

Balversa 厄达替尼




| 通用中文 | 厄达替尼 | 通用外文 | Erdafitinib |
| 品牌中文 | 品牌外文 | Balversa | |
| 其他名称 | 靶点FGFR | ||
| 公司 | 杨森(Janssen-Cilag) | 产地 | 美国(USA) |
| 含量 | 4mg | 包装 | 56片/盒 |
| 剂型给药 | 片剂 口服 | 储存 | 室温 |
| 适用范围 | 膀胱癌 | ||
| 通用中文 | 厄达替尼 |
| 通用外文 | Erdafitinib |
| 品牌中文 | |
| 品牌外文 | Balversa |
| 其他名称 | 靶点FGFR |
| 公司 | 杨森(Janssen-Cilag) |
| 产地 | 美国(USA) |
| 含量 | 4mg |
| 包装 | 56片/盒 |
| 剂型给药 | 片剂 口服 |
| 储存 | 室温 |
| 适用范围 | 膀胱癌 |
仅供参考
BALVERSA™(erdafitinib)获得美国FDA批准用于治疗局部晚期或转移性尿路上皮癌患者的某些FGFR遗传改变.
•BALVERSA是第一个获得美国FDA批准的FGFR激酶抑制剂.
•同时批准同伴诊断,旨在确定最有可能从BALVERSA中受益的患者子集,提供个性化治疗方法
宾夕法尼亚州Horsham,4月12日 - 强生公司的Janssen制药公司今天宣布,BALVERSA™(erdafitinib)获得美国食品和药物管理局(FDA)的加速批准,用于治疗局部晚期或转移性尿路上皮癌的成人( mUC)具有易感成纤维细胞生长因子受体(FGFR)3或FGFR2基因改变,并且在至少一行之前的含铂化疗期间或之后进展,包括在新辅助或辅助含铂化疗的12个月内[1]。 ] BALVERSA是FDA批准的第一种FGFR激酶抑制剂。此指示的持续批准可能取决于确认试验中的临床获益的验证和描述.1今天的批准遵循2018年3月的FDA突破治疗指定和2018年9月提交的新药申请的优先审查指定。
“我的职业生涯一直专注于转移性尿路上皮癌患者的护理,并了解对这种疾病的新疗法的必要性,”Arlene O. Siefker-Radtke医学博士,德克萨斯大学医学院泌尿生殖医学肿瘤学教授说。安德森癌症中心和首席研究调查员。 “对于这一小部分尿路上皮癌患者来说,BALVERSA是一种重要的新疗法,到目前为止,他们的治疗选择有限。”
BALVERSA是一种每日一次的口服FGFR激酶抑制剂,根据第二期临床试验(BLC2001,NCT02365597)的结果获得加速批准,该试验是一项多中心,开放标签,单臂研究,共有87例疾病进展的患者或至少一次在先化疗后至少有一种以下遗传改变:FGFR3基因突变(R248C,S249C,G370C,Y373C)或FGFR基因融合(FGFR3-TACC3,FGFR3-BAIAP2L1,FGFR2-BICC1,FGFR2- CASP7),由在中心实验室进行的临床试验测定确定.1结果显示盲法独立审查委员会(BIRC)[95%CI(22.4,42.0)]评估的客观反应率(ORR)为32.2%。 1应答者包括之前未对抗PD-L1 / PD-1治疗有反应的患者.1在试验中,ORR定义为可测量病变达到完全缓解(CR)[2.3%]或部分缓解的患者百分比(PR)[29.9%] 1使用Res进行治疗实体肿瘤评估标准1.1版(RECIST v1.1)标准,一种衡量患者对治疗的反应程度的标准方法,根据每位研究者评估肿瘤是否缩小,保持不变或变大。[2]结果用BALVERSA治疗的患者的中位反应持续时间(DoR)为5.4个月[95%CI(4.2,6.9)]。在FGFR2融合患者人群中,BALVERSA没有确诊反应(n = 6).1来自BLC2001研究的数据在美国临床肿瘤学会(ASCO)2018年会(摘要#4503)中呈现,并被认为是“最佳ASCO”选择。
警告和预防措施包括眼部疾病,高磷血症和胚胎 - 胎儿毒性.1最常见的不良反应(ARs)包括实验室异常> 20%,磷酸盐增加(76%),口腔炎(56%),疲劳(54%),肌酐增加(52%),腹泻(47%),口干(45%),甲剥离(41%),丙氨酸氨基转移酶增加(41%),碱性磷酸酶增加(41%),钠减少(40%),食欲下降(38%),白蛋白减少(37%),味觉异常(37%),血红蛋白减少(35%),皮肤干燥(34%),天冬氨酸氨基转移酶增加(30%),镁减少(30%),干眼症( 28%),脱发(26%),手掌 - 足底红斑感觉综合征(26%),便秘(28%),磷酸盐减少(24%),腹痛(23%),钙增加(22%),恶心(21%) %)和肌肉骨骼疼痛(20%)。最常见的3级或更高AR(> 1%)是口腔炎(9%),指甲营养不良*,手掌 - 足底红斑感觉综合征(6%),甲沟炎(3%),指甲紊乱*,角膜炎^,甲剥离(10%) %*)和高磷血症。 (*包括在甲状腺溶解中。^包括在干眼内。)1
FDA同时批准了与BALVERSA一起使用的伴随诊断,即QIAGENtherascreen®FGFRRGQ逆转录(RT) - 聚合酶链反应(PCR)试剂盒,这是第一个被批准用于检测FGFR改变的基于PCR的伴随诊断。 therascreen®FGFR测试检测mUC患者肿瘤组织中FGFR改变的存在.1如果检测到一种或多种遗传改变或融合,患者可能是BALVERSA治疗的候选者。有关检测尿路上皮癌中FGFR基因改变的FDA认可检测的信息,请访问:http://www.fda.gov/CompanionDiagnostics。
Janssen通过单一来源的专业药房提供商US Bioservices提供BALVERSA和相关的患者服务。该模型是Janssen不断致力于为医疗保健专业人员和患者提供高质量产品,服务,访问和支持的一部分。
“我们认识到在诊断患有这种尿路上皮癌的男性和女性的治疗中仍存在显着的未满足需求,我们已经与FDA密切协商,迅速为患者开发BALVERSA,”医学博士Peter Lebowitz博士说。 D.,全球治疗区负责人,肿瘤学,Janssen Research&Development,LLC。 “我们期待BALVERSA的持续发展,以了解这一重要的新疗法如何进一步为转移性尿路上皮癌患者提供护理及其在其他可能在未来出现FGFR改变的癌症中的研究用途。”
“FDA批准BALVERSA代表了我们致力于为破坏性疾病提供急需的治疗方法,包括缺乏治疗选择的转移性尿路上皮癌,”Janssen Research&Global全球负责人Mathai Mammen医学博士说。 Development,LLC。 “我们也很高兴看到FDA同时批准BALVERSA的伴随诊断,这将为医疗专业人员提供更加个性化的治疗方法,以治疗他们的病人。”
完整的处方信息将在www.BALVERSA.com上提供。
关于尿路上皮癌
尿路上皮癌,也称为移行细胞癌,起始于膀胱的最内层。[3]它是最常见和最常见的膀胱癌形式,占所有膀胱癌的90%以上。[4]大约五分之一的mUC患者有FGFR基因改变[5],[6] FGFRs是受体酪氨酸激酶家族,可以通过多种肿瘤类型的遗传改变激活,这些改变可能导致肿瘤增加细胞生长和存活。[7] BALVERSA专门用于治疗患有FGFR3或FGFR2遗传改变的局部mUC的患者。在美国,估计多达3,000名尿路上皮癌患者将每年检测FGFR阳性.5,6,[8],[9] FGFR基因改变可通过FDA批准的伴随诊断检测。目前已扩散到身体远端部位的IV期转移性膀胱癌患者的5年生存率为5%[10]。
关于BALVERSATM(erdafitinib)
BALVERSA(erdafitinib)是一种每日一次的口服成纤维细胞生长因子受体(FGFR)激酶抑制剂,用于治疗患有局部晚期或转移性尿路上皮癌(mUC)的成人,其具有易感FGFR3或FGFR2基因改变并且在遵循至少一行先前的含铂化疗,包括在新辅助或辅助含铂化疗的12个月内.1该指征在肿瘤应答率的加速批准下批准。对该指征的持续批准可能取决于确认试验中的临床获益的验证和描述
关键的多中心,开放标签的2期BLC2001(NCT02365597)临床试验评估了BALVERSA治疗肿瘤具有某些FGFR改变的mUC成人的有效性和安全性。 2008年,Janssen与Astex Pharmaceuticals签订了独家全球许可和合作协议,以开发和商业化BALVERSA。
迹象
BALVERSA是一种激酶抑制剂,适用于治疗局部晚期或转移性尿路上皮癌的成人患者
•易感FGFR3或FGFR2基因改变和
•在至少一行之前的含铂化疗期间或之后进行,包括在新辅助或辅助含铂化疗的12个月内。
根据FDA批准的BALVERSA伴随诊断选择治疗患者。
该指征基于肿瘤应答率在加速批准下被批准。持续批准该适应症可能取决于确认试验中的临床益处的验证和描述。
BALVERSATM(erdafitinib)重要安全信息
眼部疾病 - BALVERSA可引起眼部疾病,包括中心性浆液性视网膜病变/视网膜色素上皮脱离(CSR / RPED),导致视野缺损。
用BALVERSA治疗的患者中有25%报告了CSR / RPED,首次发病的中位时间为50天。 3%的患者报告了3级CSR / RPED,涉及中心视野。 CSR / RPED在13%的患者中得到了解决,在研究截止时,13%的患者正在进行CSR / RPED治疗。 CSR / RPED分别导致9%和14%的剂量中断和减少,3%的患者停用BALVERSA。在使用BALVERSA治疗期间,28%的患者出现干眼症状,6%的患者为3级。所有患者均应根据需要接受眼部缓解剂的干眼预防。
在治疗的前4个月和之后每3个月进行一次月度眼科检查,并在任何时候紧急进行视觉症状检查。眼科检查应包括视力评估,裂隙灯检查,眼底镜检查和光学相干断层扫描。在CSR发生时扣留BALVERSA,如果在4周内未解决或严重程度为4级,则永久停止。对于眼部不良反应,请遵循剂量调整指南[见剂量和给药方法(2.3)]。
高磷血症磷酸盐水平升高是BALVERSA的药效学作用[见药效学(12.2)]。据报道,76%的BALVERSA患者出现高磷血症是不良反应。在开始BALVERSA后,高磷血症的任何等级事件的中位起始时间为20天(范围:8-116)。 32%的患者在治疗期间接受了磷酸盐结合剂..
