 (7%) | 8 (4%) | ||
Increased intraocular Pressure
| Event |
ILUVIEN (N=375) n (%) |
Sham (N=185) n (%) |
| IOP elevation ≥ 10 mmHg from Baseline | 127 (34%) | 18 (10%) |
| IOP elevation ≥ 30 mmHg | 75 (20%) | 8 (4%) |
| Any IOP-lowering medication | 144 (38%) | 26 (14%) |
| Any surgical intervention for elevated intraocular pressure | 18 (5%) | 1 (1%) |
Figure 1: Mean IOP during the study
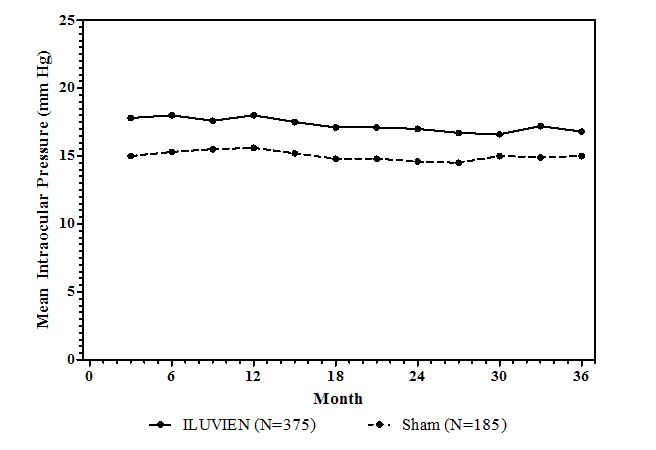
Cataracts and Cataract Surgery
At baseline, 235 of the 375 ILUVIEN subjects were phakic; 121 of 185 sham-controlled subjects were phakic. The incidence of cataract development in patients who had a phakic study eye was higher in the ILUVIEN group (82%) compared with Sham (50%). The median time of cataract being reported as an adverse event was approximately 12 months in the ILUVIEN group and 19 months in the Sham group. Among these patients, 80% of ILUVIEN subjects vs. 27% of sham-controlled subjects underwent cataract surgery, generally within the first 18 months (Median Month 15 for both ILUVIEN group and for Sham) of the studies.
The following reactions have been identified during post-marketing use of ILUVIEN in clinical practice. Because they are reported voluntarily estimates of frequency cannot be made. The reactions, which have been chosen for inclusion due to either their seriousness, frequency of reporting, possible causal connection to ILUVIEN, or a combination of these factors, include reports of drug administration error and reports of the drug being ineffective.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONSPregnancyPregnancy Category C
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of ILUVIEN in pregnant women. Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with fluocinolone acetonide. Corticosteroids have been shown to be teratogenic in laboratory animals when administered systemically at relatively low dosage levels. ILUVIEN should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Nursing MothersSystemically administered corticosteroids are present in human milk and could suppress growth and interfere with endogenous corticosteroid production. The systemic concentration of fluocinolone acetonide following intravitreal treatment with ILUVIEN is low [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. It is not known whether intravitreal treatment with ILUVIEN could result in sufficient systemic absorption to produce detectable quantities in human milk. Exercise caution when ILUVIEN is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric UseSafety and effectiveness of ILUVIEN in pediatric patients have not been established.
Geriatric UseNo overall differences in safety or effectiveness have been observed between elderly and younger patients.
Iluvien Implant DescriptionILUVIEN is a sterile non-bioerodable intravitreal implant containing 0.19 mg (190 mcg) fluocinolone acetonide in a 36-month sustained-release drug delivery system. ILUVIEN is designed to release fluocinolone acetonide at an initial rate of 0.25 µg/day. ILUVIEN is preloaded into a single-use applicator to facilitate injection of the implant directly into the vitreous. The drug substance is a synthetic corticosteroid, fluocinolone acetonide.
The chemical name for fluocinolone acetonide is (6α,11β, 16α)-6,9-difluoro-11,21-dihydroxy-16,17-[(1-methylethylidene)bis-(oxy)]-pregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione. Its chemical structure is:
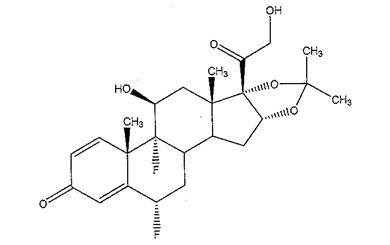
MW 452.50; molecular formula C24H30F206
Fluocinolone acetonide is a white or almost white, microcrystalline powder, practically insoluble in water, soluble in methanol, ethanol, chloroform and acetone, and sparingly soluble in ether.
Each ILUVIEN consists of a light brown 3.5mm x 0.37mm implant containing 0.19 mg of the active ingredient fluocinolone acetonide and the following inactive ingredients: polyimide tube, polyvinyl alcohol, silicone adhesive and water for injection.