使用BALVERSA Monitor监测高磷血症,并在需要时遵循剂量调整指南[见剂量和给药方法2.2,2.3]。
胚胎 - 胎儿毒性 - 根据动物生殖研究中的作用机制和发现,BALVERSA在给孕妇服用时会造成胎儿伤害。在大鼠胚胎 - 胎儿毒性研究中,erdafitinib在所研究的所有剂量下的暴露均低于人体暴露时具有胚胎毒性和致畸性。建议孕妇对胎儿有潜在风险。建议具有生殖潜力的女性患者在治疗前和治疗期间以及最后一次给药后一个月内使用有效的避孕措施。建议具有生殖潜力的女性伴侣的男性患者在使用BALVERSA治疗期间和最后一次给药后一个月内使用有效避孕[见特殊人群使用(8.1,8.3)和临床药理学(12.1)]。
最常见的不良反应包括:实验室异常> 20%:磷酸盐增加(76%),口腔炎(56%),疲劳(54%),肌酐增加(52%),腹泻(47%),口干(45%) ,onycholysis(41%),丙氨酸氨基转移酶增加(41%),碱性磷酸酶增加(41%),钠减少(40%),食欲下降(38%),白蛋白减少(37%),味觉障碍(37%),血红蛋白减少(35%),皮肤干燥(34%),天冬氨酸氨基转移酶增加(30%),镁减少(30%),干眼症(28%),脱发(26%),手掌 - 足底红斑感觉综合征(26%) ),便秘(28%),磷酸盐减少(24%),腹痛(23%),钙增加(22%),恶心(21%)和肌肉骨骼疼痛(20%)。最常见的3级或更高AR(> 1%)是口腔炎(9%),指甲营养不良*,手掌 - 足底红斑感觉综合征(6%),甲沟炎(3%),指甲紊乱*,角膜炎^,甲剥离(10%) %*)和高磷血症。
*包括在甲剥离中。 ^包括在干眼内。
1%的患者对致命结果的不良反应是急性心肌梗死。
41%的患者出现严重不良反应,包括眼部疾病(10%)。
13%的患者因不良反应而永久停药。永久停药的最常见原因包括眼部疾病(6%)。
68%的患者出现剂量中断。需要中断剂量的最常见不良反应包括高磷血症(24%),口腔炎(17%),眼部疾病(17%)和手掌 - 足底红斑麻醉综合征(8%)。
53%的患者出现剂量减少。剂量减少最常见的不良反应包括眼部疾病(23%),口腔炎(15%),高磷血症(7%),手掌 - 足底红斑麻痹综合征(7%),甲沟炎(7%)和指甲营养不良(6%) 。
药物相互作用•强CYP2C9或CYP3A4抑制剂 - 考虑替代药物或密切监测不良反应。 (7.1)
•强CYP2C9或CYP3A4诱导剂:避免与BALVERSA同时使用。 (7.1)
•中度CYP2C9或CYP3A4诱导剂:将BALVERSA剂量增加至9 mg。 (7.1)
•血清磷酸盐水平改变剂:避免同时使用可在初始剂量调整期之前改变血清磷酸盐水平的药剂。 (2.3,7.1)
•CYP3A4底物:避免同时使用敏感的CYP3A4底物,治疗指数较窄。 (7.2)
•OCT2底物:考虑替代药物或考虑基于耐受性减少OCT2底物的剂量。 (7.2)
•P-gp底物:在给予治疗指数窄的P-gp底物之前或之后至少6小时分开BALVERSA给药,(7.2)
仅供参考
BALVERSA™(erdafitinib)获得美国FDA批准用于治疗局部晚期或转移性尿路上皮癌患者的某些FGFR遗传改变.
•BALVERSA是第一个获得美国FDA批准的FGFR激酶抑制剂.
•同时批准同伴诊断,旨在确定最有可能从BALVERSA中受益的患者子集,提供个性化治疗方法
宾夕法尼亚州Horsham,4月12日 - 强生公司的Janssen制药公司今天宣布,BALVERSA™(erdafitinib)获得美国食品和药物管理局(FDA)的加速批准,用于治疗局部晚期或转移性尿路上皮癌的成人( mUC)具有易感成纤维细胞生长因子受体(FGFR)3或FGFR2基因改变,并且在至少一行之前的含铂化疗期间或之后进展,包括在新辅助或辅助含铂化疗的12个月内[1]。 ] BALVERSA是FDA批准的第一种FGFR激酶抑制剂。此指示的持续批准可能取决于确认试验中的临床获益的验证和描述.1今天的批准遵循2018年3月的FDA突破治疗指定和2018年9月提交的新药申请的优先审查指定。
“我的职业生涯一直专注于转移性尿路上皮癌患者的护理,并了解对这种疾病的新疗法的必要性,”Arlene O. Siefker-Radtke医学博士,德克萨斯大学医学院泌尿生殖医学肿瘤学教授说。安德森癌症中心和首席研究调查员。 “对于这一小部分尿路上皮癌患者来说,BALVERSA是一种重要的新疗法,到目前为止,他们的治疗选择有限。”
BALVERSA是一种每日一次的口服FGFR激酶抑制剂,根据第二期临床试验(BLC2001,NCT02365597)的结果获得加速批准,该试验是一项多中心,开放标签,单臂研究,共有87例疾病进展的患者或至少一次在先化疗后至少有一种以下遗传改变:FGFR3基因突变(R248C,S249C,G370C,Y373C)或FGFR基因融合(FGFR3-TACC3,FGFR3-BAIAP2L1,FGFR2-BICC1,FGFR2- CASP7),由在中心实验室进行的临床试验测定确定.1结果显示盲法独立审查委员会(BIRC)[95%CI(22.4,42.0)]评估的客观反应率(ORR)为32.2%。 1应答者包括之前未对抗PD-L1 / PD-1治疗有反应的患者.1在试验中,ORR定义为可测量病变达到完全缓解(CR)[2.3%]或部分缓解的患者百分比(PR)[29.9%] 1使用Res进行治疗实体肿瘤评估标准1.1版(RECIST v1.1)标准,一种衡量患者对治疗的反应程度的标准方法,根据每位研究者评估肿瘤是否缩小,保持不变或变大。[2]结果用BALVERSA治疗的患者的中位反应持续时间(DoR)为5.4个月[95%CI(4.2,6.9)]。在FGFR2融合患者人群中,BALVERSA没有确诊反应(n = 6).1来自BLC2001研究的数据在美国临床肿瘤学会(ASCO)2018年会(摘要#4503)中呈现,并被认为是“最佳ASCO”选择。
警告和预防措施包括眼部疾病,高磷血症和胚胎 - 胎儿毒性.1最常见的不良反应(ARs)包括实验室异常> 20%,磷酸盐增加(76%),口腔炎(56%),疲劳(54%),肌酐增加(52%),腹泻(47%),口干(45%),甲剥离(41%),丙氨酸氨基转移酶增加(41%),碱性磷酸酶增加(41%),钠减少(40%),食欲下降(38%),白蛋白减少(37%),味觉异常(37%),血红蛋白减少(35%),皮肤干燥(34%),天冬氨酸氨基转移酶增加(30%),镁减少(30%),干眼症( 28%),脱发(26%),手掌 - 足底红斑感觉综合征(26%),便秘(28%),磷酸盐减少(24%),腹痛(23%),钙增加(22%),恶心(21%) %)和肌肉骨骼疼痛(20%)。最常见的3级或更高AR(> 1%)是口腔炎(9%),指甲营养不良*,手掌 - 足底红斑感觉综合征(6%),甲沟炎(3%),指甲紊乱*,角膜炎^,甲剥离(10%) %*)和高磷血症。 (*包括在甲状腺溶解中。^包括在干眼内。)1
FDA同时批准了与BALVERSA一起使用的伴随诊断,即QIAGENtherascreen®FGFRRGQ逆转录(RT) - 聚合酶链反应(PCR)试剂盒,这是第一个被批准用于检测FGFR改变的基于PCR的伴随诊断。 therascreen®FGFR测试检测mUC患者肿瘤组织中FGFR改变的存在.1如果检测到一种或多种遗传改变或融合,患者可能是BALVERSA治疗的候选者。有关检测尿路上皮癌中FGFR基因改变的FDA认可检测的信息,请访问:http://www.fda.gov/CompanionDiagnostics。
Janssen通过单一来源的专业药房提供商US Bioservices提供BALVERSA和相关的患者服务。该模型是Janssen不断致力于为医疗保健专业人员和患者提供高质量产品,服务,访问和支持的一部分。
“我们认识到在诊断患有这种尿路上皮癌的男性和女性的治疗中仍存在显着的未满足需求,我们已经与FDA密切协商,迅速为患者开发BALVERSA,”医学博士Peter Lebowitz博士说。 D.,全球治疗区负责人,肿瘤学,Janssen Research&Development,LLC。 “我们期待BALVERSA的持续发展,以了解这一重要的新疗法如何进一步为转移性尿路上皮癌患者提供护理及其在其他可能在未来出现FGFR改变的癌症中的研究用途。”
“FDA批准BALVERSA代表了我们致力于为破坏性疾病提供急需的治疗方法,包括缺乏治疗选择的转移性尿路上皮癌,”Janssen Research&Global全球负责人Mathai Mammen医学博士说。 Development,LLC。 “我们也很高兴看到FDA同时批准BALVERSA的伴随诊断,这将为医疗专业人员提供更加个性化的治疗方法,以治疗他们的病人。”
完整的处方信息将在www.BALVERSA.com上提供。
关于尿路上皮癌
尿路上皮癌,也称为移行细胞癌,起始于膀胱的最内层。[3]它是最常见和最常见的膀胱癌形式,占所有膀胱癌的90%以上。[4]大约五分之一的mUC患者有FGFR基因改变[5],[6] FGFRs是受体酪氨酸激酶家族,可以通过多种肿瘤类型的遗传改变激活,这些改变可能导致肿瘤增加细胞生长和存活。[7] BALVERSA专门用于治疗患有FGFR3或FGFR2遗传改变的局部mUC的患者。在美国,估计多达3,000名尿路上皮癌患者将每年检测FGFR阳性.5,6,[8],[9] FGFR基因改变可通过FDA批准的伴随诊断检测。目前已扩散到身体远端部位的IV期转移性膀胱癌患者的5年生存率为5%[10]。
关于BALVERSATM(erdafitinib)
BALVERSA(erdafitinib)是一种每日一次的口服成纤维细胞生长因子受体(FGFR)激酶抑制剂,用于治疗患有局部晚期或转移性尿路上皮癌(mUC)的成人,其具有易感FGFR3或FGFR2基因改变并且在遵循至少一行先前的含铂化疗,包括在新辅助或辅助含铂化疗的12个月内.1该指征在肿瘤应答率的加速批准下批准。对该指征的持续批准可能取决于确认试验中的临床获益的验证和描述
关键的多中心,开放标签的2期BLC2001(NCT02365597)临床试验评估了BALVERSA治疗肿瘤具有某些FGFR改变的mUC成人的有效性和安全性。 2008年,Janssen与Astex Pharmaceuticals签订了独家全球许可和合作协议,以开发和商业化BALVERSA。
迹象
BALVERSA是一种激酶抑制剂,适用于治疗局部晚期或转移性尿路上皮癌的成人患者
•易感FGFR3或FGFR2基因改变和
•在至少一行之前的含铂化疗期间或之后进行,包括在新辅助或辅助含铂化疗的12个月内。
根据FDA批准的BALVERSA伴随诊断选择治疗患者。
该指征基于肿瘤应答率在加速批准下被批准。持续批准该适应症可能取决于确认试验中的临床益处的验证和描述。
BALVERSATM(erdafitinib)重要安全信息
眼部疾病 - BALVERSA可引起眼部疾病,包括中心性浆液性视网膜病变/视网膜色素上皮脱离(CSR / RPED),导致视野缺损。
用BALVERSA治疗的患者中有25%报告了CSR / RPED,首次发病的中位时间为50天。 3%的患者报告了3级CSR / RPED,涉及中心视野。 CSR / RPED在13%的患者中得到了解决,在研究截止时,13%的患者正在进行CSR / RPED治疗。 CSR / RPED分别导致9%和14%的剂量中断和减少,3%的患者停用BALVERSA。在使用BALVERSA治疗期间,28%的患者出现干眼症状,6%的患者为3级。所有患者均应根据需要接受眼部缓解剂的干眼预防。
在治疗的前4个月和之后每3个月进行一次月度眼科检查,并在任何时候紧急进行视觉症状检查。眼科检查应包括视力评估,裂隙灯检查,眼底镜检查和光学相干断层扫描。在CSR发生时扣留BALVERSA,如果在4周内未解决或严重程度为4级,则永久停止。对于眼部不良反应,请遵循剂量调整指南[见剂量和给药方法(2.3)]。
高磷血症磷酸盐水平升高是BALVERSA的药效学作用[见药效学(12.2)]。据报道,76%的BALVERSA患者出现高磷血症是不良反应。在开始BALVERSA后,高磷血症的任何等级事件的中位起始时间为20天(范围:8-116)。 32%的患者在治疗期间接受了磷酸盐结合剂..
使用BALVERSA Monitor监测高磷血症,并在需要时遵循剂量调整指南[见剂量和给药方法2.2,2.3]。
胚胎 - 胎儿毒性 - 根据动物生殖研究中的作用机制和发现,BALVERSA在给孕妇服用时会造成胎儿伤害。在大鼠胚胎 - 胎儿毒性研究中,erdafitinib在所研究的所有剂量下的暴露均低于人体暴露时具有胚胎毒性和致畸性。建议孕妇对胎儿有潜在风险。建议具有生殖潜力的女性患者在治疗前和治疗期间以及最后一次给药后一个月内使用有效的避孕措施。建议具有生殖潜力的女性伴侣的男性患者在使用BALVERSA治疗期间和最后一次给药后一个月内使用有效避孕[见特殊人群使用(8.1,8.3)和临床药理学(12.1)]。
最常见的不良反应包括:实验室异常> 20%:磷酸盐增加(76%),口腔炎(56%),疲劳(54%),肌酐增加(52%),腹泻(47%),口干(45%) ,onycholysis(41%),丙氨酸氨基转移酶增加(41%),碱性磷酸酶增加(41%),钠减少(40%),食欲下降(38%),白蛋白减少(37%),味觉障碍(37%),血红蛋白减少(35%),皮肤干燥(34%),天冬氨酸氨基转移酶增加(30%),镁减少(30%),干眼症(28%),脱发(26%),手掌 - 足底红斑感觉综合征(26%) ),便秘(28%),磷酸盐减少(24%),腹痛(23%),钙增加(22%),恶心(21%)和肌肉骨骼疼痛(20%)。最常见的3级或更高AR(> 1%)是口腔炎(9%),指甲营养不良*,手掌 - 足底红斑感觉综合征(6%),甲沟炎(3%),指甲紊乱*,角膜炎^,甲剥离(10%) %*)和高磷血症。
*包括在甲剥离中。 ^包括在干眼内。
1%的患者对致命结果的不良反应是急性心肌梗死。
41%的患者出现严重不良反应,包括眼部疾病(10%)。
13%的患者因不良反应而永久停药。永久停药的最常见原因包括眼部疾病(6%)。
68%的患者出现剂量中断。需要中断剂量的最常见不良反应包括高磷血症(24%),口腔炎(17%),眼部疾病(17%)和手掌 - 足底红斑麻醉综合征(8%)。
53%的患者出现剂量减少。剂量减少最常见的不良反应包括眼部疾病(23%),口腔炎(15%),高磷血症(7%),手掌 - 足底红斑麻痹综合征(7%),甲沟炎(7%)和指甲营养不良(6%) 。
药物相互作用•强CYP2C9或CYP3A4抑制剂 - 考虑替代药物或密切监测不良反应。 (7.1)
•强CYP2C9或CYP3A4诱导剂:避免与BALVERSA同时使用。 (7.1)
•中度CYP2C9或CYP3A4诱导剂:将BALVERSA剂量增加至9 mg。 (7.1)
•血清磷酸盐水平改变剂:避免同时使用可在初始剂量调整期之前改变血清磷酸盐水平的药剂。 (2.3,7.1)
•CYP3A4底物:避免同时使用敏感的CYP3A4底物,治疗指数较窄。 (7.2)
•OCT2底物:考虑替代药物或考虑基于耐受性减少OCT2底物的剂量。 (7.2)
•P-gp底物:在给予治疗指数窄的P-gp底物之前或之后至少6小时分开BALVERSA给药,(7.2)
Indications and Usage for Balversa
Balversa is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma (mUC), that has:
susceptible FGFR3 or FGFR2 genetic alterations, andprogressed during or following at least one line of prior platinum-containing chemotherapy, including within 12 months of neoadjuvant or adjuvant platinum-containing chemotherapy.Select patients for therapy based on an FDA-approved companion diagnostic for Balversa [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) and Clinical Studies (14)].