Iluvien Implant - Clinical PharmacologyMechanism of ActionCorticosteroids inhibit inflammatory responses to a variety of inciting agents including multiple inflammatory cytokines. They inhibit edema, fibrin deposition, capillary dilation, leukocyte migration, capillary proliferation, fibroblast proliferation, deposition of collagen, and scar formation associated with inflammation.
Corticosteroids are thought to act by inhibition of phospholipase A2 via induction of inhibitory proteins collectively called lipocortins. It is postulated that these proteins control biosynthesis of potent mediators of inflammation such as prostaglandins and leukotrienes by inhibiting release of the common precursor, arachidonic acid. Arachidonic acid is released from membrane phospholipids by phospholipase A2.
PharmacokineticsIn a human pharmacokinetic study of ILUVIEN, fluocinolone acetonide concentrations in plasma were below the lower limit of quantitation of the assay (100 pg/mL) at all post-administration time points from Day 7 through Month 36 following intravitreal administration of a 0.2 mcg/day or 0.5 mcg/day fluocinolone acetonide insert.
Nonclinical ToxicologyCarcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of FertilityLong-term animal studies have not been conducted to determine the carcinogenic potential or the effect on fertility of ILUVIEN.
Fluocinolone acetonide was not genotoxic in vitro in the Ames test (S. typhimurium and E. coli) and the mouse lymphoma TK assay, or in vivo in the mouse bone marrow micronucleus assay.
Clinical StudiesThe efficacy of ILUVIEN was assessed in two three year, randomized (2:1, active: sham), multicenter, double-masked, parallel-groups studies that enrolled patients with diabetic macular edema (DME) that had previously been treated with laser photocoagulation.
The primary efficacy endpoint in both trials was the proportion of subjects in whom vision had improved by 15 letters or more from baseline after 24 months of follow-up.
| Study 1 | Study 2 | |||
|
ILUVIEN (N=190) |
Sham (N=95) |
ILUVIEN (N=186) |
Sham (N=90) |
|
|
Mean (SD) Median (Range) |
53 (13) 57 (19-75) |
55 (11) 58 (25-69) |
53 (12) 56 (20-70) |
55 (11) 58 (21-68) |
|
aStudy 1: ILUVIEN, N=190; Sham, N=95 bStudy 2: ILUVIEN, N=186; Sham, N=90 |
||||
|
Study |
Outcomes | ILUVIEN | Sham | Estimated Difference (95% CI) |
|
1a |
Gain of ≥15 letters in BCVA (n (%)) | 51 (27%) | 14 (15%) | 12.1% (2.6%, 21.6%) |
| Loss of ≥15 letters in BCVA (n (%)) | 26 (14%) | 5 (5%) | 8.4% (1.8%, 15.1%) | |
| Mean change from baseline in BCVA (SD) | 3.7 (18.7) | 3.2 (13.1) | 1.8 (-2.8, 6.3) | |
|
2b |
Gain of ≥15 letters in BCVA (n (%)) | 57 (31%) | 16 (18%) | 13.0% (2.7%, 23.4%) |
| Loss of ≥15 letters in BCVA (n (%)) | 22 (12%) | 9 (10%) | 1.8% (-5.9%, 9.6%) | |
| Mean change from baseline in BCVA (SD) | 5.2 (18.0) | 0.0 (15.6) | 6.1 (1.4, 10.8) | |
Visual acuity outcomes by lens status (Phakic or Pseudophakic) at different visits are presented in Figure 2 and Figure 3. The occurrence of cataracts impacted visual acuity during the study. Patients who were pseudophakic at baseline achieved greater mean BCVA change from baseline at the Month 24 study visit.