This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on tumor response rate. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in confirmatory trials [see Clinical Studies (14)].
Balversa Dosage and AdministrationPatient SelectionSelect patients for the treatment of locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma with Balversa based on the presence of susceptible FGFR genetic alterations in tumor specimens as detected by an FDA-approved companion diagnostic [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
Information on FDA-approved tests for the detection of FGFR genetic alterations in urothelial cancer is available at: http://www.fda.gov/CompanionDiagnostics.
Recommended Dosage and ScheduleThe recommended starting dose of Balversa is 8 mg (two 4 mg tablets) orally once daily, with a dose increase to 9 mg (three 3 mg tablets) once daily based on serum phosphate (PO4) levels and tolerability at 14 to 21 days [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
Swallow tablets whole with or without food. If vomiting occurs any time after taking Balversa, the next dose should be taken the next day. Treatment should continue until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity occurs.
If a dose of Balversa is missed, it can be taken as soon as possible on the same day. Resume the regular daily dose schedule for Balversa the next day. Extra tablets should not be taken to make up for the missed dose.
Dose Increase based on Serum Phosphate Levels
Assess serum phosphate levels 14 to 21 days after initiating treatment. Increase the dose of Balversa to 9 mg once daily if serum phosphate level is < 5.5 mg/dL and there are no ocular disorders or Grade 2 or greater adverse reactions. Monitor phosphate levels monthly for hyperphosphatemia [see Pharmacodynamics (12.2)].
Dose Modifications for Adverse ReactionsThe recommended dose modifications for adverse reactions are listed in Table 1.
| Dose | 1st dose reduction | 2nd dose reduction | 3rd dose reduction | 4th dose reduction | 5th dose reduction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
9 mg ⭢ (three 3 mg tablets) |
8 mg (two 4 mg tablets) |
6 mg (two 3 mg tablets) |
5 mg (one 5 mg tablet) |
4 mg (one 4 mg tablet) |
Stop |
|
8 mg ⭢ (two 4 mg tablets) |
6 mg (two 3 mg tablets) |
5 mg (one 5 mg tablet) |
4 mg (one 4 mg tablet) |
Stop | |
Table 2 summarizes recommendations for dose interruption, reduction, or discontinuation of Balversa in the management of specific adverse reactions.
| Adverse Reaction | Balversa Dose Modification |
|---|---|
| *Dose adjustment graded using the National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (NCI CTCAEv4.03). | |
| Hyperphosphatemia | |
| In all patients, restrict phosphate intake to 600–800 mg daily. If serum phosphate is above 7.0 mg/dL, consider adding an oral phosphate binder until serum phosphate level returns to < 5.5 mg/dL. | |
| 5.6–6.9 mg/dL (1.8–2.3 mmol/L) | Continue Balversa at current dose. |
| 7.0–9.0 mg/dL (2.3–2.9 mmol/L) | Withhold Balversa with weekly reassessments until level returns to < 5.5 mg/dL (or baseline). Then restart Balversa at the same dose level. A dose reduction may be implemented for hyperphosphatemia lasting > 1 week. |
| > 9.0 mg/dL (> 2.9 mmol/L) | Withhold Balversa with weekly reassessments until level returns to < 5.5 mg/dL (or baseline). Then may restart Balversa at 1 dose level lower. |
| > 10.0 mg/dL (> 3.2 mmol/L) or significant alteration in baseline renal function or Grade 3 hypercalcemia | Withhold Balversa with weekly reassessments until level returns to < 5.5 mg/dL (or baseline). Then may restart Balversa at 2 dose levels lower. |
| Central Serous Retinopathy/Retinal Pigment Epithelial Detachment (CSR/RPED) | |
| Grade 1: Asymptomatic; clinical or diagnostic observations only | Withhold until resolution. If resolves within 4 weeks, resume at the next lower dose level. Then, if no recurrence for a month, consider re-escalation. If stable for 2 consecutive eye exams but not resolved, resume at the next lower dose level. |
| Grade 2: Visual acuity 20/40 or better or ≤ 3 lines of decreased vision from baseline | Withhold until resolution. If resolves within 4 weeks, may resume at the next lower dose level. |
| Grade 3: Visual acuity worse than 20/40 or > 3 lines of decreased vision from baseline | Withhold until resolution. If resolves within 4 weeks, may resume two dose levels lower. If recurs, consider permanent discontinuation. |
| Grade 4: Visual acuity 20/200 or worse in affected eye | Permanently discontinue. |
| Other Adverse Reactions * | |
| Grade 3 | Withhold Balversa until resolves to Grade 1 or baseline, then may resume dose level lower. |
| Grade 4 | Permanently discontinue. |
Tablets:
3 mg: Yellow, round biconvex, film-coated, debossed with "3" on one side; and "EF" on the other side.4 mg: Orange, round biconvex, film-coated, debossed with "4" on one side; and "EF" on the other side.5 mg: Brown, round biconvex, film-coated, debossed with "5" on one side; and "EF" on the other side.ContraindicationsNone.
Warnings and PrecautionsOcular DisordersBalversa can cause ocular disorders, including central serous retinopathy/retinal pigment epithelial detachment (CSR/RPED) resulting in visual field defect.
CSR/RPED was reported in 25% of patients treated with Balversa, with a median time to first onset of 50 days. Grade 3 CSR/RPED, involving central field of vision, was reported in 3% of patients. CSR/RPED resolved in 13% of patients and was ongoing in 13% of patients at the study cutoff. CSR/RPED led to dose interruptions and reductions in 9% and 14% of patients, respectively and 3% of patients discontinued Balversa.
Dry eye symptoms occurred in 28% of patients during treatment with Balversa and were Grade 3 in 6% of patients. All patients should receive dry eye prophylaxis with ocular demulcents as needed.
Perform monthly ophthalmological examinations during the first 4 months of treatment and every 3 months afterwards, and urgently at any time for visual symptoms. Ophthalmological examination should include assessment of visual acuity, slit lamp examination, fundoscopy, and optical coherence tomography.
Withhold Balversa when CSR occurs and permanently discontinue if it does not resolve within 4 weeks or if Grade 4 in severity. For ocular adverse reactions, follow the dose modification guidelines [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
HyperphosphatemiaIncreases in phosphate levels are a pharmacodynamic effect of Balversa [see Pharmacodynamics (12.2)]. Hyperphosphatemia was reported as adverse reaction in 76% of patients treated with Balversa. The median onset time for any grade event of hyperphosphatemia was 20 days (range: 8 –116) after initiating Balversa. Thirty-two percent of patients received phosphate binders during treatment with Balversa.
Monitor for hyperphosphatemia and follow the dose modification guidelines when required [see Dosage and Administration 2.2, 2.3].
Embryo-Fetal ToxicityBased on the mechanism of action and findings in animal reproduction studies, Balversa can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. In an embryo-fetal toxicity study, oral administration of erdafitinib to pregnant rats during the period of organogenesis caused malformations and embryo-fetal death at maternal exposures that were less than the human exposures at the maximum human recommended dose based on area under the curve (AUC). Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to the fetus. Advise female patients of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with Balversa and for one month after the last dose. Advise male patients with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with Balversa and for one month after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)].
Adverse ReactionsThe following serious adverse reactions are also described elsewhere in the labeling:
Ocular Disorders [see Warning and Precautions (5.1)].Hyperphosphatemia [see Warning and Precautions (5.2)].Clinical Trials ExperienceBecause clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety of Balversa was evaluated in the BLC2001 study that included 87 patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma which had susceptible FGFR3 or FGFR2 genetic alterations, and which progressed during or following at least one line of prior chemotherapy including within 12 months of neoadjuvant or adjuvant chemotherapy [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. Patients were treated with Balversa at 8 mg orally once daily; with a dose increase to 9 mg in patients with phosphate levels <5.5 mg/dL on Day 14 of Cycle 1. Median duration of treatment was 5.3 months (range: 0 to 17 months).
The most common adverse reactions (ARs) including laboratory abnormalities (≥20%) were phosphate increased, stomatitis, fatigue, creatinine increased, diarrhea, dry mouth, onycholysis, alanine aminotransferase increased, alkaline phosphatase increased, sodium decreased, decreased appetite, albumin decreased, dysgeusia, hemoglobin decreased, dry skin, aspartate aminotransferase increased, magnesium decreased, dry eye, alopecia, palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia syndrome, constipation, phosphate decreased, abdominal pain, calcium increased, nausea, and musculoskeletal pain. The most common Grade 3 or greater ARs (>1%) were stomatitis, nail dystrophy, palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia syndrome, paronychia, nail disorder, keratitis, onycholysis, and hyperphosphatemia.
An adverse reaction with a fatal outcome in 1% of patients was acute myocardial infarction.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 41% of patients including eye disorders (10%).
Permanent discontinuation due to an adverse reaction occurred in 13% of patients. The most frequent reasons for permanent discontinuation included eye disorders (6%).
Dosage interruptions occurred in 68% of patients. The most frequent adverse reactions requiring dosage interruption included hyperphosphatemia (24%), stomatitis (17%), eye disorders (17%), and palmar-plantar erythro-dysaesthesia syndrome (8%).
Dose reductions occurred in 53% of patients. The most frequent adverse reactions for dose reductions included eye disorders (23%), stomatitis (15%), hyperphosphatemia (7%), palmar-plantar erythro-dysaesthesia syndrome (7%), paronychia (7%), and nail dystrophy (6%).
Table 3 presents ARs reported in ≥10% of patients treated with Balversa at 8 mg once daily.
| Balversa 8 mg daily (N=87) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Adverse Reaction | All Grades (%) | Grade 3–4 (%) |
| *Includes abdominal pain, abdominal discomfort, abdominal pain upper, and abdominal pain lower†Includes asthenia, fatigue, lethargy, and malaise‡Includes onycholysis, onychoclasis, nail disorder, nail dystrophy, and nail ridging§Includes dry skin and xerostomia¶Includes dry eye, xerophthalmia, keratitis, foreign body sensation, and corneal erosion#Includes dyspnea and dyspnea exertionalÞIncludes back pain, musculoskeletal discomfort, musculoskeletal pain, musculoskeletal chest pain, neck pain, pain in extremityßIncludes weight decreased and cachexia | ||
| Any | 100 | 67 |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | 92 | 24 |
| Stomatitis | 56 | 9 |
| Diarrhea | 47 | 2 |
| Dry mouth | 45 | 0 |
| Constipation | 28 | 1 |
| Abdominal pain* | 23 | 2 |
| Nausea | 21 | 1 |
| Vomiting | 13 | 2 |
| Metabolism and nutrition disorders | 90 | 16 |
| Decreased appetite | 38 | 0 |
| General disorders and admin. site conditions | 69 | 13 |
| Fatigue† | 54 | 10 |
| Pyrexia | 14 | 1 |
| Skin and subcutaneous disorders | 75 | 16 |
| Onycholysis‡ | 41 | 10 |
| Dry skin§ | 34 | 0 |
| Palmar-plantar erythrodysaesthesia | 26 | 6 |
| Alopecia | 26 | 0 |
| Nail discoloration | 11 | 0 |
| Eye disorders | 62 | 11 |
| Dry eye¶ | 28 | 6 |
| Vision blurred | 17 | 0 |
| Lacrimation increased | 10 | 0 |
| Nervous system disorders | 57 | 5 |
| Dysgeusia | 37 | 1 |
| Infections and infestations | 56 | 20 |
| Paronychia | 17 | 3 |
| Urinary tract infection | 17 | 6 |
| Conjunctivitis | 11 | 0 |
| Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | 40 | 7 |
| Oropharyngeal pain | 11 | 1 |
| Dyspnea# | 10 | 2 |
| Renal and urinary tract disorders | 38 | 10 |
| Hematuria | 11 | 2 |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | 31 | 0 |
| Musculoskeletal painÞ | 20 | 0 |
| Arthralgia | 11 | 0 |
| Investigations | 44 | 5 |
| Weight decreasedß | 16 | 0 |
| Balversa 8 mg daily (N=86*) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Laboratory Abnormality | All Grades (%) | Grade 3–4 (%) |
| *One of the 87 patients had no laboratory tests. | ||
| Hematology | ||
| Hemoglobin decreased | 35 | 3 |
| Platelets decreased | 19 | 1 |
| Leukocytes decreased | 17 | 0 |
| Neutrophils decreased | 10 | 2 |
| Chemistry | ||
| Phosphate increased | 76 | 1 |
| Creatinine increased | 52 | 5 |
| Sodium decreased | 40 | 16 |
| Alanine aminotransferase increased | 41 | 1 |
| Alkaline phosphatase increased | 41 | 1 |
| Albumin decreased | 37 | 0 |
| Aspartate aminotransferase increased | 30 | 0 |
| Magnesium decreased | 30 | 1 |
| Phosphate decreased | 24 | 9 |
| Calcium increased | 22 | 3 |
| Potassium increased | 16 | 0 |
| Fasting glucose increased | 10 | 0 |
Table 5 summarizes drug interactions that affect the exposure of Balversa or serum phosphate level and their clinical management.
| Moderate CYP2C9 or Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors | |
| Clinical Impact | Co-administration of Balversa with moderate CYP2C9 or strong CYP3A4 inhibitors increased erdafitinib plasma concentrations [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].Increased erdafitinib plasma concentrations may lead to increased drug-related toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5)]. |
| Clinical Management | Consider alternative therapies that are not moderate CYP2C9 or strong CYP3A4 inhibitors during treatment with Balversa.If co-administration of moderate CYP2C9 or strong CYP3A4 inhibitor is unavoidable, monitor closely for adverse reactions and consider dose modifications accordingly [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. If the moderate CYP2C9 or strong CYP3A4 inhibitor is discontinued, the Balversa dose may be increased in the absence of drug-related toxicity. |
| Strong CYP2C9 or CYP3A4 Inducers | |
| Clinical Impact | Co-administration of Balversa with strong inducers of CYP2C9 or CYP3A4 may decrease erdafitinib plasma concentrations significantly [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].Decreased erdafitinib plasma concentrations may lead to decreased activity. |
| Clinical Management | Avoid co-administration of strong inducers of CYP2C9 or CYP3A4 with Balversa. |
| Moderate CYP2C9 or CYP3A4 Inducers | |
| Clinical Impact | Co-administration of Balversa with moderate inducers of CYP2C9 or CYP3A4 may decrease erdafitinib plasma concentrations [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].Decreased erdafitinib plasma concentrations may lead to decreased activity. |
| Clinical Management | If a moderate CYP2C9 or CYP3A4 inducer must be co-administered at the start of Balversa treatment, administer Balversa dose as recommended (8 mg once daily with potential to increase to 9 mg once daily based on serum phosphate levels on Days 14 to 21 and tolerability).If a moderate CYP2C9 or CYP3A4 inducer must be co-administered after the initial dose increase period based on serum phosphate levels and tolerability, increase Balversa dose up to 9 mg.When a moderate inducer of CYP2C9 or CYP3A4 is discontinued, continue Balversa at the same dose, in the absence of drug-related toxicity. |
| Serum Phosphate Level-Altering Agents | |
| Clinical Impact | Co-administration of Balversa with other serum phosphate level-altering agents may increase or decrease serum phosphate levels [see Pharmacodynamics (12.2)].Changes in serum phosphate levels due to serum phosphate level-altering agents (other than erdafitinib) may interfere with serum phosphate levels needed for the determination of initial dose increased based on serum phosphate levels [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. |
| Clinical Management | Avoid co-administration of serum phosphate level-altering agents with Balversa before initial dose increase period based on serum phosphate levels (Days 14 to 21) [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. |
Table 6 summarizes the effect of Balversa on other drugs and their clinical management.