Figure 2: Proportion of subjects with >=15 Letters Improvement from Baseline BCVA in the Study Eye
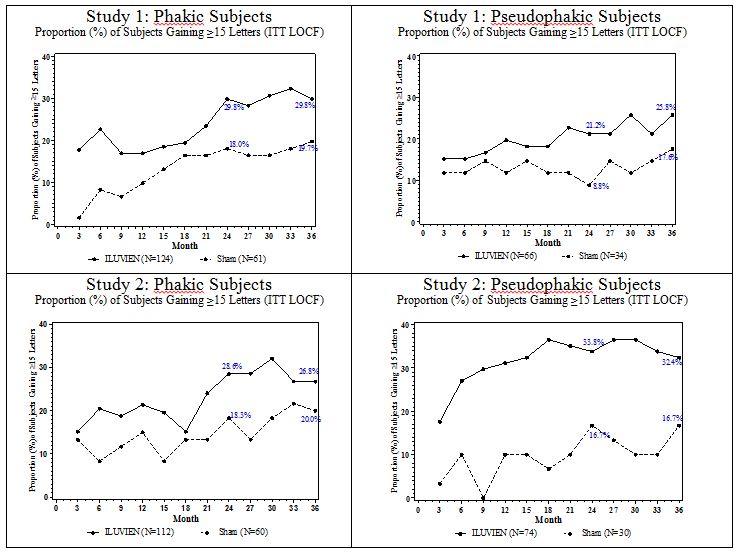
Figure 3: Mean BCVA Change from Baseline
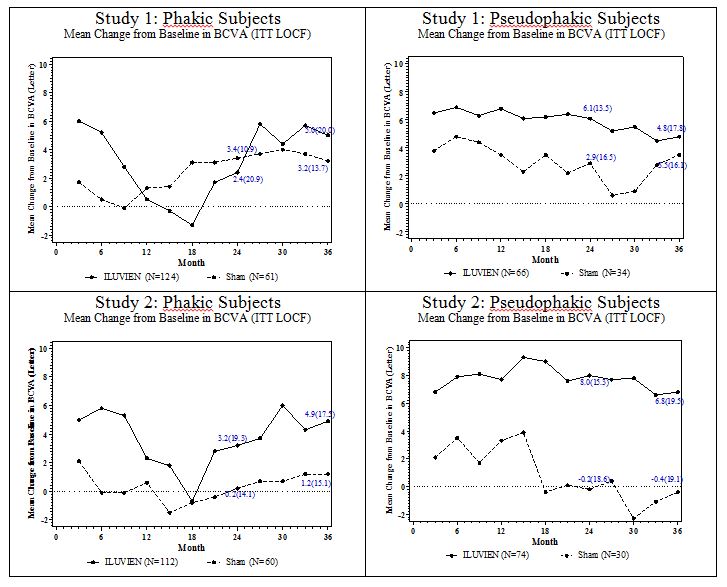
The BCVA outcomes for the Pseudophakic and Phakic subgroups from Studies 1 and 2 at Month 24 are presented in Table 5.
|
aPseudophakic : ILUVIEN, N=140; Sham, N=64 bPhakic: ILUVIEN, N=236; Sham, N=121 |
||||
| Lens Status | Outcomes | ILUVIEN | Sham | Estimated Difference (95% CI) |
|
aPseudophakic |
Gain of ≥15 letters in BCVA (n (%)) | 39 (28%) | 8 (13%) | 15.4% (4.4%, 26.3%) |
| Loss of ≥15 letters in BCVA (n (%)) | 7 (5%) | 7 (11%) | -5.9% (-14.4%, 2.5%) | |
|
Mean change from baseline in BCVA (SD) |
7.1 (14.5) | 1.5 (17.4) | 5.6 (0.7, 10.6) | |
|
bPhakic |
Gain of ≥15 letters in BCVA (n (%)) | 69 (29%) | 22 (18%) | 11.1% (2.1%, 20.1%) |
| Loss of ≥15 letters in BCVA (n (%)) | 41 (17%) | 7 (6%) | 11.6% (5.2%, 18%) | |
|
Mean change from baseline in BCVA (SD) |
2.8 (20.1) | 1.8 (12.6) | 1 (-2.5 ,4.4) | |
ILUVIEN® (fluocinolone acetonide intravitreal implant) 0.19 mg is supplied in a sterile single use preloaded applicator with a 25-gauge needle, packaged in a tray sealed with a lid inside a carton.
NDC 68611-190-02
Storage: Store at 15° - 30° C (59° - 86° F).
Patient Counseling Information
Steroid-related Effects
Advise patients that a cataract may occur after treatment with ILUVIEN. If this occurs, advise patients that their vision will decrease, and they will need an operation to remove the cataract and restore their vision.
Advise patients that they may develop increased intraocular pressure with ILUVIEN treatment, and the increased IOP may need to be managed with eye drops, or surgery.
Intravitreal Injection-related Effects
Advise patients that in the days following intravitreal injection of ILUVIEN, patients are at risk for potential complications including in particular, but not limited to, the development of endophthalmitis or elevated intraocular pressure.
When to Seek Physician Advice
Advise patients that if the eye becomes red, sensitive to light, painful, or develops a change in vision, they should seek immediate care from an ophthalmologist.
Driving and Using Machines
Inform patients that they may experience temporary visual blurring after receiving an intravitreal injection. Advise patients not to drive or use machines until this has been resolved.
Manufactured for:
Alimera Sciences, Inc.
6120 Windward Parkway
Alpharetta, GA 30005
Patented. See: www.alimerasciences.com
ALIMERA
SCIENCES
Package Label - Principal Display Panel – Carton

Package Label - Principal Display Panel – Lid

Package Label - Principal Display Panel – Inserter
|
ILUVIEN fluocinolone acetonide implant |
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Alimera Sciences, Inc. (135745292) |