| CYP3A4 Substrates | |
| Clinical Impact | Co-administration of Balversa with CYP3A4 substrates may alter the plasma concentrations of CYP3A4 substrates [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].Altered plasma concentrations of CYP3A4 substrates may lead to loss of activity or increased toxicity of the CYP3A4 substrates. |
| Clinical Management | Avoid co-administration of Balversa with sensitive substrates of CYP3A4 with narrow therapeutic indices. |
| OCT2 Substrates | |
| Clinical Impact | Co-administration of Balversa with OCT2 substrates may increase the plasma concentrations of OCT2 substrates [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].Increased plasma concentrations of OCT2 substrates may lead to increased toxicity of the OCT2 substrates. |
| Clinical Management | Consider alternative therapies that are not OCT2 substrates or consider reducing the dose of OCT2 substrates (e.g., metformin) based on tolerability. |
| P-glycoprotein (P-gp) Substrates | |
| Clinical Impact | Co-administration of Balversa with P-gp substrates may increase the plasma concentrations of P-gp substrates [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].Increased plasma concentrations of P-gp substrates may lead to increased toxicity of the P-gp substrates. |
| Clinical Management | If co-administration of Balversa with P-gp substrates is unavoidable, separate Balversa administration by at least 6 hours before or after administration of P-gp substrates with narrow therapeutic index. |
Risk Summary
Based on the mechanism of action and findings in animal reproduction studies, Balversa can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)]. There are no available data on Balversa use in pregnant women to inform a drug-associated risk. Oral administration of erdafitinib to pregnant rats during organogenesis caused malformations and embryo-fetal death at maternal exposures that were less than the human exposures at the maximum recommended human dose based on AUC (see Data). Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to the fetus.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2–4% and 15–20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
In an embryo-fetal toxicity study, erdafitinib was orally administered to pregnant rats during the period of organogenesis. Doses ≥4mg/kg/day (at total maternal exposures <0.1% of total human exposures at the maximum recommended human dose based on AUC) produced embryo-fetal death, major blood vessel malformations and other vascular anomalies, limb malformations (ectrodactyly, absent or misshapen long bones), an increased incidence of skeletal anomalies in multiple bones (vertebrae, sternebrae, ribs), and decreased fetal weight.
LactationRisk Summary
There are no data on the presence of erdafitinib in human milk, or the effects of erdafitinib on the breastfed child, or on milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions from erdafitinib in a breastfed child, advise lactating women not to breastfeed during treatment with Balversa and for one month following the last dose.
Pregnancy Testing
Pregnancy testing is recommended for females of reproductive potential prior to initiating treatment with Balversa.
Contraception
Females
Balversa can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with Balversa and for one month after the last dose [see Use in Specific Population (8.1)].
Males
Advise male patients with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with Balversa and for one month after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Infertility
Females
Based on findings from animal studies, Balversa may impair fertility in females of reproductive potential [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
Pediatric UseSafety and effectiveness of Balversa in pediatric patients have not been established.
In 4 and 13-week repeat-dose toxicology studies in rats and dogs, toxicities in bone and teeth were observed at an exposure less than the human exposure (AUC) at the maximum recommended human dose. Chondroid dysplasia/metaplasia were reported in multiple bones in both species, and tooth abnormalities included abnormal/irregular denting in rats and dogs and discoloration and degeneration of odontoblasts in rats.
Geriatric UseOf the 416 patients treated with Balversa in clinical studies, 45% were 65 years of age or older, and 12% were 75 years of age or older. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these patients and younger patients [see Clinical Studies (14)].
CYP2C9 Poor MetabolizersCYP2C9*3/*3 Genotype: Erdafitinib plasma concentrations were predicted to be higher in patients with the CYP2C9*3/*3 genotype. Monitor for increased adverse reactions in patients who are known or suspected to have CYP2C9*3/*3 genotype [see Pharmacogenomics (12.5)].
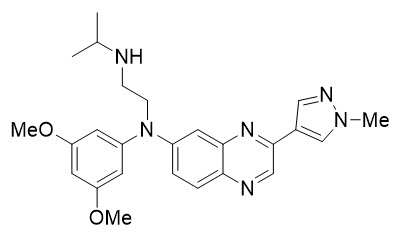
Balversa DescriptionErdafitinib, the active ingredient in Balversa, is a kinase inhibitor. The chemical name is N-(3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-N'-(1-methylethyl)-N-[3-(1-methyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)quinoxalin-6-yl]ethane-1,2-diamine. Erdafitinib is a yellow powder. It is practically insoluble, or insoluble to freely soluble in organic solvents, and slightly soluble to practically insoluble, or insoluble in aqueous media over a wide range of pH values. The molecular formula is C25H30N6O2 and molecular weight is 446.56.
Chemical structure of erdafitinib is as follows:
Balversa® (erdafitinib) tablets are supplied as 3 mg, 4 mg or 5 mg film-coated tablets for oral administration and contains the following inactive ingredients:
Tablet Core: Croscarmellose sodium, Magnesium stearate (from vegetable source), Mannitol, Meglumine, and Microcrystalline Cellulose.
Film Coating: (Opadry amb II): Glycerol monocaprylocaprate Type I, Polyvinyl alcohol-partially hydrolyzed, Sodium lauryl sulfate, Talc, Titanium dioxide, Iron oxide yellow, Iron oxide red (for the orange and brown tablets only), Ferrosoferric oxide/iron oxide black (for the brown tablets only).
Balversa - Clinical PharmacologyErdafitinib is a kinase inhibitor that binds to and inhibits enzymatic activity of FGFR1, FGFR2, FGFR3 and FGFR4 based on in vitro data. Erdafitinib also binds to RET, CSF1R, PDGFRA, PDGFRB, FLT4, KIT, and VEGFR2. Erdafitinib inhibited FGFR phosphorylation and signaling and decreased cell viability in cell lines expressing FGFR genetic alterations, including point mutations, amplifications, and fusions. Erdafitinib demonstrated antitumor activity in FGFR-expressing cell lines and xenograft models derived from tumor types, including bladder cancer.
PharmacodynamicsCardiac Electrophysiology
Based on evaluation of QTc interval in an open-label, dose escalation and dose expansion study in 187 patients with cancer, erdafitinib had no large effect (i.e., > 20 ms) on the QTc interval.
Serum Phosphate
Erdafitinib increased serum phosphate level as a consequence of FGFR inhibition. Balversa should be increased to the maximum recommended dose to achieve target serum phosphate levels of 5.5–7.0 mg/dL in early cycles with continuous daily dosing [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
In erdafitinib clinical trials, the use of drugs which can increase serum phosphate levels, such as potassium phosphate supplements, vitamin D supplements, antacids, phosphate-containing enemas or laxatives, and medications known to have phosphate as an excipient were prohibited unless no alternatives exist. To manage phosphate elevation, phosphate binders were permitted. Avoid concomitant use with agents that can alter serum phosphate levels before the initial dose increase period based on serum phosphate levels [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
PharmacokineticsFollowing administration of 8 mg once daily, the mean (coefficient of variation [CV%]) erdafitinib steady-state maximum observed plasma concentration (Cmax), area under the curve (AUCtau), and minimum observed plasma concentration (Cmin) were 1,399 ng/mL (51%), 29,268 ng∙h/mL (60%), and 936 ng/mL (65%), respectively.
Following single and repeat once daily dosing, erdafitinib exposure (maximum observed plasma concentration [Cmax] and area under the plasma concentration time curve [AUC]) increased proportionally across the dose range of 0.5 to 12 mg (0.06 to 1.3 times the maximum approved recommended dose). Steady state was achieved after 2 weeks with once daily dosing and the mean accumulation ratio was 4-fold.
Absorption
Median time to achieve peak plasma concentration (tmax) was 2.5 hours (range: 2 to 6 hours).
Effect of Food
No clinically meaningful differences with erdafitinib pharmacokinetics were observed following administration of a high-fat and high-calorie meal (800 calories to 1,000 calories with approximately 50% of total caloric content of the meal from fat) in healthy subjects.
Distribution
The mean apparent volume of distribution of erdafitinib was 29 L in patients.
Erdafitinib protein binding was 99.8% in patients, primarily to alpha-1-acid glycoprotein.
Elimination
The mean total apparent clearance (CL/F) of erdafitinib was 0.362 L/h in patients.
The mean effective half-life of erdafitinib was 59 hours in patients.
Metabolism
Erdafitinib is primarily metabolized by CYP2C9 and CYP3A4. The contribution of CYP2C9 and CYP3A4 in the total clearance of erdafitinib is estimated to be 39% and 20% respectively. Unchanged erdafitinib was the major drug-related moiety in plasma, there were no circulating metabolites.
Excretion
Following a single oral dose of radiolabeled erdafitinib, approximately 69% of the dose was recovered in feces (19% as unchanged) and 19% in urine (13% as unchanged).
Specific Populations
No clinically meaningful trends in the pharmacokinetics of erdafitinib were observed based on age (21–88 years), sex, race, body weight (36–132 kg), mild (eGFR [estimated glomerular filtration rate, using modification of diet in renal disease equation] 60 to 89 mL/min/1.73 m2) or moderate (eGFR 30–59 mL/min/1.73 m2) renal impairment or mild hepatic impairment (total bilirubin ≤ ULN and AST > ULN, or total bilirubin > 1.0–1.5 × ULN and any AST).
The pharmacokinetics of erdafitinib in patients with severe renal impairment, renal impairment requiring dialysis, moderate or severe hepatic impairment is unknown.
Drug Interaction Studies
Clinical Studies and Model-Based Approaches Moderate CYP2C9 Inhibitors:
Erdafitinib mean ratios (90% CI) for Cmax and AUCinf were 121% (99.9, 147) and 148% (120, 182), respectively, when co-administered with fluconazole, a moderate CYP2C9 and CYP3A4 inhibitor, relative to erdafitinib alone.
Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors:
Erdafitinib mean ratios (90% CI) for Cmax and AUCinf were 105% (86.7, 127) and 134% (109, 164), respectively, when co-administered with itraconazole (a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor and P-gp inhibitor) relative to erdafitinib alone.
Strong CYP3A4/2C9 Inducers:
Simulations suggested that rifampicin (a strong CYP3A4/2C9 inducer) may significantly decrease erdafitinib Cmax and AUC.
In Vitro Studies
CYP Substrates:
Erdafitinib is a time dependent inhibitor and inducer of CYP3A4. The effect of erdafitinib on a sensitive CYP3A4 substrate is unknown. Erdafitinib is not an inhibitor of other major CYP isozymes at clinically relevant concentrations.
Transporters:
Erdafitinib is a substrate and inhibitor of P-gp. P-gp inhibitors are not expected to affect erdafitinib exposure to a clinically relevant extent. Erdafitinib is an inhibitor of OCT2.
Erdafitinib does not inhibit BCRP, OATP1B, OATP1B3, OAT1, OAT3, OCT1, MATE-1, or MATE-2K at clinically relevant concentrations.
Acid-Lowering Agents:
Erdafitinib has adequate solubility across the pH range of 1 to 7.4. Acid-lowering agents (e.g., antacids, H2-antagonists, proton pump inhibitors) are not expected to affect the bioavailability of erdafitinib.
PharmacogenomicsCYP2C9 activity is reduced in individuals with genetic variants, such as the CYP2C9*2 and CYP2C9*3 polymorphisms. Erdafitinib exposure was similar in subjects with CYP2C9*1/*2 and *1/*3 genotypes relative to subjects with CYP2C9*1/*1 genotype (wild type). No data are available in subjects characterized by other genotypes (e.g., *2/*2, *2/*3, *3/*3). Simulation suggested no clinically meaningful differences in erdafitinib exposure in subjects with CYP2C9*2/*2 and *2/*3 genotypes. The exposure of erdafitinib is predicted to be 50% higher in subjects with the CYP2C9*3/*3 genotype, estimated to be present in 0.4% to 3% of the population among various ethnic groups.
Nonclinical ToxicologyCarcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, and Impairment of FertilityCarcinogenicity studies have not been conducted with erdafitinib.
Erdafitinib was not mutagenic in a bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) assay and was not clastogenic in an in vitro micronucleus or an in vivo rat bone marrow micronucleus assay.
Fertility studies in animals have not been conducted with erdafitinib. In the 3-month repeat-dose toxicity study, erdafitinib showed effects on female reproductive organs (necrosis of the ovarian corpora lutea) in rats at an exposure less than the human exposure (AUC) at maximum recommended human dose.
Study BLC2001 (NCT02365597) was a multicenter, open-label, single-arm study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of Balversa in patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma (mUC). Fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) mutation status for screening and enrollment of patients was determined by a clinical trial assay (CTA). The efficacy population consists of a cohort of eighty-seven patients who were enrolled in this study with disease that had progressed on or after at least one prior chemotherapy and that had at least 1 of the following genetic alterations: FGFR3 gene mutations (R248C, S249C, G370C, Y373C) or FGFR gene fusions (FGFR3-TACC3, FGFR3-BAIAP2L1, FGFR2-BICC1, FGFR2-CASP7), as determined by the CTA performed at a central laboratory. Tumor samples from 69 patients were tested retrospectively by the QIAGEN therascreen® FGFR RGQ RT-PCR Kit, which is the FDA-approved test for selection of patients with mUC for Balversa.
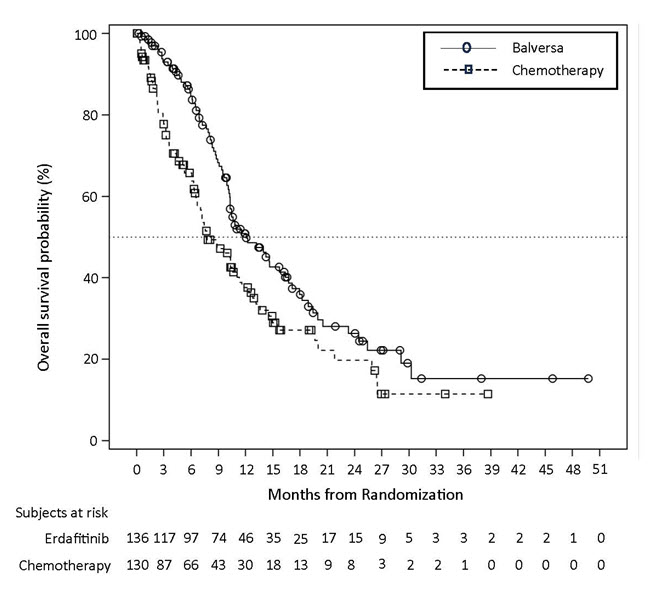
Patients received a starting dose of Balversa at 8 mg once daily with a dose increase to 9 mg once daily in patients whose serum phosphate levels were below the target of 5.5 mg/dL between days 14 and 17; a dose increase occurred in 41% of patients. Balversa was administered until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. The major efficacy outcome measures were objective response rate (ORR) and duration of response (DoR), as determined by blinded independent review committee (BIRC) according to RECIST v1.1.
The median age was 67 years (range: 36 to 87 years), 79% were male, and 74% were Caucasian. Most patients (92%) had a baseline Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status of 0 or 1. Sixty-six percent of patients had visceral metastases. Eighty-four (97%) patients received at least one of cisplatin or carboplatin previously. Fifty-six percent of patients only received prior cisplatin-based regimens, 29% received only prior carboplatin-based regimens, and 10% received both cisplatin and carboplatin-based regimens. Three (3%) patients had disease progression following prior platinum-containing neoadjuvant or adjuvant therapy only. Twenty-four percent of patients had been treated with prior anti PD-L1/PD-1 therapy.
Efficacy results are summarized in Table 7 and Table 8. Overall response rate was 32.2%. Responders included patients who had previously not responded to anti PD-L1/PD-1 therapy.
| BIRC* assessment | |
|---|---|
| Endpoint | N=87 |
|
ORR = CR + PR CI = Confidence Interval |
|
| *BIRC: Blinded Independent Review Committee | |
| ORR (95% CI) | 32.2% (22.4, 42.0) |
| Complete response (CR) | 2.3% |
| Partial response (PR) | 29.9% |
| Median DoR in months (95% CI) | 5.4 (4.2, 6.9) |
| BIRC* assessment | |
|---|---|
|
ORR = CR + PR CI = Confidence Interval |
|
| *BIRC: Blinded Independent Review Committee†Both responders had FGFR3-TACC3_V1 fusion‡One patient with a FGFR2-CASP7/FGFR3-TACC3_V3 fusion is reported in both FGFR2 fusion and FGFR3 fusion above | |
| FGFR3 Point Mutation | N=64 |
| ORR (95% CI) | 40.6% (28.6, 52.7) |
| FGFR3 Fusion †, ‡ | N=18 |
| ORR (95% CI) | 11.1% (0, 25.6) |
| FGFR2 Fusion ‡ | N=6 |
| ORR | 0 |
Balversa® (erdafitinib) tablets are available in the strengths and packages listed below:
3 mg tablets: Yellow, round biconvex, film-coated, debossed with "3" on one side and "EF" on the other side.–Bottle of 56-tablets with child resistant closure (NDC 59676-030-56).–Bottle of 84-tablets with child resistant closure (NDC 59676-030-84).4 mg tablets: Orange, round biconvex, film-coated, debossed with "4" on one side and "EF" on the other side.–Bottle of 28-tablets with child resistant closure (NDC 59676-040-28).–Bottle of 56-tablets with child resistant closure (NDC 59676-040-56).5 mg tablets: Brown, round biconvex, film-coated, debossed with "5" on one side and "EF" on the other side.–Bottle of 28-tablets with child resistant closure (NDC 59676-050-28).Store at 20°C–25°C (68°F–77°F); excursions permitted between 15°C and 30°C (59°F and 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Patient Counseling InformationAdvise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
FGFR genetic alterations: Advise patients that evidence of a susceptible FGFR3 or FGFR2 mutation or gene fusion within the tumor specimen is necessary to identify patients for whom treatment is indicated [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
Ocular disorders: Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider if they experience any visual changes [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. In order to prevent or treat dry eyes, advise patients to use artificial tear substitutes, hydrating or lubricating eye gels or ointments frequently, at least every 2 hours during waking hours [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
Skin, mucous or nail disorders: Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider if they experience progressive or intolerable skin, mucous or nail disorders [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Hyperphosphatemia: Advise patients that their healthcare provider will assess their serum phosphate level between 14 and 21 days of initiating treatment and will adjust the dose if needed [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. During this initial phosphate-assessment period, advise patients to avoid concomitant use with agents that can alter serum phosphate levels. Advise patients that, after the initial phosphate assessment period, monthly phosphate level monitoring for hyperphosphatemia should be performed during treatment with Balversa [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Drug Interactions: Advise patients to inform their healthcare providers of all concomitant medications, including prescription medicines, over-the-counter drugs, and herbal products [see Drug Interactions (7.1, 7.2)].
Dosing Instructions: Instruct patients to swallow the tablets whole once daily with or without food. If vomiting occurs any time after taking Balversa, advise patients to take the next dose the next day. [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
Missed dose: If a dose is missed, advise patients to take the missed as soon as possible. Resume the regular daily dose schedule for Balversa the next day. Extra tablets should not be taken to make up for the missed dose [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to the fetus. Advise females to inform their healthcare providers of a known or suspected pregnancy [see Warning and Precautions (5.3) and Use in Specific Population (8.1)]. Advise female patients of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment and for one month after the last dose of Balversa. Advise male patients with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment and for one month after the last dose of Balversa [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Lactation: Advise females not to breastfeed during treatment with Balversa and for one month after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Product of Switzerland
Manufactured for:
Janssen Products, LP
Horsham, PA 19044
Under license from Astex Therapeutics Limited.
©2019 Janssen Pharmaceutical Companies
| This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. | Issued: April 2020 | |
|
PATIENT INFORMATION Balversa® (bal-VER-sah) (erdafitinib) tablets |
||
|
What is Balversa? Balversa is a prescription medicine used to treat adults with bladder cancer (urothelial cancer) that has spread or cannot be removed by surgery:which has a certain type of abnormal "FGFR" gene, andwho have tried at least one other chemotherapy medicine that contains platinum, and it did not work or is no longer working.Your healthcare provider will test your cancer for certain types of abnormal FGFR genes and make sure that Balversa is right for you. It is not known if Balversa is safe and effective in children. |
||
|
Before taking Balversa tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you: have vision or eye problems.are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. Balversa can harm your unborn baby. You should not become pregnant during treatment with Balversa. Females who can become pregnant:Your healthcare provider may do a pregnancy test before you start treatment with Balversa.You should use effective birth control during treatment and for 1 month after the last dose of Balversa. Talk to your healthcare provider about birth control methods that may be right for you.Tell your healthcare provider right away if you become pregnant or think you may be pregnant.Males with female partners who can become pregnant:You should use effective birth control when sexually active during treatment with Balversa and for 1 month after the last dose.are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. Do not breastfeed during treatment and for 1 month after the last dose of Balversa.Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. |
||
| How should I take Balversa?Take Balversa exactly as your healthcare provider tells you.Take Balversa 1 time each day.Swallow Balversa tablets whole with or without food.Your healthcare provider may change your dose of Balversa, temporarily stop or completely stop treatment if you get certain side effects.If you miss a dose of Balversa, take the missed dose as soon as possible on the same day. Take your regular dose of Balversa the next day. Do not take more Balversa than prescribed to make up for the missed dose.If you vomit after taking Balversa, do not take another Balversa tablet. Take your regular dose of Balversa the next day. | ||
|
What are the possible side effects of Balversa? Balversa may cause serious side effects, including:Eye problems. Eye problems are common with Balversa but can also be serious. Eye problems include dry or inflamed eyes, inflamed cornea (front part of the eye) and disorders of the retina, an internal part of the eye. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you develop blurred vision, loss of vision or other visual changes. You should use artificial tear substitutes, hydrating or lubricating eye gels or ointments at least every 2 hours during waking hours to help prevent dry eyes. During treatment with Balversa, your healthcare provider will send you to see an eye specialist.High phosphate levels in the blood (hyperphosphatemia). Hyperphosphatemia is common with Balversa but can also be serious. Your healthcare provider will check your blood phosphate level between 14 and 21 days after starting treatment with Balversa, and then monthly, and may change your dose if needed.The most common side effects of Balversa include: |
||
| mouth soresfeeling tiredchange in kidney functiondiarrheadry mouthnails separate from the bed or poor formation of the nailchange in liver functionlow salt (sodium) levelsdecreased appetitechange in sense of taste | low red blood cells (anemia)dry skindry eyeshair lossredness, swelling, peeling or tenderness, mainly on the hands or feet ('hand-foot syndrome')constipationstomach (abdominal) painnauseamuscle pain | |
|
Tell your healthcare provider right away if you develop any nail or skin problems including nails separating from the nail bed, nail pain, nail bleeding, breaking of the nails, color or texture changes in your nails, infected skin around the nail, an itchy skin rash, dry skin, or cracks in the skin. Balversa may affect fertility in females who are able to become pregnant. Talk to your healthcare provider if this is a concern for you. These are not all possible side effects of Balversa. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist. Call your healthcare provider for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
||
| How should I store Balversa?Store Balversa tablets at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).Keep Balversa and all medicines out of the reach of children. | ||
|
General information about the safe and effective use of Balversa. Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in Patient Information leaflets. Do not use Balversa for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Balversa to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. If you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your healthcare provider for information about Balversa that is written for healthcare professionals. |
||
|
What are the ingredients in Balversa? Active ingredient: erdafitinib Inactive ingredients: Tablet Core: Croscarmellose sodium, Magnesium stearate (from vegetable source), Mannitol, Meglumine, and Microcrystalline Cellulose. Film Coating (Opadry amb II): Glycerol monocaprylocaprate Type I, Polyvinyl alcohol-partially hydrolyzed, Sodium lauryl sulfate, Talc, Titanium dioxide, Iron oxide yellow, Iron oxide red (for the orange and brown tablets only), Ferrosoferric oxide/iron oxide black (for the brown tablets only). Manufactured by: Janssen-Cilag SpA, Latina, Italy Manufactured for: Janssen Products, LP, Horsham, PA 19044 © 2019 Janssen Pharmaceutical Companies For more information call Janssen Products, LP at 1-800-526-7736 (1-800-JANSSEN) or go to www.Balversa.com. |
||
NDC 59676-030-56
Balversa™
(erdafitinib) tablets
3 mg
Each film-coated tablet
contains 3 mg of erdafitinib.
Rx only
56 film-coated tablets
NDC 59676-040-56
Balversa™
(erdafitinib) tablets
4 mg
Each film-coated tablet
contains 4 mg of erdafitinib.
Rx only
56 film-coated tablets
NDC 59676-050-28
Balversa™
(erdafitinib) tablets
5 mg
Each film-coated tablet
contains 5 mg of erdafitinib.
Rx only
28 film-coated tablets
|
Balversa erdafitinib tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Balversa erdafitinib tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Balversa erdafitinib tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Janssen Products LP (804684207) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Operations |
| Cilag AG | 483237103 | API MANUFACTURE(59676-030, 59676-040, 59676-050) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Operations |
| Johnson & Johnson Private Limited | 677603030 | ANALYSIS(59676-030, 59676-040, 59676-050) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Operations |
| Janssen Cilag SpA | 542797928 | MANUFACTURE(59676-030, 59676-040, 59676-050), ANALYSIS(59676-030, 59676-040, 59676-050), PACK(59676-030, 59676-040, 59676-050) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Operations |
| AndersonBrecon Inc. | 053217022 | PACK(59676-030, 59676-040, 59676-050) | |